Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide
Sun Microsystems, Inc
Please Recycle
FCC Class A Notice
Regulatory Compliance Statements
DOC Class A Notice - Avis DOC, Classe A
BSMI Class A Notice
iv Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Safety
Declaration of Conformity
Supplementary Information
USA-FCC Class A
vi Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Safety Agency Compliance Statements
Safety Precautions
Symbols
Placement of a Sun Product
Power Cord Connection
Lithium Battery
Battery Pack
System Unit Cover
Symbole
Einhaltung sicherheitsbehördlicher Vorschriften
CD-ROM
Sicherheitsvorkehrungen
Anschluß des Netzkabels
Lithiumbatterie
Batterien
Gehäuseabdeckung
Symboles
Conformité aux normes de sécurité
Mesures de sécurité
Modification du matériel
Positionnement d’un produit Sun
Conformité SELV
Connexion du cordon d’alimentation
Batterie au lithium
Normativas de seguridad
Bloc-batterie
Couvercle
Conformité aux certifications Laser
Cumplimiento de la normativa SELV
Modificaciones en el equipo
Ubicación de un producto Sun
Conexión del cable de alimentación eléctrica
GOST-R Certification Mark Nordic Lithium Battery Cautions
Aviso de cumplimiento con requisitos de láser
Batería de litio
Paquete de pilas
Sverige
Danmark
Suomi
xvi Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Contents
Safety Agency Compliance Statements Preface
2. System Setup
Regulatory Compliance Statements Declaration of Conformity
3. Administration and Network Setup
4. Hardware Configuration
Contents
6. Using Storage Devices
7. Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
5. Replacing a Disk Drive
xx Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
A. Connector Signal Descriptions
B. System Specifications Index
xxii Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Preface
How This Book Is Organized
xxiv Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Typographic and Command Entry Conventions
Using UNIX Commands
Solaris Handbook for Sun Peripherals
Shell Prompts
Related Documentation
Accessing Sun Documentation Online
Sun Welcomes Your Comments
http//docs.sun.com
docfeedback@sun.com
xxviii Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
System Overview
About the Sun Enterprise 220R Server
2 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Error-correcting code ECC on memory and all data paths
Locating Front Panel Features
Keyswitch
CD-ROM or
optional Tape drive
page
screw hole
Locating Back Panel Features
6 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
LED indicators Power button Power On/Off position Keyswitch
About the Status and Control Panel
Locked position Standby position
Keyswitch Settings
Power-on/ Activity General fault
System LED Indicators
This green LED lights continuously when the system power is on
10 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
System Setup
Tools Required for Setup and Rackmounting
Using the Setup and Rackmounting Guide
About the Parts Shipped to You
Before You Begin
How to Install the Sun Enterprise 220R Server
What to Do
2. Install any optional drive shipped with your system
3. Install the system into the rack
Note -Each outlet must connect the system to a 15A circuit for North America and Japan, and to a 10A circuit for Europe. See your local electrical codes
6. Set up a console for your server
7. Configure the network interface
8. Turn on power to your server
9. Install and boot the operating system software
11. Load additional software from the server media kit
About Server Rackmounting
Holes 99, 100, or Holes 27, 28, or Holes 15, 16, or Holes 3, 4, or
Ninth
Third
First
How to Remove the System From the Rack
2. Locate the flat spring catch shown in the following figure
What Next
3. Prepare to remove the system
5. Set the system on a workbench or other stable surface
7. Reattach, close, and lock the rack doors as appropriate
How to Place the System Into the Rack
