Dell Converged Enhanced Ethernet
Page
Contents
This chapter IP static routes overview
Chapter Using the CEE CLI
Chapter Configuring STP, RSTP, and Mstp using the CEE CLI
Chapter Configuring Link Aggregation using the CEE CLI
Chapter Configuring Lldp using the CEE CLI
This chapter
Chapter Configuring QoS using the CEE CLI
Chapter Configuring Port Mirroring using the CEE CLI
Chapter CEE configuration management
Figures
Page
Tables
Page
How this document is organized
About This Document
This chapter
Text formatting
Supported hardware and software
Document conventions
Command syntax conventions
Contacting Dell
Getting technical help
FCoE overview
Introducing FCoE
FCoE terminology
FCoE hardware
Layer 2 Ethernet overview
Layer 2 Ethernet overview
Layer 2 forwarding
Vlan tagging
Frame classification incoming
Loop-free network environment
Congestion control and queuing
Access Gateway
Access control
Trunking
FCoE Initialization Protocol
Flow Control
FIP discovery
FIP login
FCoE logout
FCoE login
FIP logout
FC zoning
Logincfg
Name server
FCoE queuing
Management Tools
Using the CEE CLI
CEE Command Line Interface
Saving configuration changes with the copy command
Saving your configuration changes
Saving configuration changes with the write command
CEE CLI Rbac permissions
Accessing the CEE CLI from the Fabric OS shell
Accessing the CEE CLI through the console or Telnet
CEE CLI command modes
CEE Command Line Interface
Interface port-channel
Lists CEE CLI keyboard shortcuts
CEE Command Line Interface CEE CLI command modes
CEE CLI keyboard shortcuts
Displaying CEE CLI commands and command syntax
Using the do command as a shortcut
CEE CLI command output modifiers
CEE CLI command completion
Internal and external 10 Gbps Ethernet interfaces syntax
Overview
Initial FCoE and CEE Configuration
Configuring the FCoE interfaces
Configuring FCoE Vlan
Configuring the CEE interfaces
Configuring the CEE interfaces
To disable the interface
Repeat this procedure for any additional interfaces
Configuring Dcbx
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol Activate the protocol
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
Configuring Vlan membership
Configure the interface as an IP interface
Configuring protect mode
Return to Privileged Exec mode
Enable protect mode
IP static routes overview
Configuring IP static routes
Configuring IP static routes
Recursive IP static routes
Configuring IP static routes
Floating IP static routes
Displaying and clearing IP static routes
Ip route All
Use the clear ip route command to remove a static ip route
Ingress Vlan filtering
Configuring VLANs Using the CEE CLI
Vlan overview
Displays the frame processing logic for an incoming frame
Default Vlan configuration
Vlan configuration guidelines and restrictions
Configuring the MTU on an interface port
Vlan configuration and management
Vlan configuration and management
To disable the CEE interface
Disabling STP on a Vlan
Creating a Vlan interface
Enabling STP on a Vlan
Configuring an interface port as an access interface
Configuring a Vlan interface to forward FCoE traffic
Configuring an interface port as a Layer 2 switch port
Disabling a Vlan on a trunk interface
Configuring an interface port as a trunk interface
Configuring an interface port as a converged interface
Disabling a Vlan on a converged interface
Configuring protocol-based Vlan classifier rules
Configuring MAC address-based Vlan classifier rules
Configuring a Vlan classifier rule
Deleting a Vlan classifier rule
Creating a Vlan classifier group and adding rules
Activating a Vlan classifier group with an interface port
Configuring the MAC address table
Clearing Vlan counter statistics
Displaying Vlan information
Adding static addresses to the MAC address table
Specifying or disabling the aging time for MAC addresses
Configuring the MAC address table
STP overview
Configuring STP, RSTP, and Mstp using the CEE CLI
Configuring STP on Dell FCoE hardware
Is the interface learning MAC addresses?
