the standard IEEE format, whereas the 40-bit IEEE extended- precision format has eight additional LSBs of mantissa for greater accuracy.
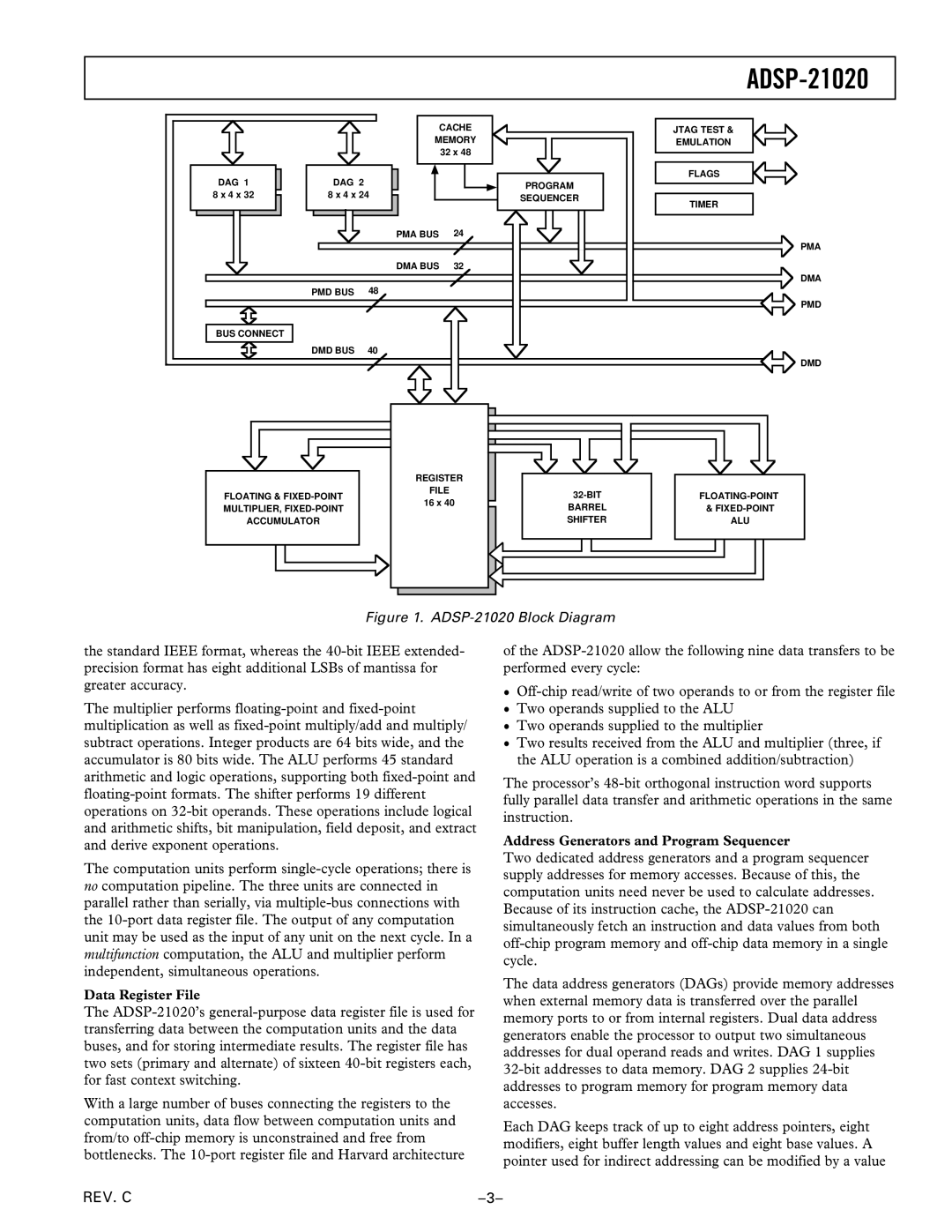
The multiplier performs floating-point and fixed-point multiplication as well as fixed-point multiply/add and multiply/ subtract operations. Integer products are 64 bits wide, and the accumulator is 80 bits wide. The ALU performs 45 standard arithmetic and logic operations, supporting both fixed-point and floating-point formats. The shifter performs 19 different operations on 32-bit operands. These operations include logical and arithmetic shifts, bit manipulation, field deposit, and extract and derive exponent operations.
The computation units perform single-cycle operations; there is no computation pipeline. The three units are connected in parallel rather than serially, via multiple-bus connections with the 10-port data register file. The output of any computation unit may be used as the input of any unit on the next cycle. In a multifunction computation, the ALU and multiplier perform independent, simultaneous operations.
Data Register File
The ADSP-21020’s general-purpose data register file is used for transferring data between the computation units and the data buses, and for storing intermediate results. The register file has two sets (primary and alternate) of sixteen 40-bit registers each, for fast context switching.
With a large number of buses connecting the registers to the computation units, data flow between computation units and from/to off-chip memory is unconstrained and free from bottlenecks. The 10-port register file and Harvard architecture
of the ADSP-21020 allow the following nine data transfers to be performed every cycle:
•Off-chip read/write of two operands to or from the register file
•Two operands supplied to the ALU
•Two operands supplied to the multiplier
•Two results received from the ALU and multiplier (three, if the ALU operation is a combined addition/subtraction)
The processor’s 48-bit orthogonal instruction word supports fully parallel data transfer and arithmetic operations in the same instruction.
Address Generators and Program Sequencer
Two dedicated address generators and a program sequencer supply addresses for memory accesses. Because of this, the computation units need never be used to calculate addresses. Because of its instruction cache, the ADSP-21020 can simultaneously fetch an instruction and data values from both off-chip program memory and off-chip data memory in a single cycle.
The data address generators (DAGs) provide memory addresses when external memory data is transferred over the parallel memory ports to or from internal registers. Dual data address generators enable the processor to output two simultaneous addresses for dual operand reads and writes. DAG 1 supplies 32-bit addresses to data memory. DAG 2 supplies 24-bit addresses to program memory for program memory data accesses.
Each DAG keeps track of up to eight address pointers, eight modifiers, eight buffer length values and eight base values. A pointer used for indirect addressing can be modified by a value

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() PMD
PMD![]()
![]()
![]() DMD
DMD