Parallel Scsi Interface
Page
Parallel Scsi Interface
Page
Revision Date Writer/Engineer
Revision status summary sheet
Parallel Scsi Interface Product Manual, Rev. a
Table of Contents
Parallel Scsi Interface Product Manual, Rev. a
Wide transfer
Logical characteristics
Message system specification
Miscellaneous Scsi bus characteristics
Scsi commands
SPI information units
Drive features
List of Figures
Xii Parallel Scsi Interface Product Manual, Rev. a
Interface requirements
How to use this interface manual
Scope of Scsi standards
Applicable standards
General interface description
Scsi client-server model
Glossary
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Keywords
Physical interface characteristics
Summary of Scsi messages
Message Name Hex Code Number
Scsi bus
Priority
Scsi IDs and associated Scsi bus arbitration priorities
Scsi bus signals overview
Scsi target usage of Pcrca
Pcrc signal usage requirements
LVD signals
Signal states
Signal values
SE signals
Voltage and current definitions
OR-tied signals
DB7-0
Signal sources
Signal sources
Data bit P cable Data bit a cable I/O DB15-8 Scsi bus phase
Reference Type Value ns Unless Timing description
Scsi bus timing
Scsi bus control timing values in nanoseconds
Timing
Timing values for negotiated transfer rate in nanoseconds
Scsi bus data and information phase ST timing values
Timing values for negotiated transfer rate
Nanoseconds unless otherwise noted
Page
ATN transmit setup time Min
Receive Scsi bus data and information phase DT timing values
Total transmitter error budget Receiver errors
Fast-160 Fast-320 Comments
Interconnect and system margin
ISI of data
ATN transmit setup time
ATN receive setup time
Crosstalk time shift
Bus settle delay
Bus clear delay
Bus free delay
Bus set delay
PCRC transmit setup time
Flow control receive setup time
Flow control transmit setup time
PCRC receive setup time
QAS arbitration delay
Data release delay
Physical disconnection delay
Power on to selection
Receive negation period
Receive internal setup time
Receive setup time
Receive internal hold time
Residual skew error
Reset delay
Reset hold time
Reset to selection
System noise at launch
System deskew delay
Skew correction range
Strobe offset tolerance
Measurement points
LVD measurement points
Clocking methods for data transfers
ST latching data vs. DT latching data
DT synchronous transfer example
Paced transfer on a Scsi bus
Paced transfers
Data transfer modes
Asynchronous transfers
Synchronous transfers
Information unit transfers
ST Data phase parallel transfers
DT Data phase parallel transfers
Data group transfers
Negotiation algorithm
Negotiation
Negotiation message pair Field name
When to negotiate
Negotiable fields
Negotiable fields and effects of successful negotiation
Responding message requirements
Response shall be
Field Name Message Numerically
Transfer agreements
Synchronous
Transfer period factor
Transfer period factor relationships
Value Description Message Transfer rate
Transfer width exponent
12.6 REQ/ACK offset
Protocol options
Protocol options bits
Iureq
PPR negotiation keeping Iureq set to zero
Bus phases resulting from Iureq changes
Sdtr negotiation PPR negotiation setting Iureq to one
PPR negotiation setting Iureq to zero
Pcompen
Wrflow
Rdstrm
RTI Retain Training Information
Negotiable field combinations