Rstp overview
Configuring Rstp on Dell FCoE hardware
For details, see Specifying the port priority on
Mstp overview
Configuring Mstp on Dell FCoE hardware
Switchconf-mstp#max-hops
Default STP, RSTP, and Mstp configuration
Default STP, RSTP, and Mstp configuration
STP, RSTP, and Mstp configuration and management
STP, RSTP, and Mstp configuration and management
Enabling STP, RSTP, or Mstp
Disabling STP, RSTP, or Mstp
Specifying the bridge priority
Specifying the bridge forward delay
Specify the bridge forward delay
Specifying the error disable timeout interval
Enabling the error disable timeout timer
Enable the error disable timeout timer
Specifying the bridge maximum aging time
Specifying the bridge hello time STP and Rstp
Specifying the port-channel path cost
Specifying the transmit hold count Rstp and Mstp
Specify the port-channel path cost
Disabling Cisco interoperability Mstp
Enabling Cisco interoperability Mstp
Mapping a Vlan to an Mstp instance
Map a Vlan to an Mstp instance
Enter the region command to assign a name to an Mstp region
Specifying a revision number for an Mstp configuration
Specifying the maximum number of hops for a Bpdu Mstp
Specifying a name for an Mstp region
Clearing spanning tree-detected protocols
Flushing MAC addresses Rstp and Mstp
Clearing spanning tree counters
Configuring the path cost
Configuring STP, RSTP, or Mstp on CEE interface ports
Displaying STP, RSTP, and MSTP-related information
Enabling automatic edge detection
Enabling the guard root
Enabling a port interface as an edge port
Specifying restrictions for an Mstp instance
Enter the no shutdown command to enable the CEE interface
Specifying the Mstp hello time
Specifying the port priority
Specifying a link type
Enabling port fast STP
Enabling spanning tree
Restricting the port from becoming a root port
Restricting the topology change notification
Disabling spanning tree
Configuring STP, RSTP, or Mstp on CEE interface ports
Link aggregation overview
Configuring Link Aggregation using the CEE CLI
Link Aggregation Group configuration
Dell Converged Enhanced Ethernet Administrator’s Guide
Configuring LAGs for a top-of-the-rack CEE switch-Example
Dynamic link aggregation
Link Aggregation Control Protocol
Static link aggregation
Dell-proprietary aggregation
Default Lacp configuration
Lacp configuration guidelines and restrictions
Lacp configuration and management
Lacp configuration guidelines and restrictions
Configuring minimum links feature
Configuring the Lacp system priority
Configuring the Lacp timeout period on a CEE interface
Configure the minimum links
Configuring interface tracking
Enable tracking
Clearing Lacp counter statistics on a LAG
Displaying Lacp information
Lacp troubleshooting tips
Clearing Lacp counter statistics on all LAG groups
Deskew calculation failed for link link-name
Lacp troubleshooting tips
Lldp overview
Configuring Lldp using the CEE CLI
Layer 2 topology mapping
Layer 2 topology mapping
Page
Dcbx overview
Dcbx overview
Enhanced Transmission Selection ETS
Dcbx interaction with other vendor devices
Lldp configuration guidelines and restrictions
Priority Flow Control PFC
