General Tuning Concepts
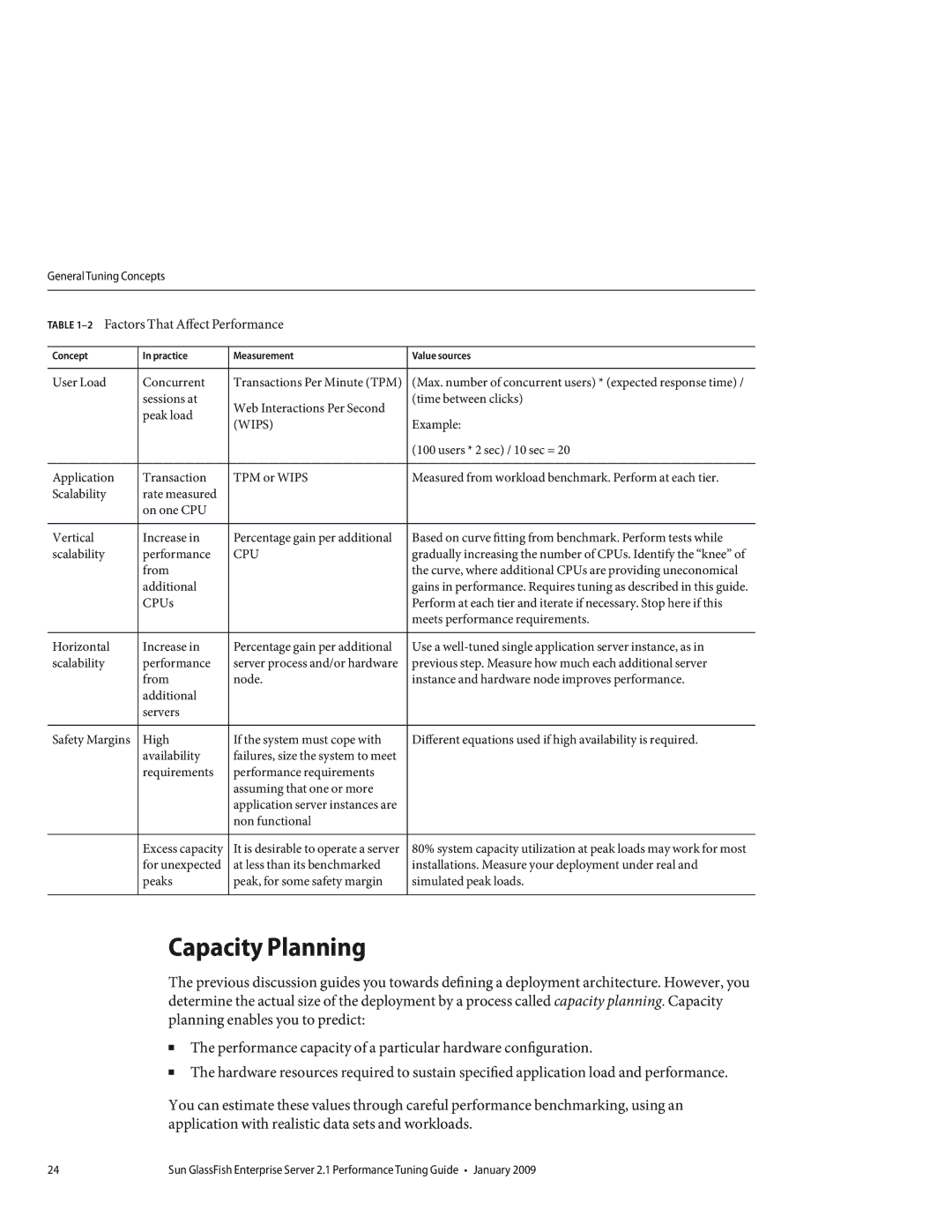
TABLE 1–2 Factors That Affect Performance
Concept | In practice | Measurement | Value sources |
|
|
|
|
User Load | Concurrent | Transactions Per Minute (TPM) | (Max. number of concurrent users) * (expected response time) / |
| sessions at | Web Interactions Per Second | (time between clicks) |
| peak load |
| |
| (WIPS) | Example: | |
|
| ||
|
|
| (100 users * 2 sec) / 10 sec = 20 |
|
|
|
|
Application | Transaction | TPM or WIPS | Measured from workload benchmark. Perform at each tier. |
Scalability | rate measured |
|
|
| on one CPU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vertical | Increase in | Percentage gain per additional | Based on curve fitting from benchmark. Perform tests while |
scalability | performance | CPU | gradually increasing the number of CPUs. Identify the “knee” of |
| from |
| the curve, where additional CPUs are providing uneconomical |
| additional |
| gains in performance. Requires tuning as described in this guide. |
| CPUs |
| Perform at each tier and iterate if necessary. Stop here if this |
|
|
| meets performance requirements. |
|
|
|
|
Horizontal | Increase in | Percentage gain per additional | Use a |
scalability | performance | server process and/or hardware | previous step. Measure how much each additional server |
| from | node. | instance and hardware node improves performance. |
| additional |
|
|
| servers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Safety Margins | High | If the system must cope with | Different equations used if high availability is required. |
| availability | failures, size the system to meet |
|
| requirements | performance requirements |
|
|
| assuming that one or more |
|
|
| application server instances are |
|
|
| non functional |
|
|
|
|
|
| Excess capacity | It is desirable to operate a server | 80% system capacity utilization at peak loads may work for most |
| for unexpected | at less than its benchmarked | installations. Measure your deployment under real and |
| peaks | peak, for some safety margin | simulated peak loads. |
|
|
|
|
Capacity Planning
The previous discussion guides you towards defining a deployment architecture. However, you determine the actual size of the deployment by a process called capacity planning. Capacity planning enables you to predict:
■The performance capacity of a particular hardware configuration.
■The hardware resources required to sustain specified application load and performance.
You can estimate these values through careful performance benchmarking, using an application with realistic data sets and workloads.
24 | Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server 2.1 Performance Tuning Guide • January 2009 |