Understanding Operational Requirements
Client-Side
Presentation
Browser
Pure
HTML
Java
Applet
Desktop
Java
Application
Other
Device
J2EE
Client
Web
Server
JSP
JSP
Java
Servlet
J2EE
Platform
Server-Side Enterprise
Business Logic Information
System
EJB
Container
EJB
EJB
EJB
J2EE
Platform
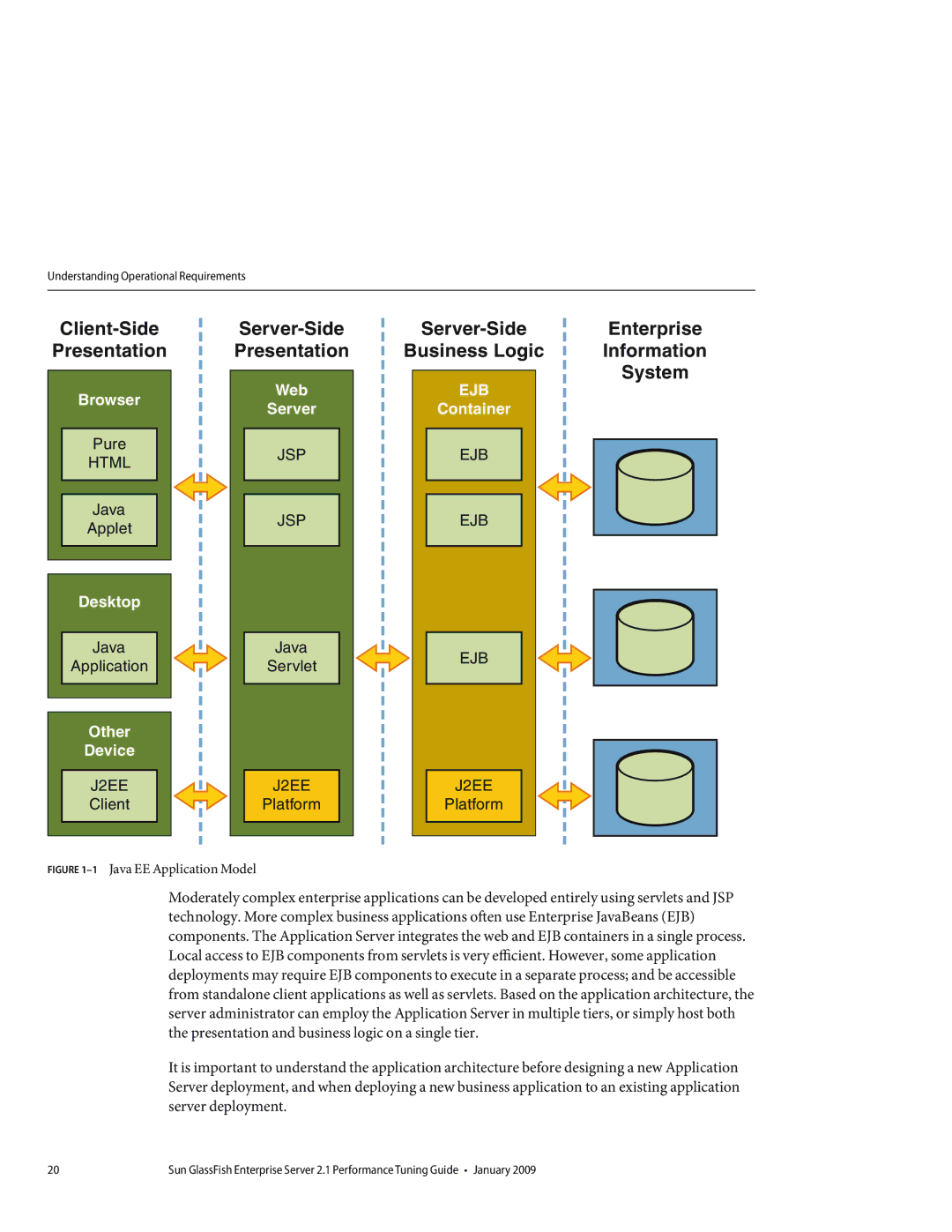
FIGURE 1–1 Java EE Application Model
Moderately complex enterprise applications can be developed entirely using servlets and JSP technology. More complex business applications often use Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) components. The Application Server integrates the web and EJB containers in a single process. Local access to EJB components from servlets is very efficient. However, some application deployments may require EJB components to execute in a separate process; and be accessible from standalone client applications as well as servlets. Based on the application architecture, the server administrator can employ the Application Server in multiple tiers, or simply host both the presentation and business logic on a single tier.
It is important to understand the application architecture before designing a new Application Server deployment, and when deploying a new business application to an existing application server deployment.
20 | Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server 2.1 Performance Tuning Guide • January 2009 |