Dual Channel Digital Motor Controller
AX1500
AX1500 Motor Controller User’s Manual
Date Version Changes
Revision History
Revision History
AX1500 Motor Controller User’s Manual
Section
Section
Section
100
122
144
173
AX1500 Motor Controller User’s Manual
Beware of Motor Runaway in Improperly Closed Loop
Important Safety
Do not Connect to a RC Radio with a Battery Attached
Important Safety Warnings
What you will need
Locating the Connectors
AX1500
Quick Start
AX1500 Controller Rear View
AX1500 Quick Start
Connecting to the Batteries and Motors
Connecting to the Batteries and Motors
Signal Pin RC Mode RS232 Mode Analog Mode
Connecting to the 15-pin Connector
Connecting the R/C Radio
Connecting the R/C Radio
Parameter Default Values Letter
Powering On the Controller
Default Controller Configuration
Connecting the controller to your PC using Roborun
Connecting the controller to your PC using Roborun
Exploring further
Obtaining the Controller’s Software Revision Number
Product Description
AX1500 Motor Controller Overview
Technical features
Optical Encoder Inputs optional
Technical features
Low Power Consumption
High Efficiency Motor Power Outputs
Compact Open Frame PCB Design
Advanced Safety Features
Data Logging Capabilities
Power Connections
Connecting Power and Motors to the Controller
Power Connections
Connecting Power and Motors to the Controller
Controller Power
Mended Off Configuration
Controller Power
Powering the Controller from a single Battery
Controller Powering Schemes
Controller Powering Schemes
Powering the Controller Using a Main and Backup Battery
Powering the AX1500 with a Main and Backup Supply
Connecting the Motors
Converting the AX1500 to Single Channel
Single Channel Operation
Wire Length Limits
Power Fuses
Electrical Noise Reduction Techniques
Power Regeneration Considerations
Electrical Noise Reduction Techniques
Undervoltage Protection
Using the Controller with a Power Supply
Overvoltage Protection
Using the Controller with a Power Supply
Connecting Power and Motors to the Controller
Basic Operation
Input Command Modes
General Operation
Basic Operation
General Operation
Selecting the Motor Control Modes
Open Loop, Separate Speed Control
Open Loop, Mixed Speed Control
Selecting the Motor Control Modes
Closed Loop Speed Control
Close Loop Position Control
Temperature Max Amps
User Selected Current Limit Settings
Temperature-Based Current Limitation
Motor Current = Battery Current / PWM ratio
Battery Current vs. Motor Current
Battery Current vs. Motor Current
Off
Regeneration Current Limiting
Programmable Acceleration
Programmable Acceleration
Command Control Curves
Exponentiation Parameter Value Selected Curve
Left / Right Tuning Adjustment
Left / Right Tuning Adjustment
Parameter Value Speed Adjustment
Activating Brake Release or Separate Motor Excitation
Emergency Stop using External Switch
Activating Brake Release or Separate Motor Excitation
Inverted Operation
Using the Inputs to Activate the Buffered Output
Special Use of Accessory Digital Inputs
AX1500 Connections
Connecting Sensors and Actuators to Input/Outputs
AX1500 Connections