3. Lift the system
1. Extend the cabinet’s anti-tip legs
24 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
5. Insert the system glides into the inner slides of the rack glides
26 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
10. Reattach, close, and lock the rack doors as appropriate
About Communicating With the Server
How to Attach an Alphanumeric ASCII Terminal
2. Connect the terminal’s power cable to an AC outlet
3. Set the terminal to receive
How to Configure a Local Graphics Console
1. Install the graphics card into a vacant PCI slot
3. Connect the monitor’s power cord to an appropriate AC power outlet
32 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
4. Connect the keyboard cable to the server’s keyboard/mouse port
1. Turn on power to any peripherals and external storage devices
How to Power On the System
2. Turn on power to the monitor or terminal
4. Press the front panel Power button once
3. Turn the front panel keyswitch to the Power-On/Off position
Power-On/Off position Power button
Locked position
5. Turn the keyswitch to the Locked position
36 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
How to Install the System Software
Installing the Operating System From CD-ROM
Solaris 2.6 Hardware 5/98 Installation Requirement
Installing the Operating System From a Network Boot Server
Solaris 7 Software Installation
How to Select the Boot Device
40 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
2. To reboot the system from the new boot device, type
1. At the ok prompt, type
42 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
How to Power Off the System
1. Notify users that the system will be powered down
3. Halt the operating system using the appropriate commands
2. Back up the system files and data, if necessary
44 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Administration and Network Setup
About Network Interface Options
How to Configure the Standard Ethernet Interface
3. Resume the installation of the system
1. Assign a host name to the machine
2. Determine the IP address for the interface
48 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
How to Add an Ethernet Interface
1. Assign a network host name to the interface
3. Boot the operating system and log on to the system as superuser
4. Create an appropriate /etc/hostname file for the new interface
zardoz # cat /etc/hostname.hme0
zardoz # cat /etc/hostname.hme1
zardoz # reboot -- -r
7. Reboot the system type
zardoz # cat /etc/hosts
How to Attach a Twisted-Pair Ethernet TPE Cable
1. Locate the RJ-45 connector for the appropriate Ethernet interface
What Next
How to Attach an MII Ethernet Transceiver
1. Locate the appropriate MII Ethernet connector
4. Lock the AUI connector
56 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
How to Boot the System Using the Standard Ethernet Interface
At the ok prompt, type either of the two following commands
ok boot net - install
58 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
How to Boot the System Using a PCI-Based Ethernet Interface
pci@1f,4000/pci@5/SUNW,hme@0,1
2. Change the default net device. At the ok prompt, type
60 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Hardware Configuration
About Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability Features
Error Correction and Parity Checking
Status LEDs
Hot-Pluggable Disk Drives
Power Supply Redundancy
Hot-Swappable Power Supplies
Four Levels of Diagnostics
64 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
At the application level, you have access to SunVTS diagnostics. Like OBDiag, SunVTS provides a comprehensive test of the system, including its external interfaces. SunVTS also allows you to run tests remotely over a network connection. You can only use SunVTS if the operating system is running. For more information about SunVTS, see “About SunVTS Software” on page 132, “How to Use SunVTS Software” on page 135, and “How to Check Whether SunVTS Software Is Installed” on page
