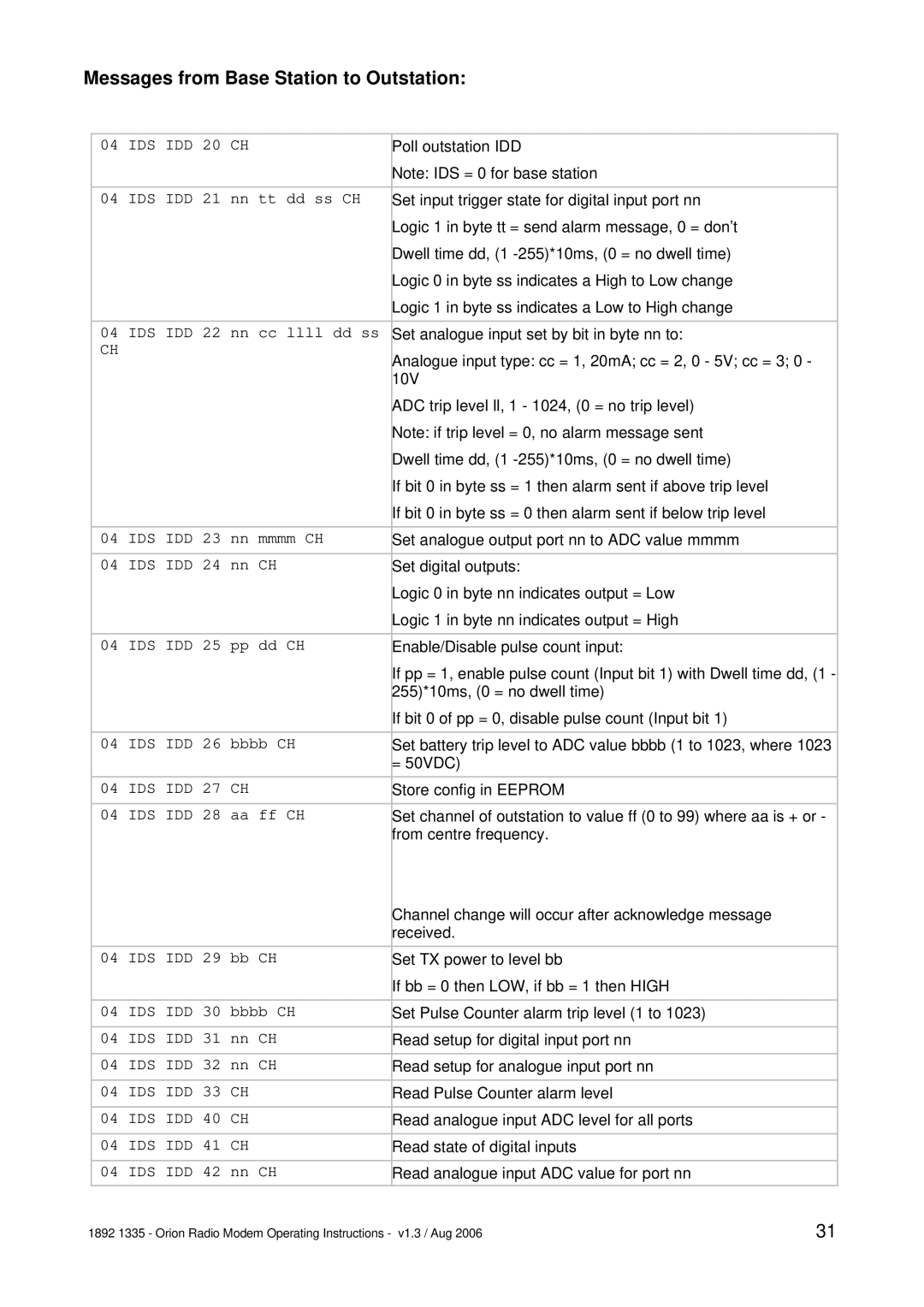
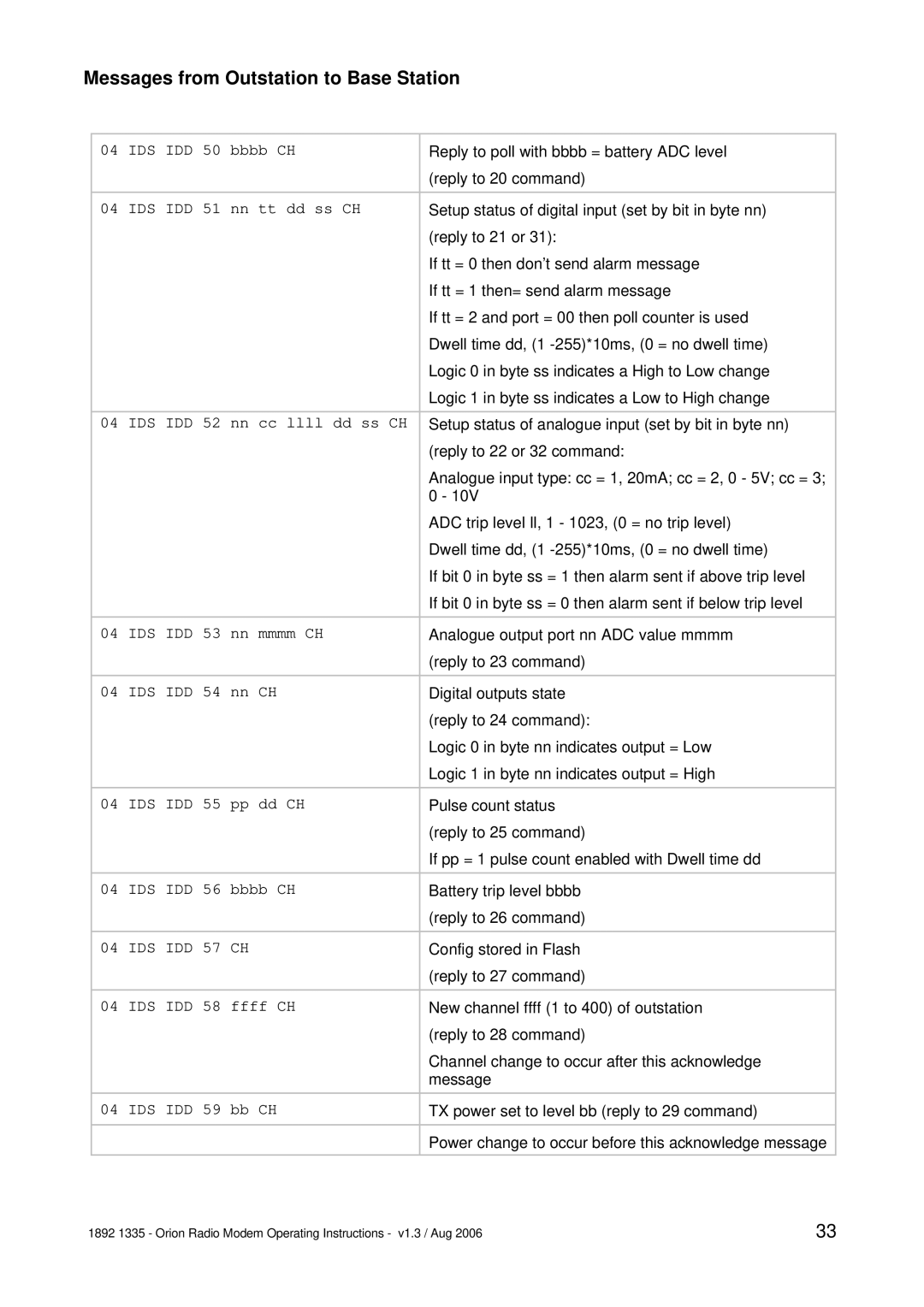
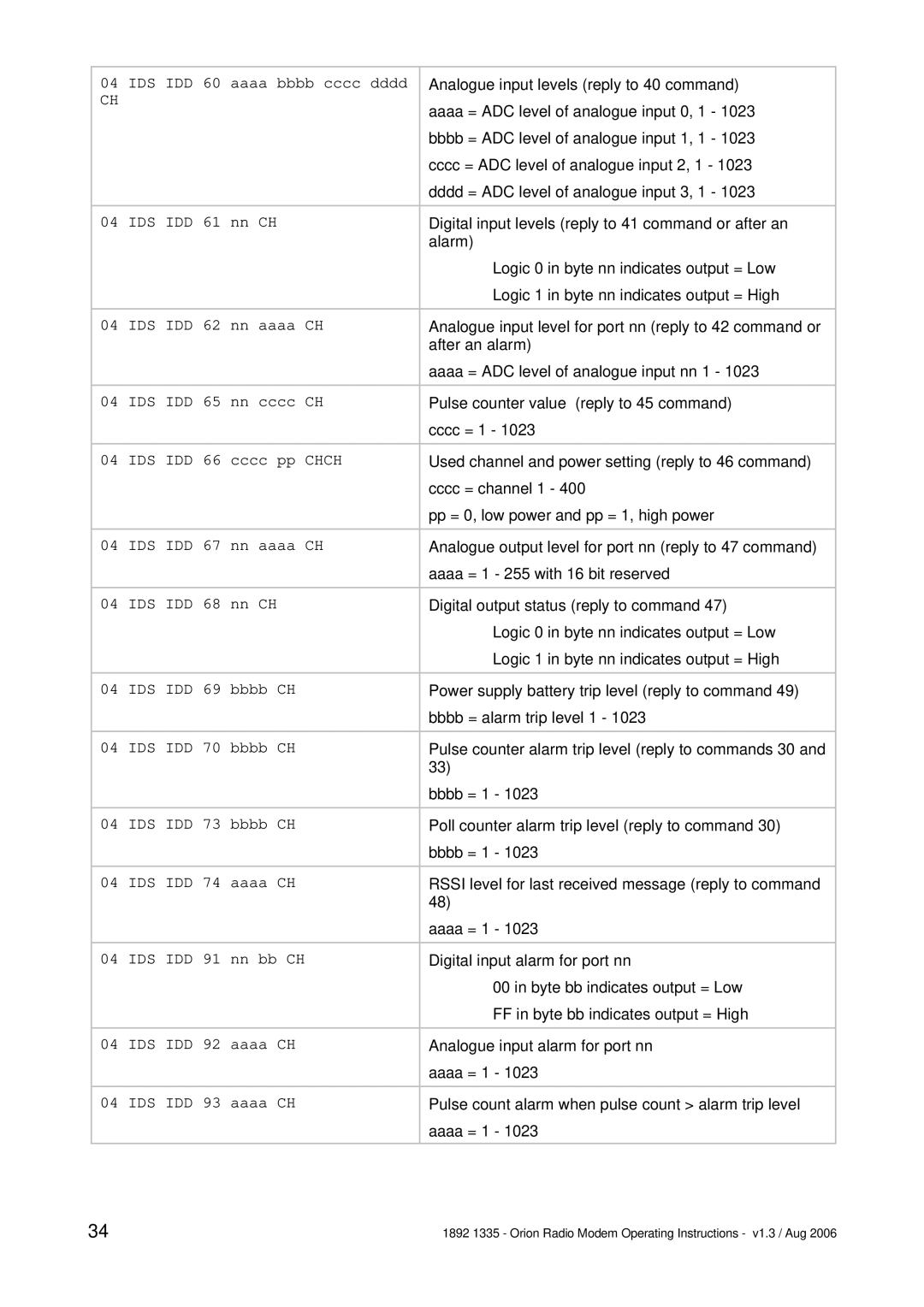
APPENDIX B: OVER-AIR COMMAND CODES
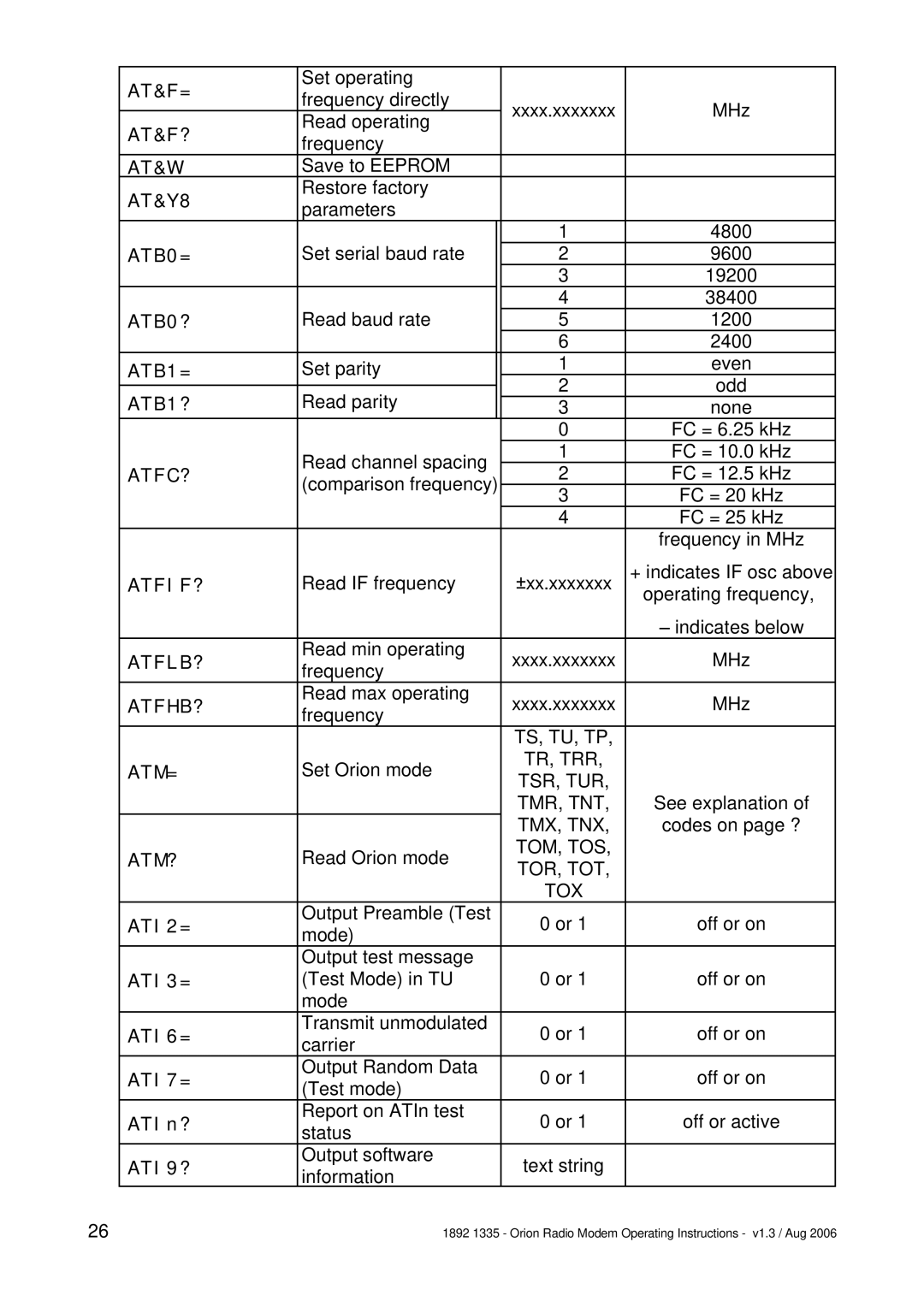
