'Radio Transmission Wireless Flash Shooting
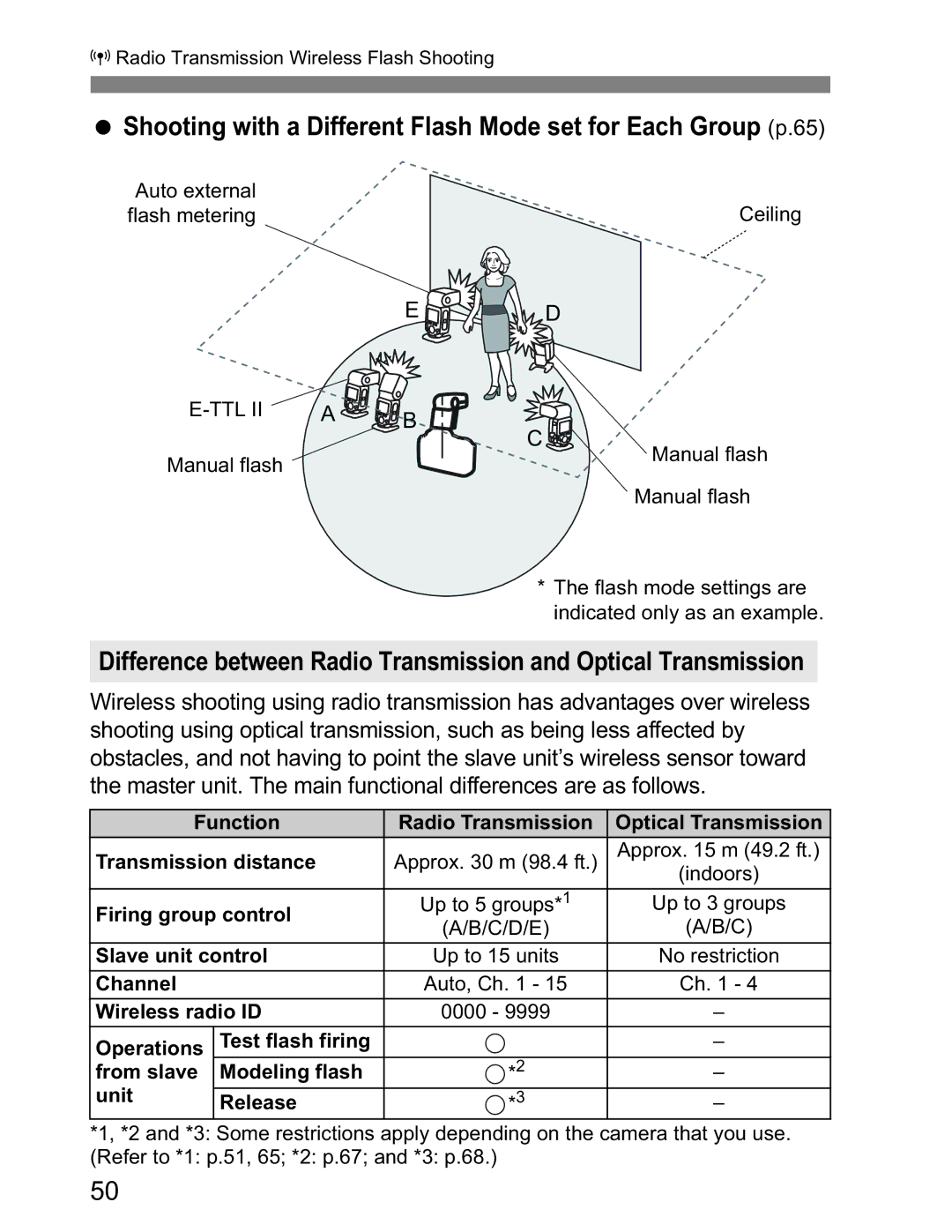
Shooting with a Different Flash Mode set for Each Group (p.65)
Auto external |
|
| Ceiling |
flash metering |
|
| |
|
| E | D |
A | B | C | |
|
|
| |
Manual flash |
|
| Manual flash |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Manual flash |
* The flash mode settings are indicated only as an example.
Difference between Radio Transmission and Optical Transmission
Wireless shooting using radio transmission has advantages over wireless shooting using optical transmission, such as being less affected by obstacles, and not having to point the slave unit’s wireless sensor toward the master unit. The main functional differences are as follows.
Function | Radio Transmission | Optical Transmission | ||
Transmission distance | Approx. 30 m (98.4 ft.) | Approx. 15 m (49.2 ft.) | ||
|
|
| (indoors) | |
Firing group control | Up to 5 groups*1 | Up to 3 groups | ||
(A/B/C/D/E) | (A/B/C) | |||
|
| |||
Slave unit control | Up to 15 units | No restriction | ||
Channel |
| Auto, Ch. 1 - 15 | Ch. 1 - 4 | |
Wireless radio ID | 0000 - 9999 | – | ||
Operations | Test flash firing |
| – | |
from slave | Modeling flash | *2 | – | |
unit |
|
|
| |
Release | *3 | – | ||
*1, *2 and *3: Some restrictions apply depending on the camera that you use.
(Refer to *1: p.51, 65; *2: p.67; and *3: p.68.)
50