LSISAS6160 SAS Switch
Revision History
Table of Contents
SAS Domain Manager Command Line Interface
Chapter
Features
LSISAS6160 Switch
Serial Attached Scsi and the SAS6160 Switch
LSISAS6160 Resource Management
Block Diagram of the LSISAS6160 Switch
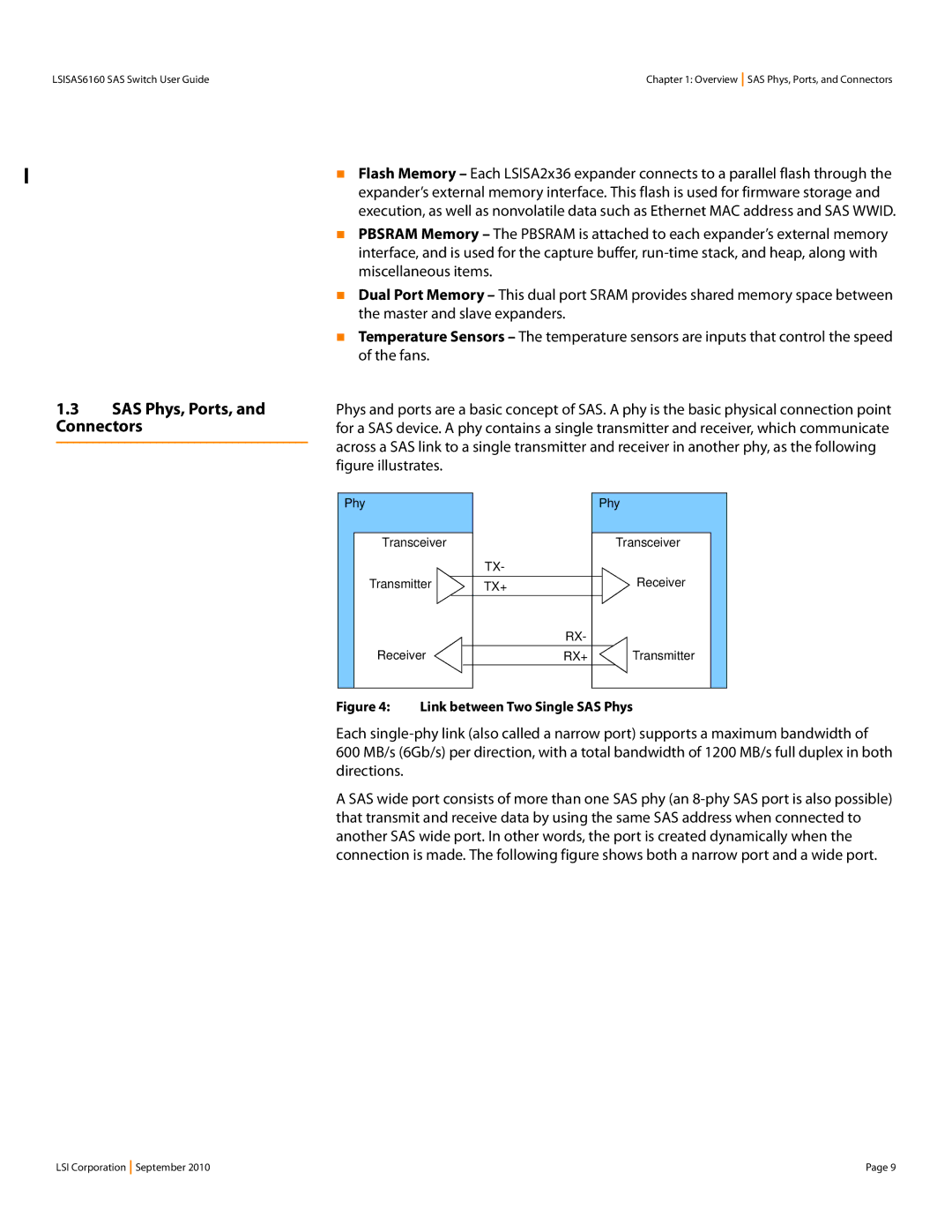
Link between Two Single SAS Phys
SAS Phys, Ports, and Connectors
Narrow and Wide SAS Ports
Mini SAS 4x Cable
SAS Connectors and Cabling
Only the storage within its zone or zones
Minimize conflicts
Across the entire Zpsds
SAS Zoning Overview
Groups and zone sets manually by using the SDM utility
Following figure shows a simple example of zoning
Creating SAS Zones
Overview SAS Routing and Zoning
Configuration for Zoning Example
Creating Zone Groups
Connecting Devices to the SAS6160 Switch
Example 1, Multiple Servers and JBODs
Example 3, Multiple Servers and a Cascading Switch
Example 4, High Availability
Example 5, Large Data Storage Topology
Example 6, Cascaded Switches
Example 7, Switches in a Star Tree Configuration
Identifying Switch Components
Unpacking the Switch
To interpret the LEDs on the switch
Carton contains the following items
SAS6160 Connectors
Installing the SAS6160 Switch
Cables
SAS6160 LEDs
Rack. These options are shown in the following figure
Mounting Shelf in a Rack
Setting a Static IP Address
Connecting to a Host Changing the Default Static IP Address
Exit SDM-CLI and power cycle the switch
Exit SDM-GUI and power cycle the switch
Using SDM-GUI
For example
1 FCC
Connecting SAS and Sata Hardware Safety Notices
Canada Mark Vcci Bsmi
5 CCC
Installation and Hardware Setup Safety Notices
Starting SDM-GUI
SDM-GUI Accounts
Embedded SDM only supports a single domain
Options
File, Server, and Help Menu Options
Views Tab
Information is available to both admin and user accounts
For zoning
View End Device Table
Alias Table
View Zone Groups
View Zone Groups
View Zone Sets
View Zone Sets
This section, click the hyperlinks on the Domain tab
Domain Tab
Node100, and so on
Alias Management
View/Delete Aliases command
Domain. You also can also this command to delete aliases
View/Delete Aliases
Zone set and the two associated zone groups
Connector Wizard
Box and clicking the Delete button
Group to communicate with each other
Maximum number of 248, the wizard displays an error message