Configuration Rules
About Memory
About CPU Modules
About Peripheral Component Interconnect PCI Buses
Clock
About Disk Array Configurations and Concepts
Disk Concatenation
Disk Mirroring RAID
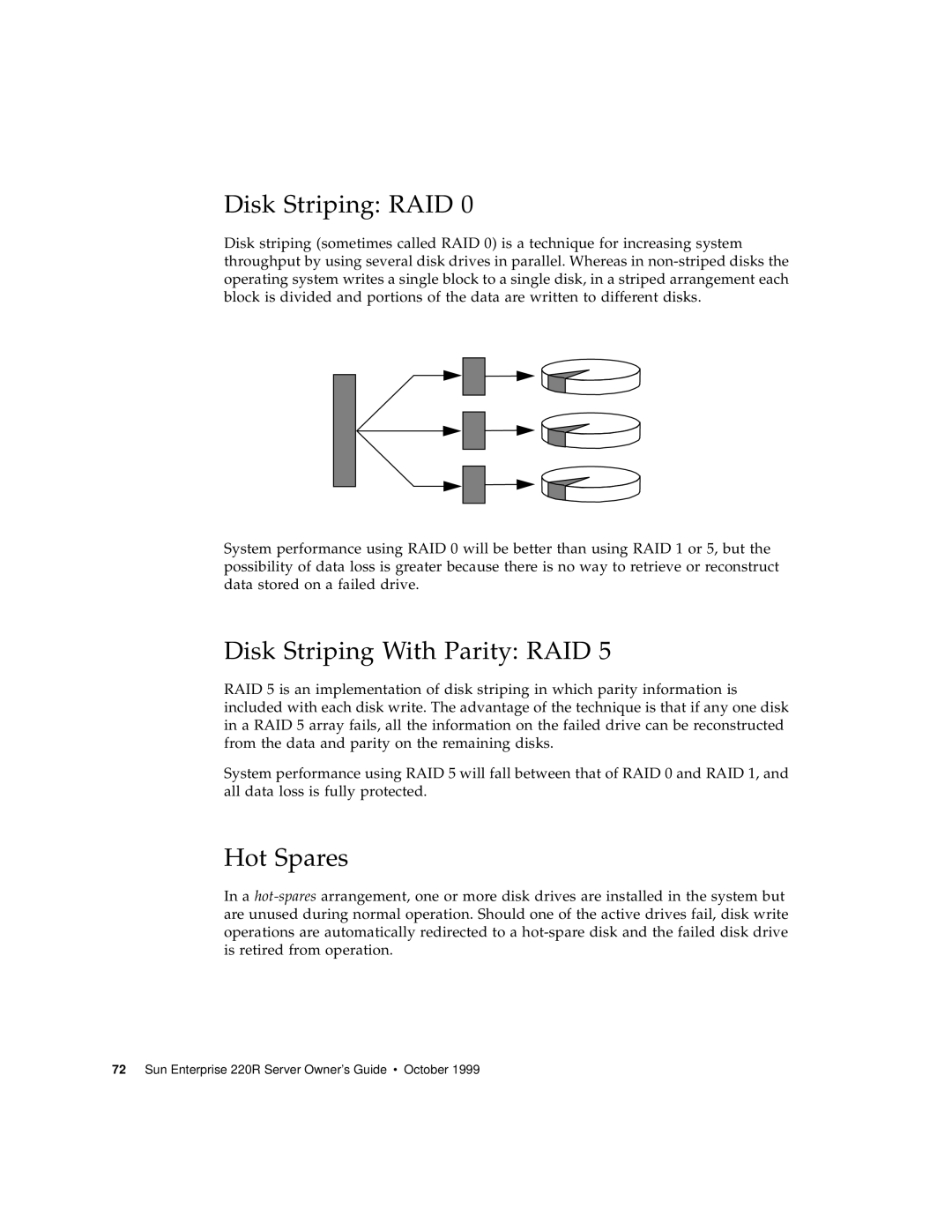
Disk Striping RAID
Disk Striping With Parity RAID
Hot Spares
72 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Hot Plug
For More Information
About Internal Disk Drives
Disk drive LEDs
Internal
disk bays
devices/pci@1f,4000/scsi@3/sd@0,0
devices/pci@1f,4000/scsi@3/sd@1,0
Disk Slot Number
Logical Device Name
About Power Supplies
Page
About the Standard Ethernet Port
78 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
About the Serial Ports
About the Parallel Port
80 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
About the Main Logic Board Jumpers
About Serial Port Jumpers
82 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
About Flash PROM Jumpers
Target Devices
About the External SCSI Port
Bus Length
External SCSI Cabling and Termination
Multi-initiator Support
The following figures provide a summary of the cabling guidelines
Chapter 4 Hardware Configuration
88 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Replacing a Disk Drive
How to Avoid Electrostatic Discharge
2. Use an antistatic mat or similar surface
3. Use an antistatic wrist strap
1. Prepare the system for disk removal
How to Remove a Disk Drive
3. Unlock the front doors and swing them open
7. Place the disk drive on an antistatic mat
8. Repeat the procedure for the other drive if necessary
6. Holding the disk drive by the handle, slide it out of the drive bay
94 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
1. Prepare the system to receive the new disk drive
How to Install a Disk Drive
4. Release the drive handle on the disk drive
5. Align the disk drive to its drive bay
10. Repeat the procedure for the other drive if necessary
11. Close and then lock the system front doors
How to Initiate a Reconfiguration Boot
2. Turn on power to the monitor or terminal, and open your console
5. When the ok prompt is displayed, type the following command
ok boot -r
100 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Using Storage Devices
2. Place a CD into the drive tray, label side up
How to Insert a Compact Disc Into the Drive
3. Gently push the tray back into the drive
Manually see “How to Eject a Compact Disc Manually” on page
1. Kill processes accessing the CD-ROM drive, if necessary
How to Eject a Compact Disc With Software Commands
2. From the console device, type
You can also eject a compact disc by using one of these methods
2. Press the Eject button on the front panel
How to Eject a Compact Disc Manually
106 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
What Next
1. Turn off the power to your system
How to Eject a Compact Disc in an Emergency
2. Unfold and straighten one end of a large wire paper clip
You can also eject a compact disc by using one of these methods
Handling and Storing Tape Cartridges
About the Tape Drive and Tape Cartridges
Thermal Conditioning
2. Insert the cartridge into the drive, label side up
How to Insert a Tape Cartridge
3. Push gently on the cartridge until it is pulled into the drive
112 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
1. Check that there is no drive activity
How to Remove a Tape Cartridge
2. Push the Eject button and remove the tape cartridge
How to Control the Tape Drive
114 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
How to Clean the Tape Drive
Insert a cleaning cartridge into the drive
How to Clean a Compact Disc
1. Clean the disc with compressed air
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
About Diagnostic Tools
System yes boots ? yes Fault LED lit ?
disk problem
Chapter 7 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Run POST no POST failure ?