Dcbx interaction with other vendor devices
Lldp configuration and management
Default Lldp configuration
Disabling and resetting Lldp globally
Default Lldp configuration
Specifying a user description for Lldp
Configuring Lldp global command options
Specifying a system name for the Dell FCoE hardware
Advertising the optional Lldp TLVs
Configuring the transmit frequency of Lldp frames
Configuring the hold time for receiving devices
Configuring FCoE priority bits
Configuring the advertisement of Lldp Dcbx -related TLVs
Configuring Lldp profiles
Advertise the Lldp DCBX-related TLVs using these commands
Enable the transmitting and receiving of Lldp frames
Configuring Lldp interface-level command options
Configure the transmission frequency of Lldp updates
Specify a description for the profile
Displaying LLDP-related information
Clearing LLDP-related information
Lldp configuration and management
ACL overview
Configuring ACLs using the CEE CLI
ACL configuration guidelines and restrictions
Default ACL configuration
ACL configuration and management
Creating a standard MAC ACL and adding rules
Modifying MAC ACL rules
Creating an extended MAC ACL and adding rules
Reordering the sequence numbers in a MAC ACL
Enter the no seq command to delete the existing rule
Removing a MAC ACL
Applying a MAC ACL to a Vlan interface
Applying a MAC ACL to a CEE interface
ACL configuration and management
QoS overview
Configuring QoS using the CEE CLI
Rewriting
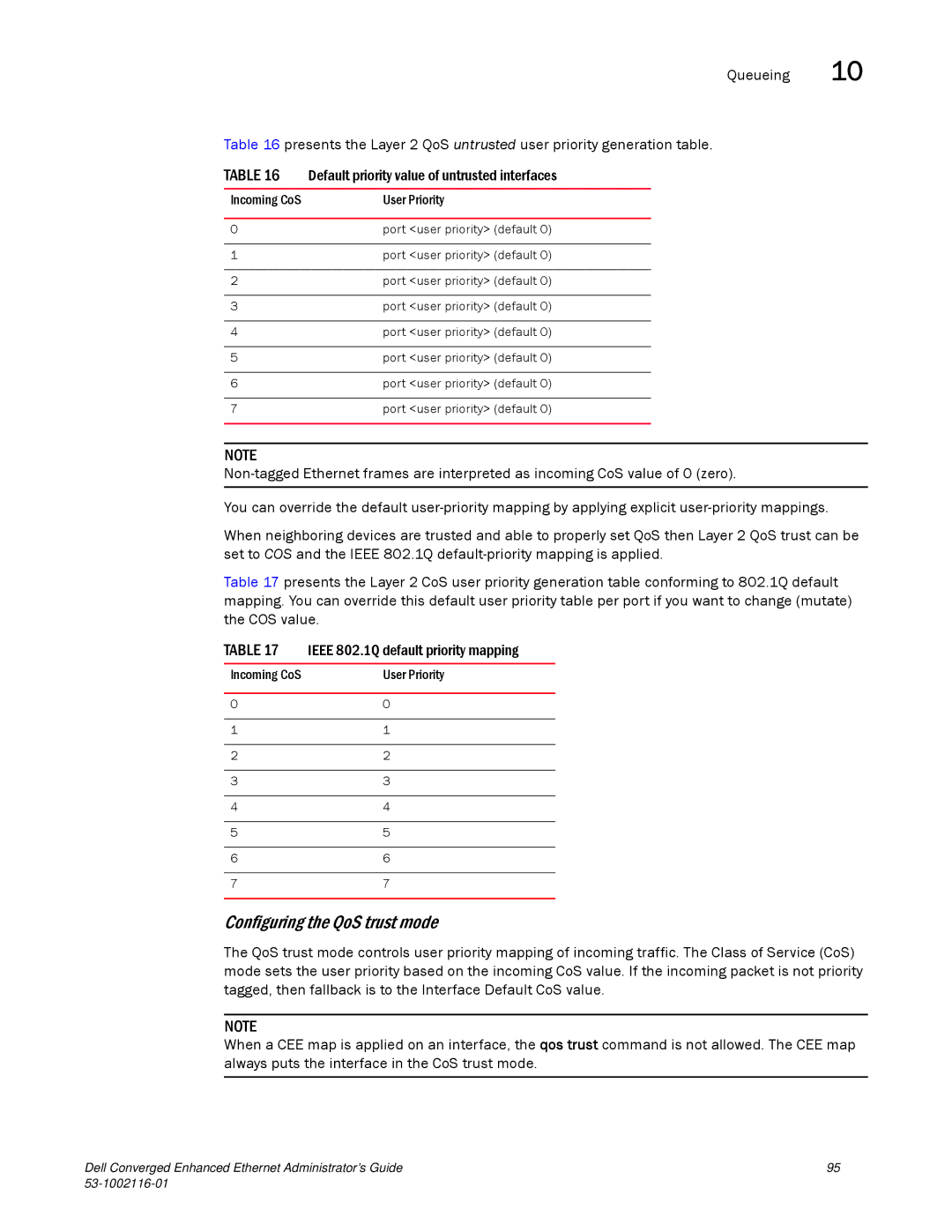
Default user-priority mappings for untrusted interfaces
Queueing
User-priority mapping
Incoming CoS User Priority
Configuring the QoS trust mode
Creating a CoS-to-CoS mutation QoS map
Configuring user-priority mappings
Applying a CoS-to-CoS mutation QoS map
Traffic class mapping
Unicast traffic
Queueing
Mapping CoS-to-Traffic-Class
Multicast traffic
Activate the CoS-to-Traffic-Class mapping by name
Activating a mapping CoS-to-Traffic-Class
Verifying a mapping CoS-to-Traffic-Class
Congestion control
Congestion control
Tail drop
Changing the Tail Drop threshold
Ethernet pause
Enabling an Ethernet PFC
Ethernet Priority Flow Control
Enabling Ethernet Pause
Creating a receive queue multicast rate-limit
Enable an Ethernet PFC on the interface
Multicast rate limiting
Scheduling
Deficit weighted round robin scheduling
Strict priority scheduling
Scheduling
SP0 SP1 SP2 SP3 SP4 SP5 SP6 SP8
Traffic class scheduling policy
Scheduling the QoS queue
Multicast queue scheduling
Scheduling the QoS multicast queue
Converged Enhanced Ethernet map configuration
Pgid
Defining a priority group table
Creating a CEE map
Create a CEE map
Define the CEE map for Pgid
Verifying the CEE maps
Defining a priority-table map
Applying a CEE provisioning map to an interface
802.1x protocol overview
Configuring 802.1x Port Authentication
802.1x configuration guidelines and restrictions
Interface-specific administrative tasks for
802.1x authentication configuration tasks
Configure authentication Between the switch and CNA or NIC
11 802.1x authentication configuration tasks
Configuring 802.1x timeouts on specific interface ports
Configuring 802.1x on specific interface ports