Guide you through the configuration process
Check box and clicking the Delete button
Zone group to communicate with each other
Create Zone Group
Manually Configure Zone Groups Create Zone Group
View Zone Group
Time of activation. shows the View Zone Group window
Modify Zone Group
Delete Zone Group
Binary 0, as defined by the SAS 2.0 specification
Maximum password length is 32 characters
Password
Matrix
Zone set
View Zone Set window
View Zone Set
Modify Zone Set
Activate/Deactivate Zone Set
Activate/Deactivate Zone Set
Delete Zone Set
Window and then clicking Delete
Device Tree and Properties Tab
Devices Tab
Selected device. In , the domain properties are shown
Following figure shows the Properties tab
Properties Tab
Environmentals Tab
Background loop
Those connections
Following figure shows the Attached Devices tab
Attached Devices Tab
Following figure shows the Phys tab
Selected expander
Zone Group Tab
Zone Group Tab
Successful update
This tab contains the following commands
Update Firmware
Operations Tab
Enable/Disable/Reset
Following figure shows the Enable/Disable/Reset window
Reset Switch
Phys
As shown in the following figures
Configure IP
Command arguments
Command Usage Syntax
Help command
SDM-CLI Commands
„ help command
Domain focus domain name
„ passwd admin
Passwd admin user
„ passwd user
Exit
„ alias delete
„ show phy
„ show alias
„ show zonegroup
„ show zoneset
„ zonegroup create name
„ zonegroup add name sas addressaliasphy
„ zonegroup delete single name
„ zonegroup delete all noconfirm
„ zoneset activate name
Set membership
„ zoneset add name zone group zone group
„ zoneset create name
„ zoneset passwd
Sample Output for Show Command
Sdmcli show alias
Sdmcli show alias Calhoun
Sdmcli show device Calhoun
Sdmcli show phy
Sdmcli show domain
Show domain
Show phy
Sdmcli show phy Calhoun
Alias Phy Device Capabilities SAS Address Type
RA Routing Attributes VP Virtual PHY Zone Grp
Show phy alias
Zoning Inactive * phy may be assigned to a zone group
Zoning Active Zone Group Number
Sdmcli show version
Sdmcli show phy Lincoln01
SDM-CLI Version SDM-D Version
Show phy alias phy
Sdmcli show zoneset active
Sdmcli show zonegroup ZoneOne#001
Show zoneset data name Sdmcli show zoneset data ZoneOne
Show zonegroup name
Xip -i 500062b15555557f get exp
Xip -i get avail
Troubleshooting