About Power-On Self-Test POST Diagnostics
How to Use POST Diagnostics
Setting Up a tip Connection
3. To use serial port A
a. Copy and paste the serial port B remote file
b. Modify the serial port B system remote file as follows
4. In a shell window on the Sun system, type
5. When POST is completed, disconnect the tip window as follows
c. Type the following to kill the tip hardwire process
3. Verify the following serial port default settings as follows
Verifying the Baud Rate
Results
1. When the ok prompt is displayed, type the following command
Observing POST in Progress
If a Sun Type-5 keyboard is attached to the system, POST status and error indications are also displayed via the four LEDs on the keyboard. When POST starts, all four keyboard LEDs blink on and off simultaneously. After that, the Caps Lock LED blinks slowly to indicate POST is running. If an error is detected, the pattern of the lit LEDs provides an error indication. See “Error Indications” on page 138 for more information
About OpenBoot Diagnostics OBDiag
OBDiag Menu
OBDiag Configuration Variable Settings
2. Optional Select a diagnostic level
How to Use OpenBoot Diagnostics OBDiag
3. Then type
4. At the ok prompt, type
5. At the ok prompt, type
The OBDiag menu is displayed
The OBDiag Test menu is displayed
How to Set the Diagnostic Level for POST and OBDiag
2. To set the diag-level variable, type the following
About SunVTS Software
SunVTS Test Reference Manual
SunVTS User’s Guide
SunVTS Quick Reference Card
How to Check Whether SunVTS Software Is Installed
1. Type the following
2. Remotely log in to the server as superuser or root
How to Use SunVTS Software
3. Check whether SunVTS software is loaded on the server
4. To start the SunVTS software, type
# cd /opt/SUNWvts/bin # ./sunvts -display localhostname0
About Sun Enterprise SyMON Software
Error Indications
About Troubleshooting Your System
Front Panel LEDs
Keyboard LEDs
Stop
D key
Scroll Lock
The following table provides error code definitions
Power Supply LEDs
The following table provides a description of each LED
Disk LEDs
Error Messages
Internal disk drive LEDs
Software Commands
Solaris prtdiag Command
prtdiag output
ok /usr/platform/sun4u/sbin/prtdiag
OBP printenv Command
OBP show-devs Command
OBP probe-scsi and probe-scsi-all Commands
probe-scsi output
probe-scsi-all output
ok probe-scsi
ok probe-scsi
About Diagnosing Specific Problems
Symptom
Network Communications Failure
Action
Solution
3. Reboot the system to make the changes effective
4. Reboot the system to make the changes effective
Determining the Device Name of the Ethernet Interface
Power-On Failure
1. Run POST diagnostics
4. If the POST output contains an error message, then POST has failed
Video Output Failure
Replace the drive indicated by the failure message
Disk or CD-ROM Drive Failure
1. At the system ok prompt, type
SCSI Controller Failure
2. If a disk doesn’t respond, replace the unresponsive drive
DIMM Failure
Power Supply Failure
152 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Page
154 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Connector Signal Descriptions
Keyboard/Mouse Connector Diagram
Reference for the Keyboard/Mouse Connector
Keyboard/Mouse Connector Signals
Serial Port A and B Connector Diagram
Reference for the Serial Port A and B Connectors
Serial Port Signals
158 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Not connected
TPE Connector Diagram
Reference for the Twisted-Pair Ethernet TPE Connector
TPE Connector Signals
UltraSCSI Connector Diagram
Reference for the UltraSCSI Connector
UltraSCSI Connector Signals
162 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Dat13
164 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Reference for the Parallel Port Connector
Parallel Port Connector Diagram
166 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Signal ground
Reference for the Media Independent Interface MII Connector
MII Connector Diagram
MII Connector Signals
120 2140
Txclk
36GndGround 37GndGround 38GndGround 39GndGround 40PwrPower
170 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
System Specifications
“Physical Specifications” on page “Electrical Specifications” on page
“System Specifications” on page
A P P E N D I X B
Physical Specifications
Reference for System Specifications
Electrical Specifications
Environmental Specifications
The environmental requirements for the system are as follows
174 Sun Enterprise 220R Server Owner’s Guide October
Index
Page
Page
diag-switch?, 121, 129 operating system software
See also Ethernet ATM
Page
watch-net-all command