Transfer
Transfer Period
Negotiation message sequences
Message restrictions
Parallel Scsi Interface Product Manual, Rev. a
Scsi bus phases overview
BUS Free phase
Unexpected and expected bus free phases
Arbitration and QAS overview
Expected bus free phases
Normal Arbitration phase
QAS protocol
QAS phase overview
Selection phase
Information unit transfers disabled
Information unit transfers enabled
Selection overview
Selection using attention condition timeout procedure
Reselection phase
Reselection phase overview
Physical reconnection
Scsi bus fairness
Physical reconnection timeout procedure
Information transfer phases
Information transfer phases
Signal Phase Direction of transfer Comment
Asynchronous transfer
Synchronous transfer
ST synchronous data transfer
Information unit transfer
DT synchronous transfer
Page
Data group data field transfer
Page
Page
Page
Paced transfer training pattern
Paced transfer
DT Data in phase training pattern
Start of section a
Start of section B
Start of section C
DT Data OUT phase training pattern
3.2 P1 data valid/invalid state transitions
Starting pacing transfers with no training pattern
Starting pacing transfers at end of training pattern
Paced information unit transfer
Ending pacing transfers
Wide transfer
Deskewing
Data phase
Command phase
Message phase
Status phase
Message OUT phase exception condition handling
Signal restrictions between phases
Message in phase exception condition handling
Message OUT phase
Scsi bus phase sequences overview
Scsi bus phase sequences
Hard reset or protocol error
Reselection Selection Arbitration DT Data Message OUT
Data bus protection overview
ST data bus protection using parity
Parity checking rules for Selection and Reselection phases
Data bus protection
Order of bytes in the CRC field
Error detection capabilities
Message formats
General message protocols and formats
Extended messages
Message format
One-byte messages
Two-byte messages
Message categories
Extended Message Codes
Link Control Messages Link Control message codes
Key
Bit Byte
Disconnect
Identify
Identify message format
Invalid data bits
Ignore Wide Residue
Ignore Wide Residue message format
Ignore field definition
Message Reject
Initiator Detected Error
Linked Command Complete
Message Parity Error
Modify Bidirectional Data Pointer
Modify Data Pointer message format
No Operation
Modify Bidirectional Data Pointer message format
Parallel Protocol Request message format
Parallel Protocol Request
Value 00h 01h-FEh FFh Description Timing values
Use ST Data in and ST Data OUT phases to transfer data
Valid protocol options bit combinations
Use QAS for arbitration
Parallel Protocol Request messages implied agreement
Restore Pointers
QAS Request
Save Data Pointers
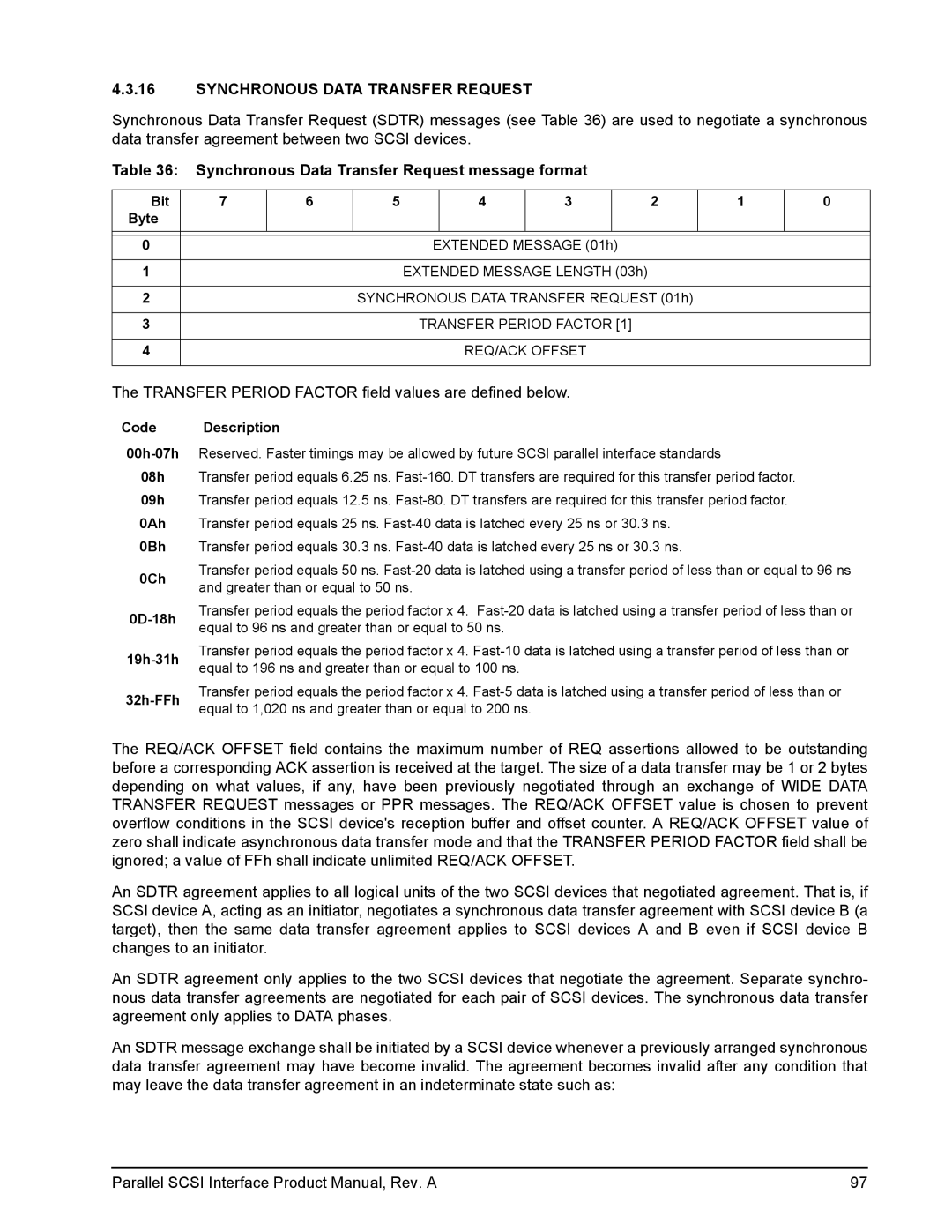
Synchronous Data Transfer Request message format
Synchronous Data Transfer Request
Sdtr messages implied agreements
Target initiated Sdtr negotiation
Initiator initiated Sdtr negotiation
Task Complete
Wide Data Transfer Request message format
Wide Data Transfer Request
Wdtr message implied agreement
Target initiated Wdtr negotiation
Responding Scsi device Wdtr response Implied agreement
Task attribute message overview and codes
Task attribute messages
Task attribute message codes
ACA Auto Contingent Allegiance
ACA message format