AX1500’s Inputs and Outputs
Connecting Sensors and Actuators to Input/Outputs
AX1500’s Inputs and Outputs
Signal Type Use Activated
List and Pin Assignment
Pin1
Connecting devices to Output C
Connecting devices to Output C
Connecting Switches or Devices to Input F
Connecting Switches or Devices to Input E
Connecting Switches or Devices to EStop/Invert Input
Connecting Switches or Devices to EStop/Invert Input
Analog Inputs
Connecting Position Potentiometers to Analog Inputs
Ana Ana2 Operating Mode Pin
Connecting Tachometer to Analog Inputs
Connecting Tachometer to Analog Inputs
Operating Mode Ana 1 p11 Ana2 p10 Ana 3 p12 Ana 4 p8
Resistance kOhm
Connecting External Thermistor to Analog Inputs
Connecting External Thermistor to Analog Inputs
Temp oC
Using the Analog Inputs to Monitor External Voltages
Internal Voltage Monitoring Sensors
Connecting User Devices to Analog Inputs
Internal Heatsink Temperature Sensors
Temperature Conversion C Source Code
Internal Heatsink Temperature Sensors
Connecting Sensors and Actuators to Input/Outputs
Optical Incremental Encoders Overview
Installing Connecting Using Encoder Module
Optical Incremental Encoders Overview
Recommended Encoder Types
Installing, Connecting and Using the Encoder Mod
Pulse Frequency in Hz = RPM / 60 * PPR
Installing the Encoder Module
Installing the Encoder Module
Connecting the Encoder
Pin Name Cable Color
Cable Length and Noise Considerations
Cable Length and Noise Considerations
Motor Encoder Polarity Matching
Voltage Levels, Thresholds and Limit Switches
Wiring Optional Limit Switches
Wiring Optional Limit Switches
SW1 SW2 GND
Motor 1 Fwd Motor 1 Rev
Wiring Limit Switches Without Encoders
Effect of Limit Switches
Wiring Limit Switches Without Encoders
Motor Fwd Motor Rev
Using the Encoder Module to Measure Distance
Using the Encoder to Measure Speed
Using the Encoder to Track Position
Using the Encoder to Track Position
Distance = Destination Counter value / Divider
RS232 Communication with the Encoder Module
Encoder Testing and Setting Using the PC Utility
Encoder Testing and Setting Using the PC Utility
Installing, Connecting and Using the Encoder Mod
Mode Description
Closed Loop Position Mode
Mode Description
Selecting the Position Mode
Sensor Mounting
Closed Loop Position Mode
Position Sensor Selection
Feedback Potentiometer wiring
Feedback Potentiometer wiring
Feedback Potentiometer wiring in RC or RS232 Mode
Pot wiring for RS232 or RC Command and Analog Feedback
Feedback Potentiometer wiring in Analog Mode
Analog Feedback on Single Channel Controllers
Analog Feedback on Single Channel Controllers
Sensor and Motor Polarity
Using Optical Encoders in Position Mode
Encoder Error Detection and Protection
Encoder Error Detection and Protection
Adding Safety Limit Switches
SW1 SW2
Control Loop Description
Using Current Limiting as Protection
Using Current Limiting as Protection
PID tuning in Position Mode
PID tuning in Position Mode
Closed Loop Position Mode
Selecting the Speed Mode
Closed Loop Speed Mode
Tachometer or Encoder Mounting
Tachometer wiring
Closed Loop Speed Mode
Speed Sensor and Motor Polarity
