Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
THEORY OF OPERATION |
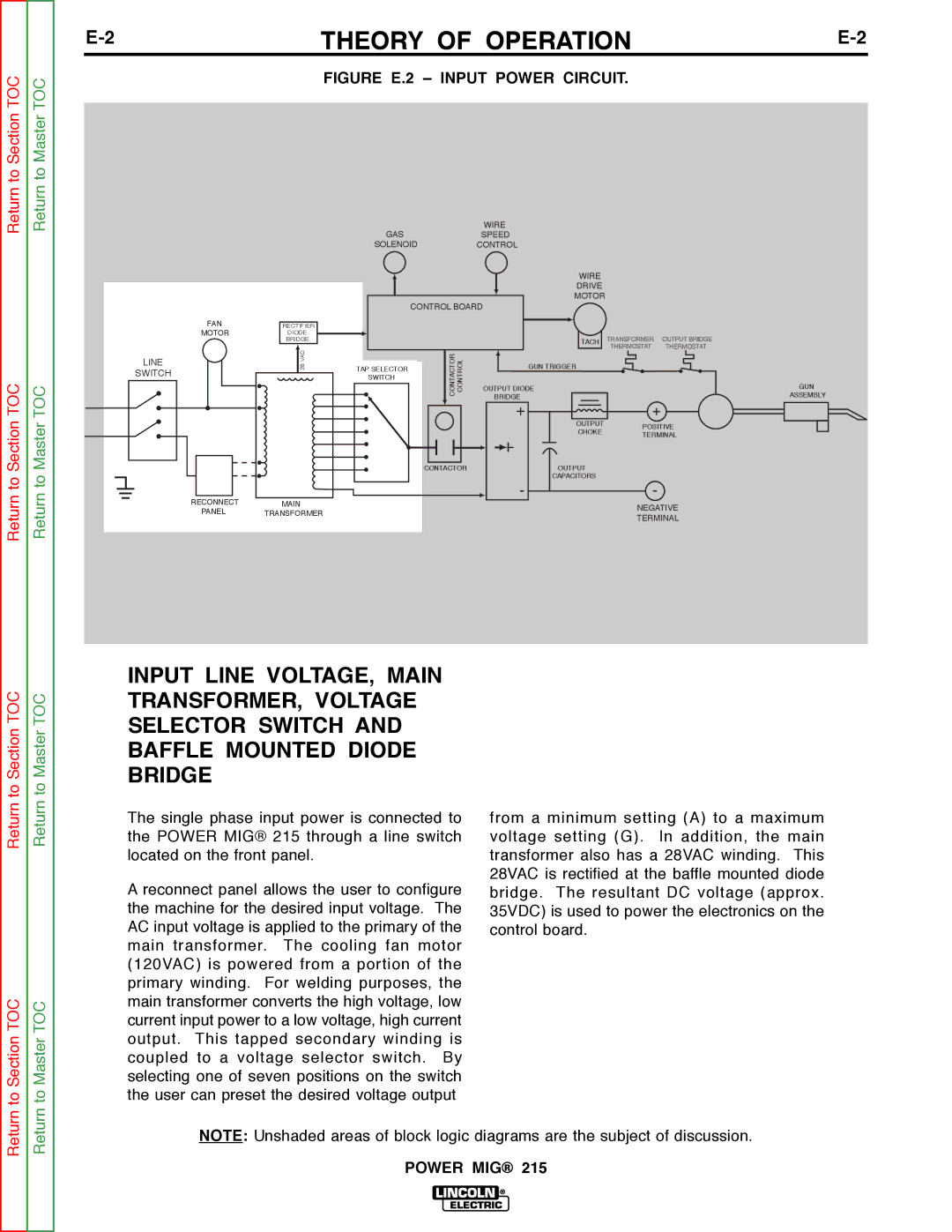
FIGURE E.2 – INPUT POWER CIRCUIT.
WIRE
GASSPEED
SOLENOIDCONTROL
FAN
MOTOR
LINE
SWITCH
RECTIFIER
DIODE
BRIDGE
VAC28TAP SELECTOR SWITCH
CONTROL BOARD
CONTACTOR | CONTROL |
CONTACTOR
WIRE
DRIVE
MOTOR
TACH
GUN TRIGGER
OUTPUT DIODE
BRIDGE
+
OUTPUT
CHOKE
OUTPUT
CAPACITORS
-
TRANSFORMER | OUTPUT BRIDGE | ||||||
THERMOSTAT | THERMOSTAT | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+
POSITIVE
TERMINAL
-
GUN
ASSEMBLY
INPUT LINE VOLTAGE, MAIN TRANSFORMER, VOLTAGE SELECTOR SWITCH AND BAFFLE MOUNTED DIODE BRIDGE
Return
to Section TOC
Return
to Master TOC
The single phase input power is connected to the POWER MIG® 215 through a line switch located on the front panel.
A reconnect panel allows the user to configure the machine for the desired input voltage. The AC input voltage is applied to the primary of the main transformer. The cooling fan motor (120VAC) is powered from a portion of the primary winding. For welding purposes, the main transformer converts the high voltage, low current input power to a low voltage, high current output. This tapped secondary winding is coupled to a voltage selector switch. By selecting one of seven positions on the switch the user can preset the desired voltage output
from a minimum setting (A) to a maximum voltage setting (G). In addition, the main transformer also has a 28VAC winding. This 28VAC is rectified at the baffle mounted diode bridge. The resultant DC voltage (approx. 35VDC) is used to power the electronics on the control board.