Disabling 802.1x on specific interface ports
SFlow protocol overview
Configuring sFlow using the CEE CLI
Interface flow samples
Packet counter samples
Disabling sFlow on specific interfaces
Configuring the sFlow protocol globally
Interface-specific administrative tasks for sFlow
Disable sFlow on the interface
Configuring sFlow on specific interfaces
Enable sFlow for the interface
Configure the sFlow polling interval
Interface-specific administrative tasks for sFlow
Port Mirroring limitations
Configuring Port Mirroring using the CEE CLI
Port Mirroring protocol overview
Configuring egress Port Mirroring
Configuring ingress Port Mirroring
Configuring bidirectional Port Mirroring
Configuring ingress Port Mirroring
Deleting a Port Mirroring session
Deleting a Port Mirroring connection from a session
Open an existing monitor session
Use the no option to delete a particular port connection
Deleting a Port Mirroring session
Rmon configuration and management
Configuring Rmon using the CEE CLI
Default Rmon configuration
Configuring Rmon settings
Configure the Rmon event
Configuring Rmon events
Configuring Rmon group statistics collection
Configuring Rmon history collection
Rmon configuration and management
Active Igmp snooping
Configuring Igmp
About Igmp
Configuring Igmp snooping querier
Configuring Igmp
Configuring Igmp
Configure a Vlan port member to be a multi-router interface
Monitoring Igmp
Page
FCoE configuration guidelines and restrictions
FCoE configuration using the Fabric OS CLI
Configuring Fcmap values for a Vlan
Managing and displaying the FCoE configuration
Configuring FIP multicast advertisement intervals
Managing and displaying the FCoE configuration
Clearing logins
Managing and displaying the FCoE login configuration
Displaying FCoE configuration-related information
Enabling or disabling FCoE login configuration management
Cleaning up login groups and VNport mappings
Displaying or aborting the current configuration transaction
Displaying the FCoE login configuration
Creating and managing the FCoE login group configuration
Saving the current FCoE configuration
Creating an FCoE login group
To delete an FCoE login group, perform the following task
Modifying the FCoE login group device list
Deleting an FCoE login group
To rename an FCoE login group, perform the following task
Renaming an FCoE login group
Creating and managing the FCoE login group configuration
CEE configuration management tasks
CEE configuration management
CEE configuration management guidelines and restrictions
Saving the running configuration file
Display the running configuration file
Loading the startup configuration file
Erasing the startup configuration file
Restore an archived running configuration file
Archiving the running configuration file
Archiving the startup configuration file
Restore an archived startup configuration file
Restore a startup configuration file from Flash
Flash file management commands
CEE configuration management commands
Flash file management commands
Switch#erase flash
Debugging and logging commands
Debugging and logging commands
Index
Symbols Numerics
QoS, 100 queuing
FIP
PEAP, 27
Rstp
Vlan