Ordered
Head of Queue
0Eh
Task management messages
Task management message codes Task management message codes
Abort Task
Clear ACA
Logical Unit Reset
Target Reset
Abort Task SET
Miscellaneous Scsi bus characteristics
Hard reset
Bus reset condition
Asynchronous condition recovery
Reset events
Saved pointers
Active pointers
Command processing considerations and exception conditions
Asynchronous event notification
Incorrect initiator connection
Unexpected Reselection phase
Information unit transfer logical operations
SPI information units
Page
Parallel Scsi Interface Product Manual, Rev. a 115
116 Parallel Scsi Interface Product Manual, Rev. a
Parallel Scsi Interface Product Manual, Rev. a 117
SPI information units
SPI command information unit
SPI command information unit Bit Byte
Task Management flags Codes Description
Task Attribute Codes Description
SPI LQ information unit Bit Byte
SPI LQ information unit
Bidi Direction
FFh All
SPI LQ information unit type
Codes Type Description
F0H
Page
SPI data information unit
SPI data stream information unit
SPI data information unit Bit Byte
SPI status data stream information unit Bit Byte
SPI status information unit
SPI status information unit Bit Byte
Reserved Reserved for FCP
Task management function not supported
SPI command information unit fields invalid
Packetized Failures field Bit Byte
Packetized Failures code Codes Description
Page
130 Parallel Scsi Interface Product Manual, Rev. a
Command implementation requirements
Command Descriptor Block CDB
Reserved
Page
Fixed and variable length Command Descriptor Block formats
Typical CDB for 12-byte commands Bit Byte
Typical CDB for 16-byte commands Bit Byte
Additional CDB Data if required
Additional CDB Length n-7
Typical variable length CDB Bit Byte Operation Code 7Fh
Page
Control field Bit Byte Last
Naca a
Link b
Status
Status precedence
Single command example
Command examples
Disconnect example
Disconnect example
Auto Contingent Allegiance or Contingent Allegiance
Timing examples
Clearing an Auto Contingent Allegiance condition
Overlapped commands
Incorrect logical unit selection
Sense data
Asynchronous Event Reporting
Autosense
Unit Attention condition
Untagged task queuing
Target hard reset
Logical unit reset
Queued tasks formerly queued I/O processes
Tagged task queuing
Programmable operating definition
Parameter rounding
Incorrect initiator connection
Short and extended self-tests
Default self-test
S.M.A.R.T. system
Self-test operations
Foreground mode
Background mode
Self-test modes
Device type a Command Reference All device types
Exception commands for background self-tests
Self-test mode summary
Error detection for asynchronous information phases
Protection code
Word Location Signal Meaning
Covered signals
Page
Error detection properties
Code description
Protection code usage
Disabling protection code checking
Error handling
Protection code transmission
Enabling protection code checking
Case 1-Power off during removal or insertion
SPI-3 to SCSI-2 terminology mapping
SPI-3 to SCSI-2 terminology mapping
SPI-3 equivalent term SCSI-2 term
Index
Code value reserved
Disconnect privilege 148 domain 5, 9 dormant
Initiator 3, 6, 14, 131, 140 faulted
Multidrop 7 multimode
Page
Scsi
Page
Wdtr 40
170 Parallel Scsi Interface Product Manual, Rev. a
Page
Seagate Technology LLC