RangeMax Dual Band
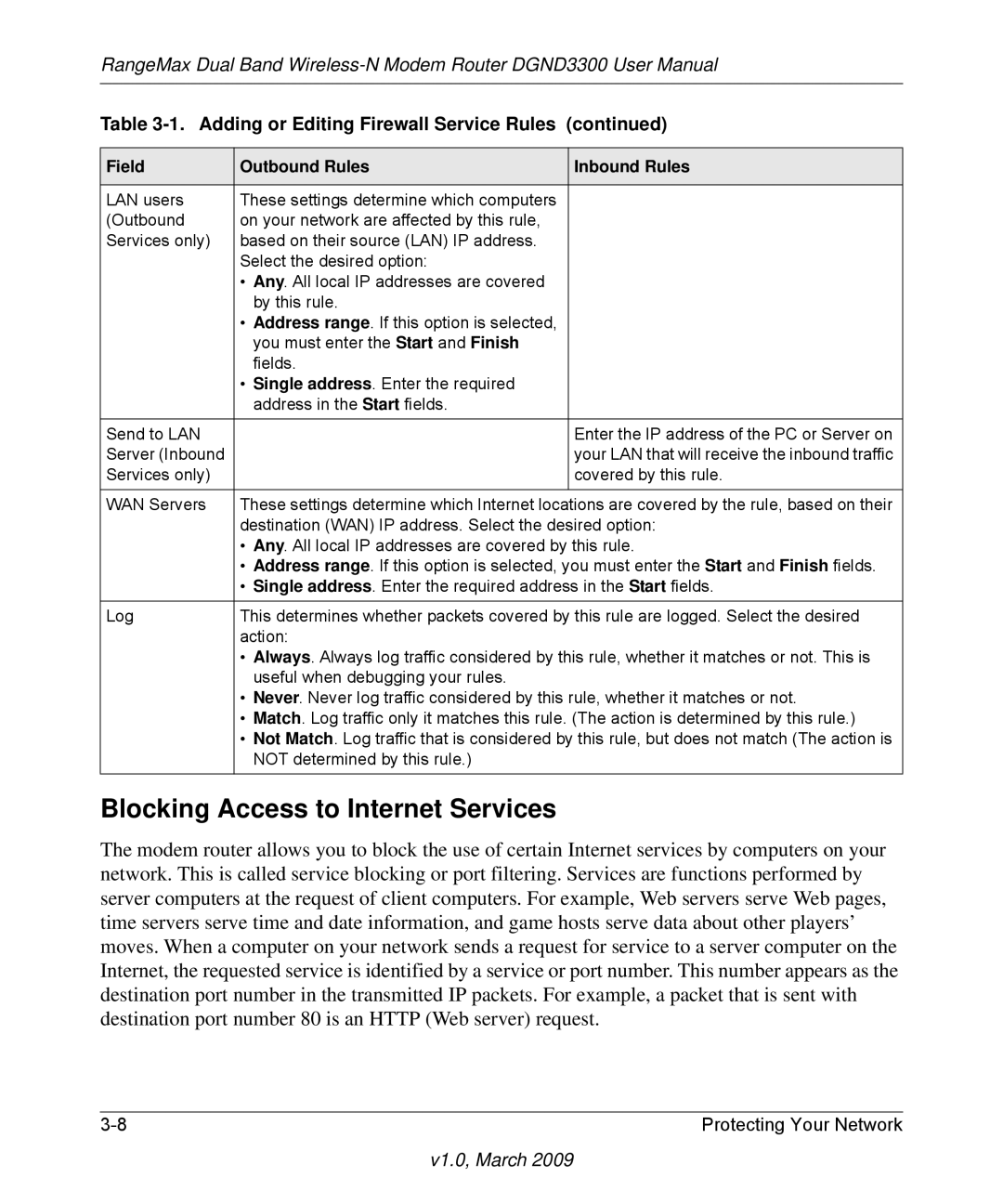
Table 3-1. Adding or Editing Firewall Service Rules (continued)
Field | Outbound Rules | Inbound Rules |
|
|
|
LAN users | These settings determine which computers |
|
(Outbound | on your network are affected by this rule, |
|
Services only) | based on their source (LAN) IP address. |
|
| Select the desired option: |
|
| • Any. All local IP addresses are covered |
|
| by this rule. |
|
| • Address range. If this option is selected, |
|
| you must enter the Start and Finish |
|
| fields. |
|
| • Single address. Enter the required |
|
| address in the Start fields. |
|
Send to LAN |
| Enter the IP address of the PC or Server on |
Server (Inbound |
| your LAN that will receive the inbound traffic |
Services only) |
| covered by this rule. |
|
|
|
WAN Servers | These settings determine which Internet locations are covered by the rule, based on their | |
| destination (WAN) IP address. Select the desired option: | |
| • Any. All local IP addresses are covered by this rule. | |
| • Address range. If this option is selected, you must enter the Start and Finish fields. | |
| • Single address. Enter the required address in the Start fields. | |
Log | This determines whether packets covered by this rule are logged. Select the desired | |
| action: |
|
| • Always. Always log traffic considered by this rule, whether it matches or not. This is | |
| useful when debugging your rules. |
|
| • Never. Never log traffic considered by this rule, whether it matches or not. | |
| • Match. Log traffic only it matches this rule. (The action is determined by this rule.) | |
| • Not Match. Log traffic that is considered by this rule, but does not match (The action is | |
| NOT determined by this rule.) |
|
|
|
|
Blocking Access to Internet Services
The modem router allows you to block the use of certain Internet services by computers on your network. This is called service blocking or port filtering. Services are functions performed by server computers at the request of client computers. For example, Web servers serve Web pages, time servers serve time and date information, and game hosts serve data about other players’ moves. When a computer on your network sends a request for service to a server computer on the Internet, the requested service is identified by a service or port number. This number appears as the destination port number in the transmitted IP packets. For example, a packet that is sent with destination port number 80 is an HTTP (Web server) request.
Protecting Your Network |