Speed Sensor and Motor Polarity
Adjust Offset and Max Speed
PID tuning in Speed Mode
PID tuning in Speed Mode
Closed Loop Speed Mode
Power On LED
Normal Fault Condition LED Messages
Power On LED
Diagnostic LED
Normal and Fault Condition LED Messages
Output Off / Fault Condition
C Operation
C radio control mode
Operation
Selecting the R/C Input Mode
Connector I/O Pin Assignment R/C Mode
Pin Input or Number Output Signal Description
Input Circuit Description
Input Circuit Description
Supplied Cable Description
RC Cable wiring diagram
Powering the Radio from the controller
Wiring for powering R/C radio from controller
Powering the Radio from the controller
Operating the Controller in R/C mode
Connecting to a Separately Powered Radio
Reception Watchdog
Reception Watchdog
Joystick Deadband Programming
Transmitter/Receiver Quality Considerations
Effect of deadband on joystick position vs. motor speed
Command Control Curves
Joystick Calibration
Left/Right Tuning Adjustment
Activating the Accessory Outputs
Data Logging in R/C Mode
Data Logging in R/C Mode
112
Analog Control and Operation
Analog Control and Operation
Connector I/O Pin Assignment Analog Mode
Pin Input or Number Signal Output Description
Connecting to a Voltage Source
Connecting to a Voltage Source
Connecting a Potentiometer
= U/R = 5V / 1000 Ohms = 0.005A = 5mA
Selecting the Potentiometer Value
Analog Deadband Adjustment
Analog Deadband Adjustment
Data Logging in Analog Mode
Power-On Safety
Under Voltage Safety
Modified Analog cable with RS232 output data logging for PC
Data Logging in Analog Mode
120
Use and benefits of RS232
Serial RS-232 Controls Operation
Use and benefits of RS232
Serial RS-232 Controls and Operation
Connector I/O Pin Assignment RS232 Mode
Extending the RS232 Cable
Cable configuration
Cable configuration
Establishing Manual Communication with a PC
Communication Settings
Bits/s, 7-bit data, 1 Start bit, 1 Stop bit, Even Parity
Roboteq v1.9b 06/01/07 s
RS232 Communication with the Encoder Module
Establishing Manual Communication with a PC
Data Logging String in R/C or Analog mode
Entering RS232 from R/C or Analog mode
Commands Acknowledge and Error Messages
RS-232 Watchdog
Controller Commands and Queries
Command Type Description
Controller Commands and Queries
Set Motor Command Value
Set Accessory Output
Syntax
Query Power Applied to Motors
Query Amps from Battery to each Motor Channel
?r or ?R
Query Heatsink Temperatures
Query Battery Voltages
Query Analog Inputs
Query Digital Inputs
Reset Controller
Read parameter
Accessing & Changing Configuration Parameter in Flash
Accessing & Changing Configuration Parameter in Flash
Apply Parameter Changes
Location Description Active after
Flash Configuration Parameters List
Value Mode See pages
Input Control Mode
Motor Control Mode
Address Access Read/Write Effective After Reset
Bit Definition See pages
Amps Limit
Acceleration
Input Switches Function
Exponentiation on Channel 1 and Channel
Address Channel Access Read/Write Effective Instantly
RC Joystick or Analog Deadband
Default Encoder Time Base 1
Left/Right Adjust
Joystick Min, Max and Center Values
