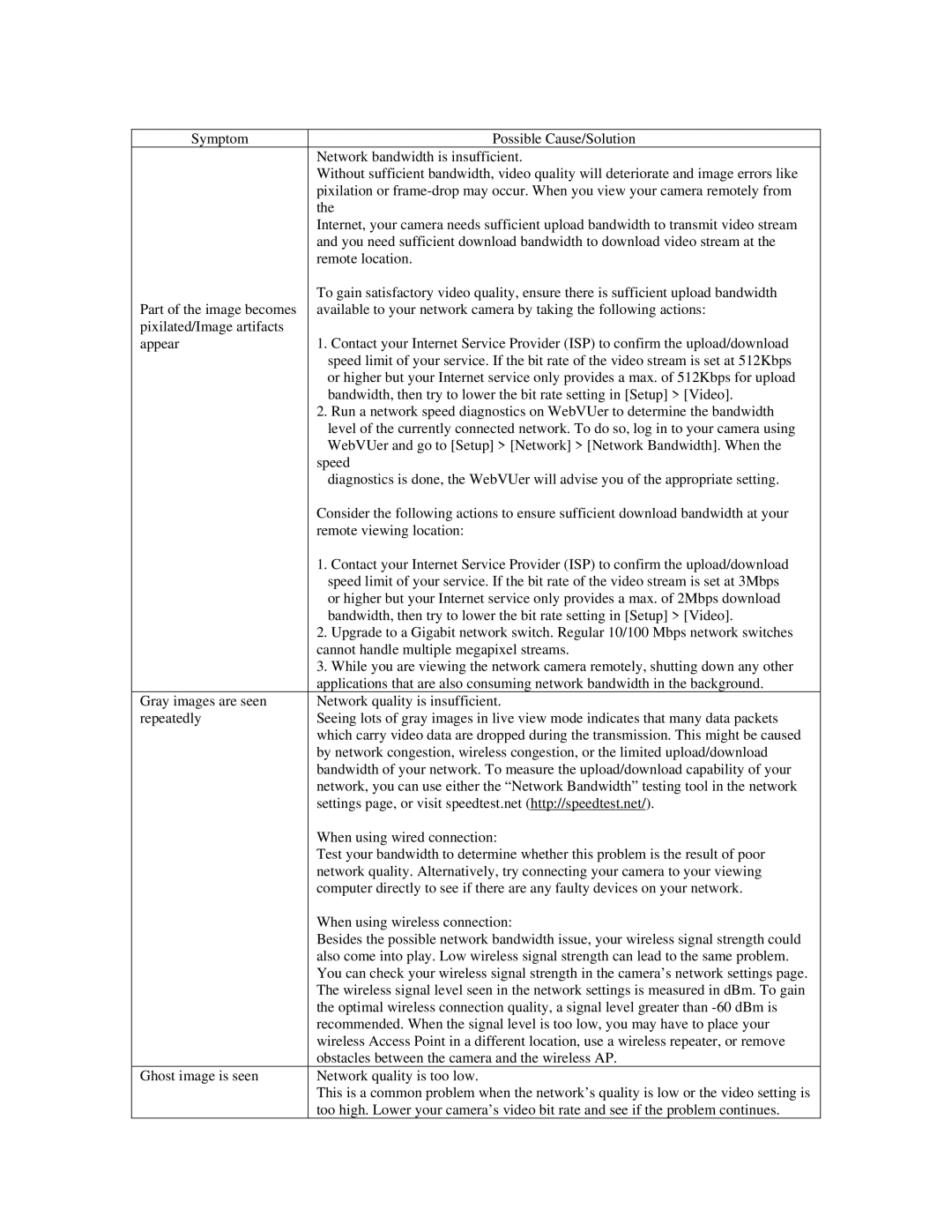
Symptom | Possible Cause/Solution |
| Network bandwidth is insufficient. |
| Without sufficient bandwidth, video quality will deteriorate and image errors like |
| pixilation or |
| the |
| Internet, your camera needs sufficient upload bandwidth to transmit video stream |
| and you need sufficient download bandwidth to download video stream at the |
| remote location. |
| To gain satisfactory video quality, ensure there is sufficient upload bandwidth |
Part of the image becomes | available to your network camera by taking the following actions: |
pixilated/Image artifacts |
|
appear | 1. Contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to confirm the upload/download |
| speed limit of your service. If the bit rate of the video stream is set at 512Kbps |
| or higher but your Internet service only provides a max. of 512Kbps for upload |
| bandwidth, then try to lower the bit rate setting in [Setup] > [Video]. |
| 2. Run a network speed diagnostics on WebVUer to determine the bandwidth |
| level of the currently connected network. To do so, log in to your camera using |
| WebVUer and go to [Setup] > [Network] > [Network Bandwidth]. When the |
| speed |
| diagnostics is done, the WebVUer will advise you of the appropriate setting. |
| Consider the following actions to ensure sufficient download bandwidth at your |
| remote viewing location: |
| 1. Contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to confirm the upload/download |
| speed limit of your service. If the bit rate of the video stream is set at 3Mbps |
| or higher but your Internet service only provides a max. of 2Mbps download |
| bandwidth, then try to lower the bit rate setting in [Setup] > [Video]. |
| 2. Upgrade to a Gigabit network switch. Regular 10/100 Mbps network switches |
| cannot handle multiple megapixel streams. |
| 3. While you are viewing the network camera remotely, shutting down any other |
| applications that are also consuming network bandwidth in the background. |
Gray images are seen | Network quality is insufficient. |
repeatedly | Seeing lots of gray images in live view mode indicates that many data packets |
| which carry video data are dropped during the transmission. This might be caused |
| by network congestion, wireless congestion, or the limited upload/download |
| bandwidth of your network. To measure the upload/download capability of your |
| network, you can use either the “Network Bandwidth” testing tool in the network |
| settings page, or visit speedtest.net (http://speedtest.net/). |
| When using wired connection: |
| Test your bandwidth to determine whether this problem is the result of poor |
| network quality. Alternatively, try connecting your camera to your viewing |
| computer directly to see if there are any faulty devices on your network. |
| When using wireless connection: |
| Besides the possible network bandwidth issue, your wireless signal strength could |
| also come into play. Low wireless signal strength can lead to the same problem. |
| You can check your wireless signal strength in the camera’s network settings page. |
| The wireless signal level seen in the network settings is measured in dBm. To gain |
| the optimal wireless connection quality, a signal level greater than |
| recommended. When the signal level is too low, you may have to place your |
| wireless Access Point in a different location, use a wireless repeater, or remove |
| obstacles between the camera and the wireless AP. |
Ghost image is seen | Network quality is too low. |
| This is a common problem when the network’s quality is low or the video setting is |
| too high. Lower your camera’s video bit rate and see if the problem continues. |
Page 62
Image 62