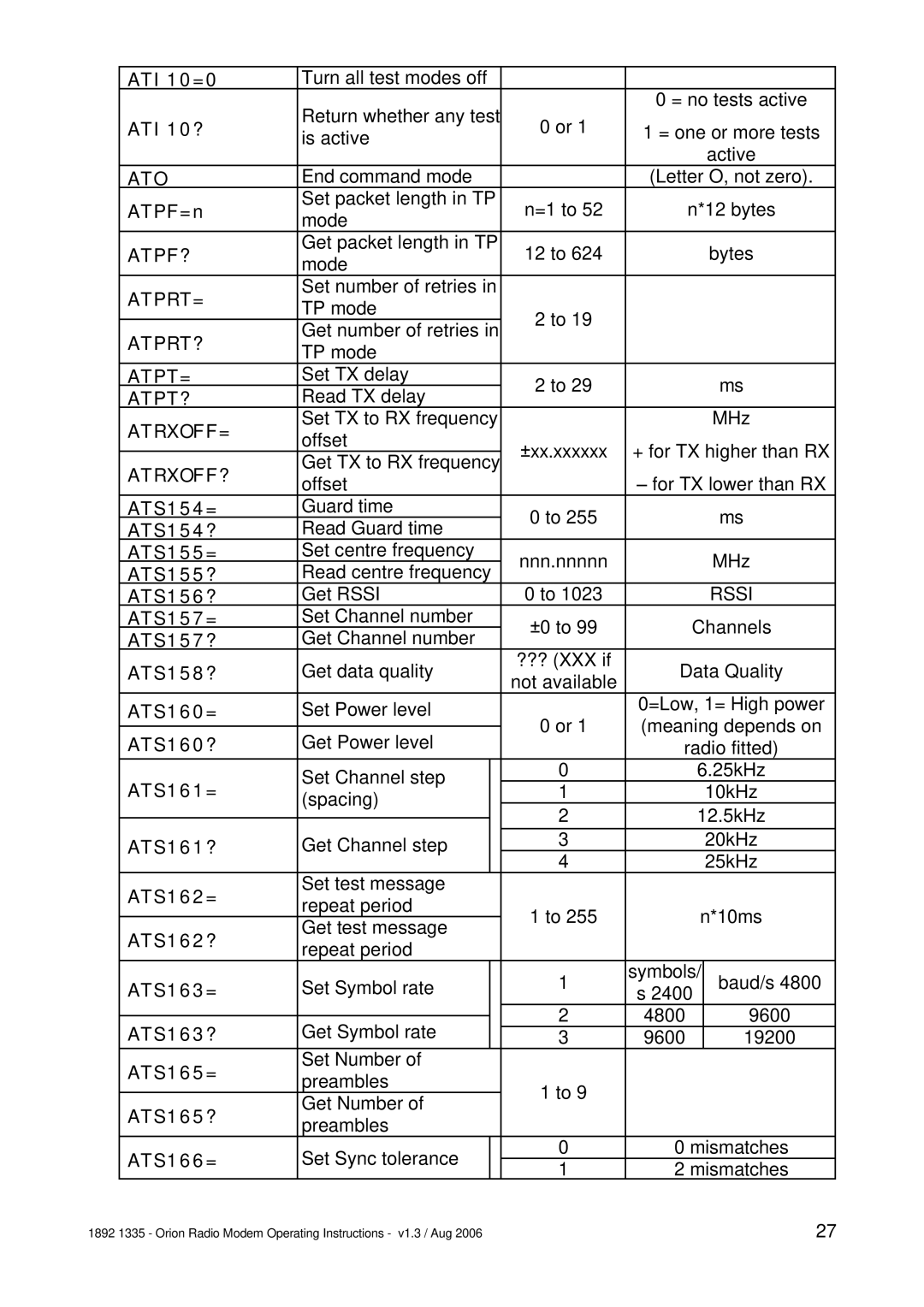
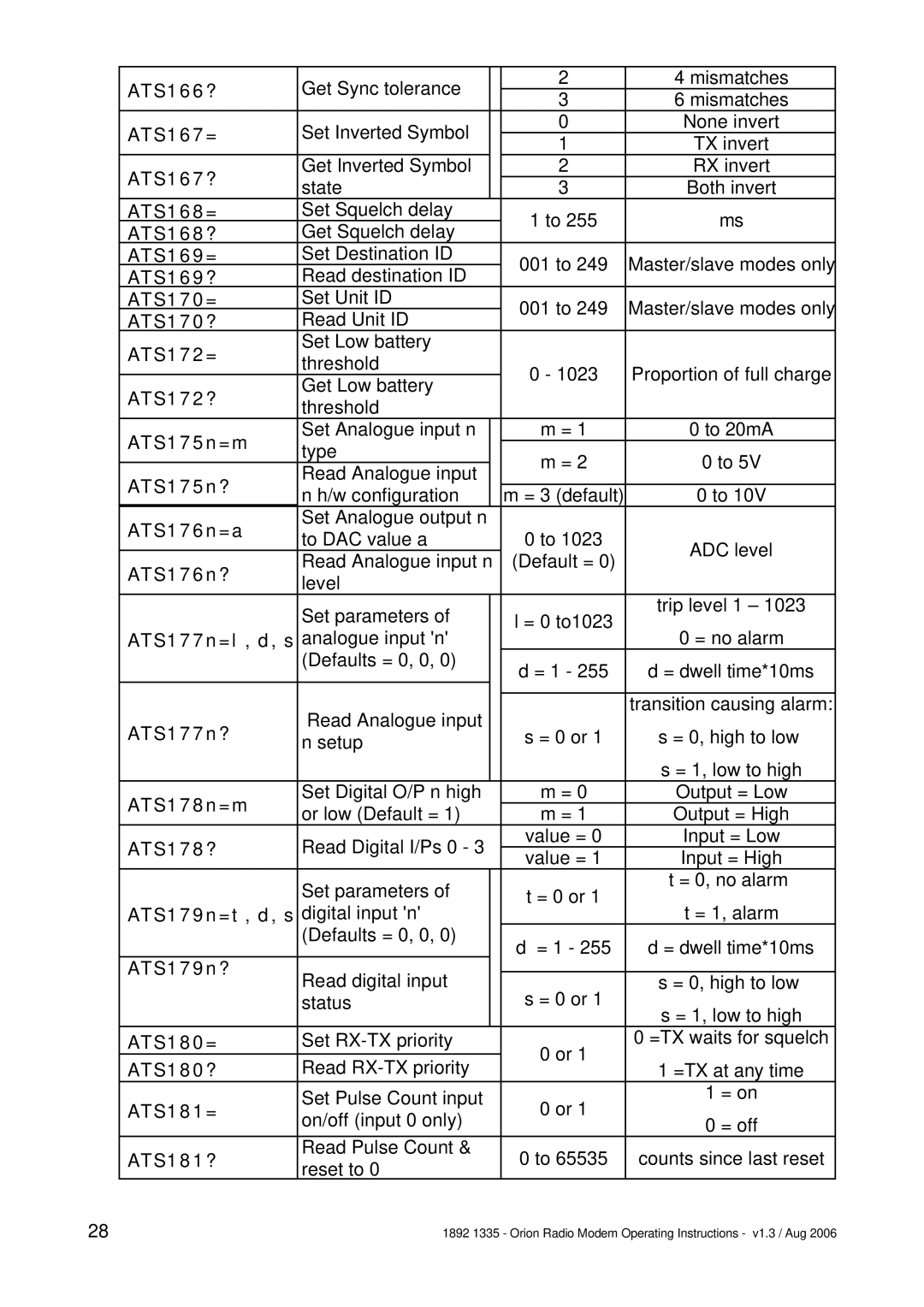
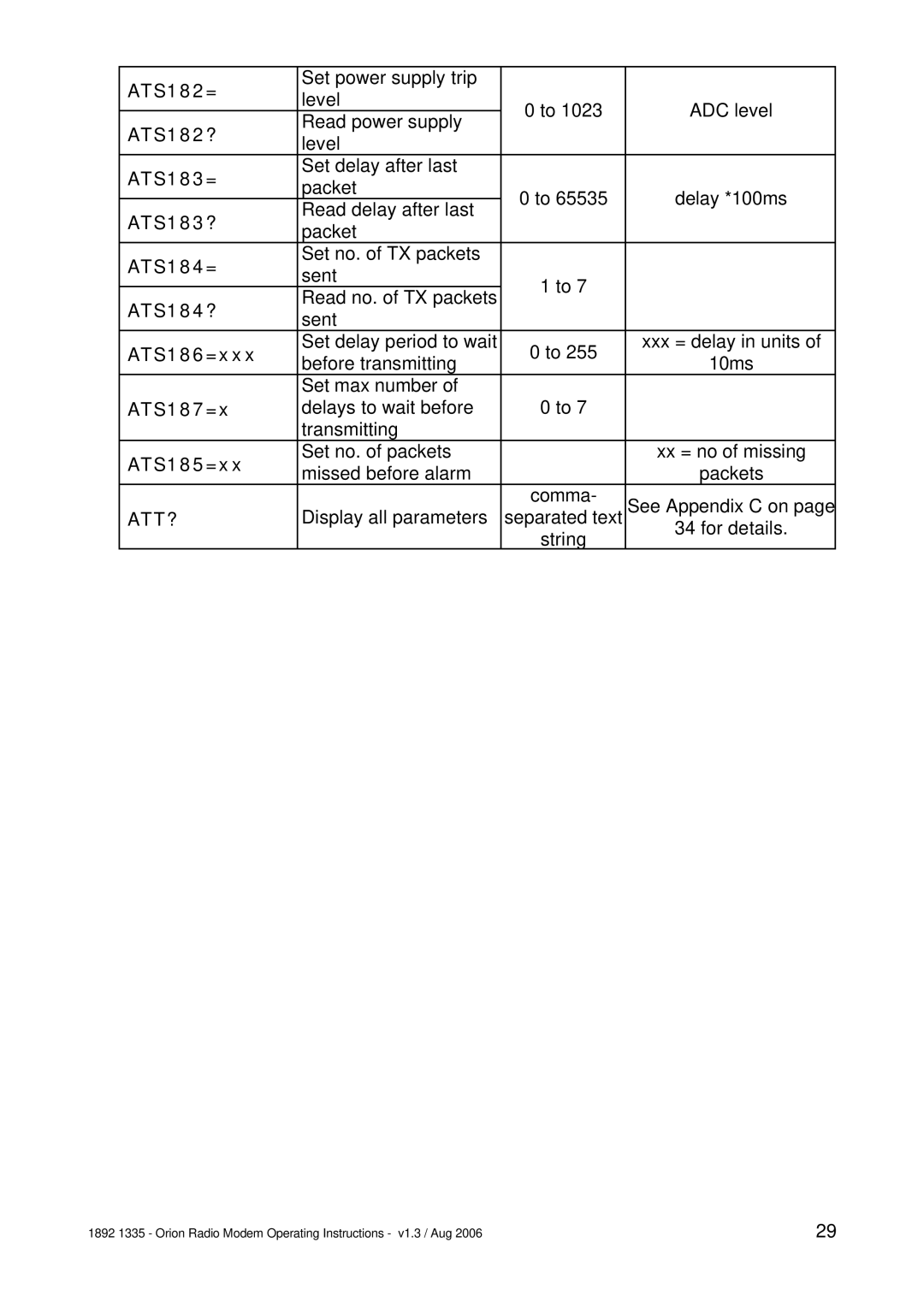
Normally the GUI is the best way to configure, control and interrogate a remote Orion unit. However, if you want to use your own equipment and software to do this, you can use the serial port of the local Orion to send
Introduction
In the sections listing the various commands the following abbreviations etc are used:
Pulse Count Input | = | 2 byte value which is state of counter from last poll or |
Analogue input | = | 10 bit ADC value sent as 2 bytes |
Analogue output | = | 10 bit ADC value sent as 2 bytes |
IDS | = | ID bytes (1 digit ID number) of source |
IDD | = | ID bytes (1 digit ID number) of destination |
|
| Note that base station will always be ID = 0 |
CH | = | CHECKSUM additive sum of bytes in message where CH is the |
|
| low order byte of the sum of all the bytes in the message, apart |
|
| from the first three. i.e. for an 04 IDS IDH 20 message, CH = the |
|
| sum of 20. |
nn | = | 1 byte data |
mmmm | = | 2 byte data |
After a set command is sent, the unit will reply with a confirmation message. All I/O config will be stored in EEPROM until an AT&W command is issued (serial port) or store config
30 | 1892 1335 - Orion Radio Modem Operating Instructions - v1.3 / Aug 2006 |