Camera sensitivity – ISO speed
Five camera sensitivity settings can be selected with a still image. The auto setting automatically adjusts the camera sensitivity to the light conditions between ISO 50 and ISO 200. The camera sen- sitivity can also be specified among ISO 50, 100, 200, and 400. The numerical values are based on an ISO equivalent. As the ISO value doubles, the camera sensitivity doubles. Noise increases with the sensitivity in digital imaging; the ISO setting of 50 has the least noise and 400 has the most.
The flash range changes with camera sensitivity. Because of the optical system, the flash range is not the same at the lens’
ISO speed | Flash range (wide angle) | Flash range (telephoto) |
AUTO | 0.5m ~ 3.0m (1.6ft ~ 9.8ft) | 0.8m ~ 1.7m ( 2.6ft ~ 5.6ft) |
50 | 0.5m ~ 1.5m ( 1.6ft ~ 4.9ft) | 0.8m ~ 0.86m ( 2.6ft ~ 2.8ft) |
100 | 0.5m ~ 2.1m ( 1.6ft ~ 6.9ft) | 0.8m ~ 1.2m ( 2.6ft ~ 3.9ft) |
200 | 0.5m ~ 3.0m ( 1.6ft ~ 9.8ft) | 0.8m ~ 1.7m ( 2.6ft ~ 5.6ft) |
400 | 0.5m ~ 4.3m ( 1.6ft ~ 14.1ft) | 0.8m ~ 2.4m ( 2.6ft ~ 7.9ft) |
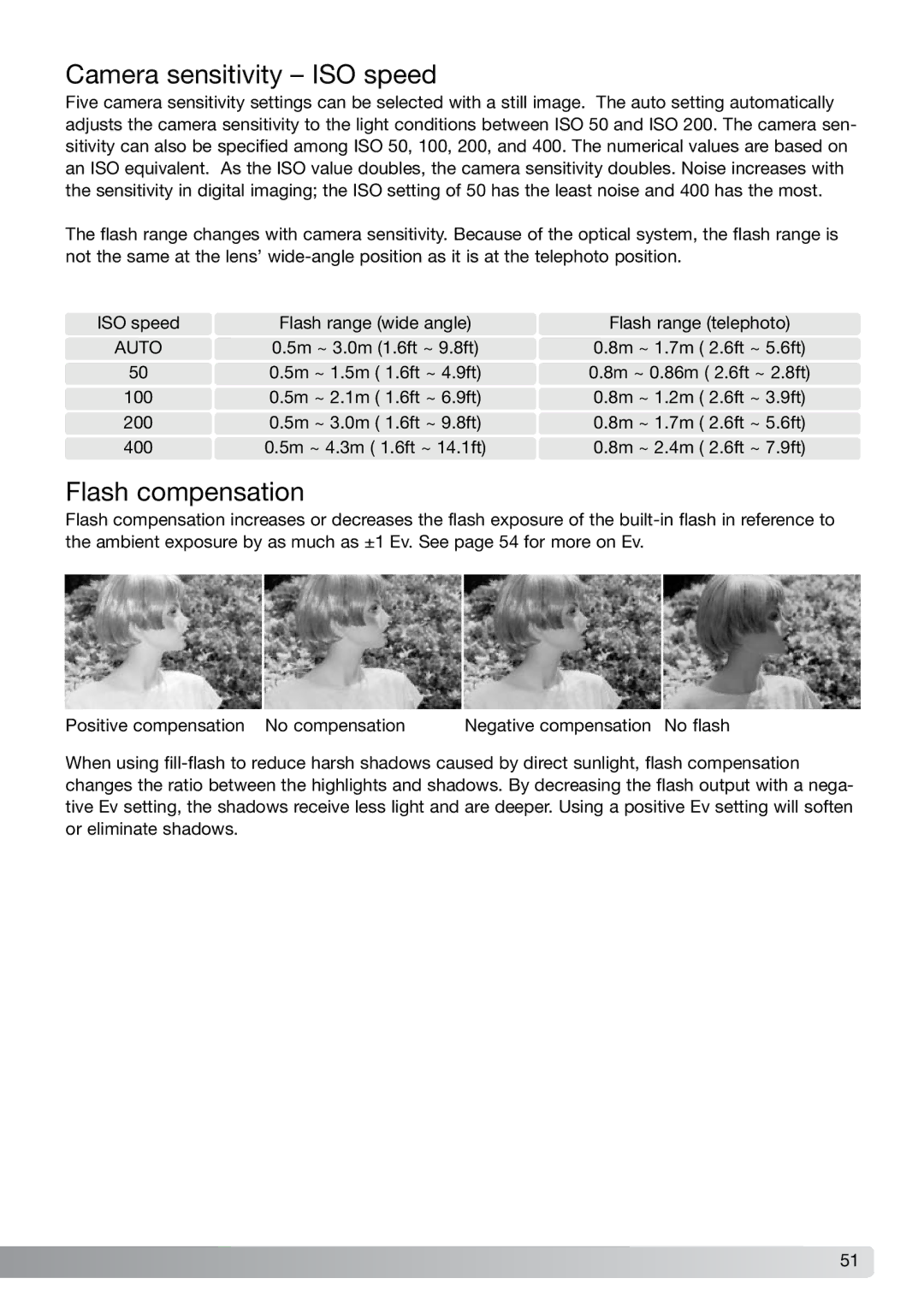
Flash compensation
Flash compensation increases or decreases the flash exposure of the
Positive compensation No compensation | Negative compensation No flash |
When using
51