Default Encoder Distance Divider
Default PID Gains
Location Function
Reading & Changing Operating Parameters at Runtime
Address 82 P1 83 I1 84 D1 85 P2
Operating Modes Registers
Read/Change PID Values
Bit Function
Controller Status Register
PWM Frequency Register
Bit Model or Function
Controller Identification Register
Current Amps Limit Registers
Read Encoder Counter
RS232 Encoder Command Set
Set/Reset Encoder Counters and Destination Registers
Or !Q n
Read Speed
Read Speed/Distance
Read Encoder Limit Switch Status
Read Distance
DD= parameter value
Switch Value
Read / Modify Encoder Module Registers and Parameters
Address Parameter Description Size Access
Speed or Distance 1 or
Switch Status
Register Description
Encoder Hardware ID code
Register Description
Counter Read/Write Mailbox
Counter 1
Destination Register 1
Encoder Threshold
Distance 1
Speed 1
Time Base 1
Decimal Bit Hex Controller Output
Counter Read Data Format
Counter Read Data Format
154
Automatic Switching from RS232 to RC Mode
Automatic Switching from RS232 to RC Mode
Data Logging Cables
Analog and R/C Modes Data Logging String Format
Dec Hex
Decimal to Hexadecimal Conversion Table
Decimal to Hexadecimal Conversion Table
UDec Hex
AX1500 Motor Controller User’s Manual 159
160
System Requirements
Using the Roborun Configuration Utility
Downloading and Installing the Utility
Using the Roborun Configuration Utility
Connecting the Controller to the PC
Roborun Frame, Tab and Menu Descriptions
Parameter Selection and Setting and Special Functions
Roborun Frame, Tab and Menu Descriptions
Loading, Changing Controller Parameters
File and Program Management Commands
View Controller Connector Pinout
Getting On-Screen Help
Loading, Changing Controller Parameters
Control Settings
Motor Control Mode
Input Command Adjustment
Power Settings
Joystick Timing
Analog or R/C Specific Settings
Deadband
Closed Loop Parameters
Encoder Setting and Testing
Encoder Setting and Testing
Encoder Module Parameters Setting
Viewing Encoder Data
Running the Motors
Exercising the Motors
Measurement
Motor Power setting
Running the Motors
Run/Stop Button
Transmit and Receive Data
Real-Time Strip Chart Recorder
Input Status and Output Setting
Logging Data to Disk
Connecting a Joystick
Using the Console
Keep Watchdog Alive
Using the Console
Command Entry
Terminal Screen
Loading and Saving Profiles to Disk
Operating the AX1500 over a Wired or Wireless LAN
Using the Roborun Configuration Utility Send Reset String
Viewing and Logging Data in Analog and R/C Modes
Roboserver screenshot when idle
Operating the AX1500 over a Wired or Wireless LAN
Updating the Encoder Software
Updating the Controller’s Software
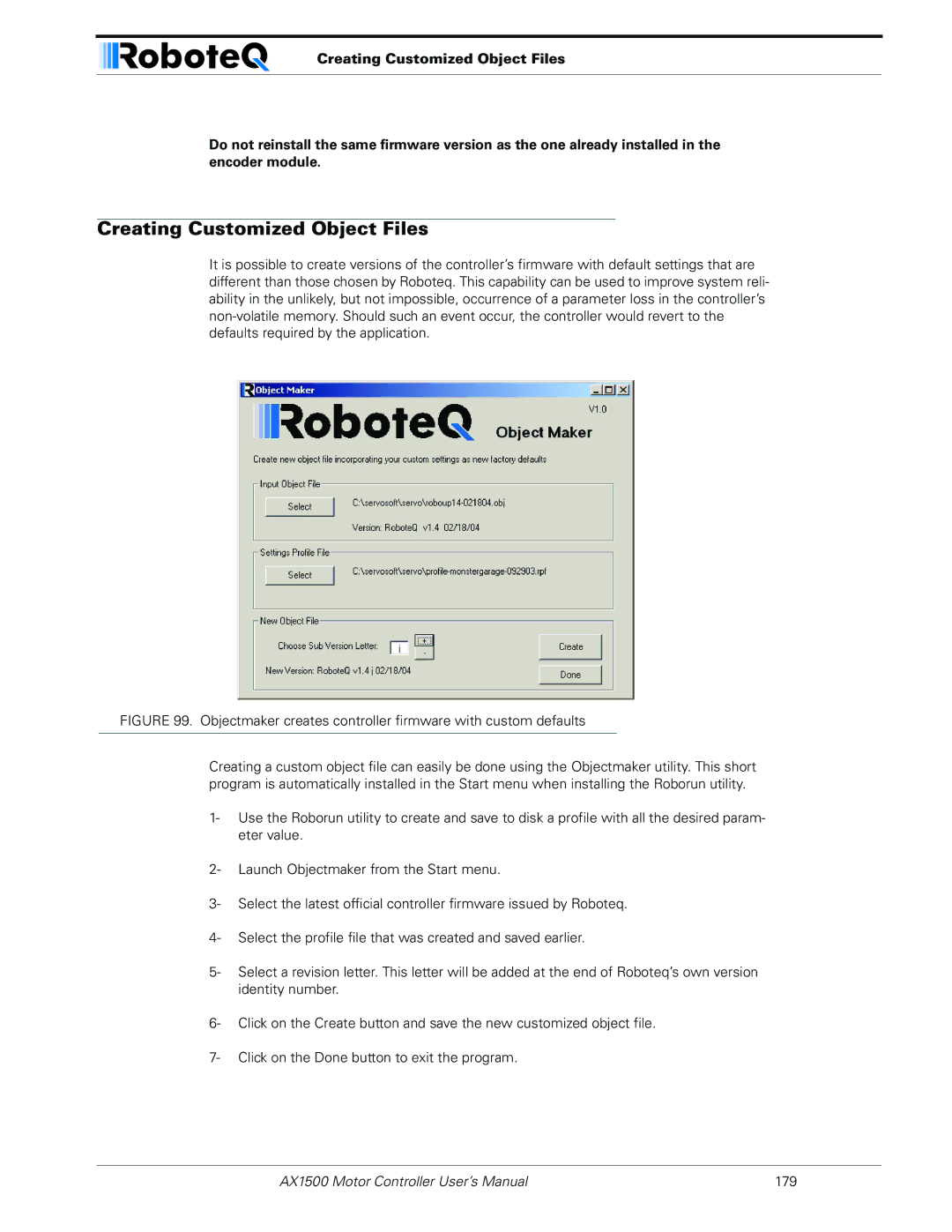
Creating Customized Object Files
Objectmaker creates controller firmware with custom defaults
180
Mechanical Dimensions
Mechanical Specifications
Mechanical Dimensions
Thermal Considerations
Mechanical Specifications
Mounting Considerations
Attaching the Controller Directly to a Chassis
Attaching the Controller Directly to a Chassis
Precautions to observe
Wire Dimensions
Wire Dimensions
Weight
186