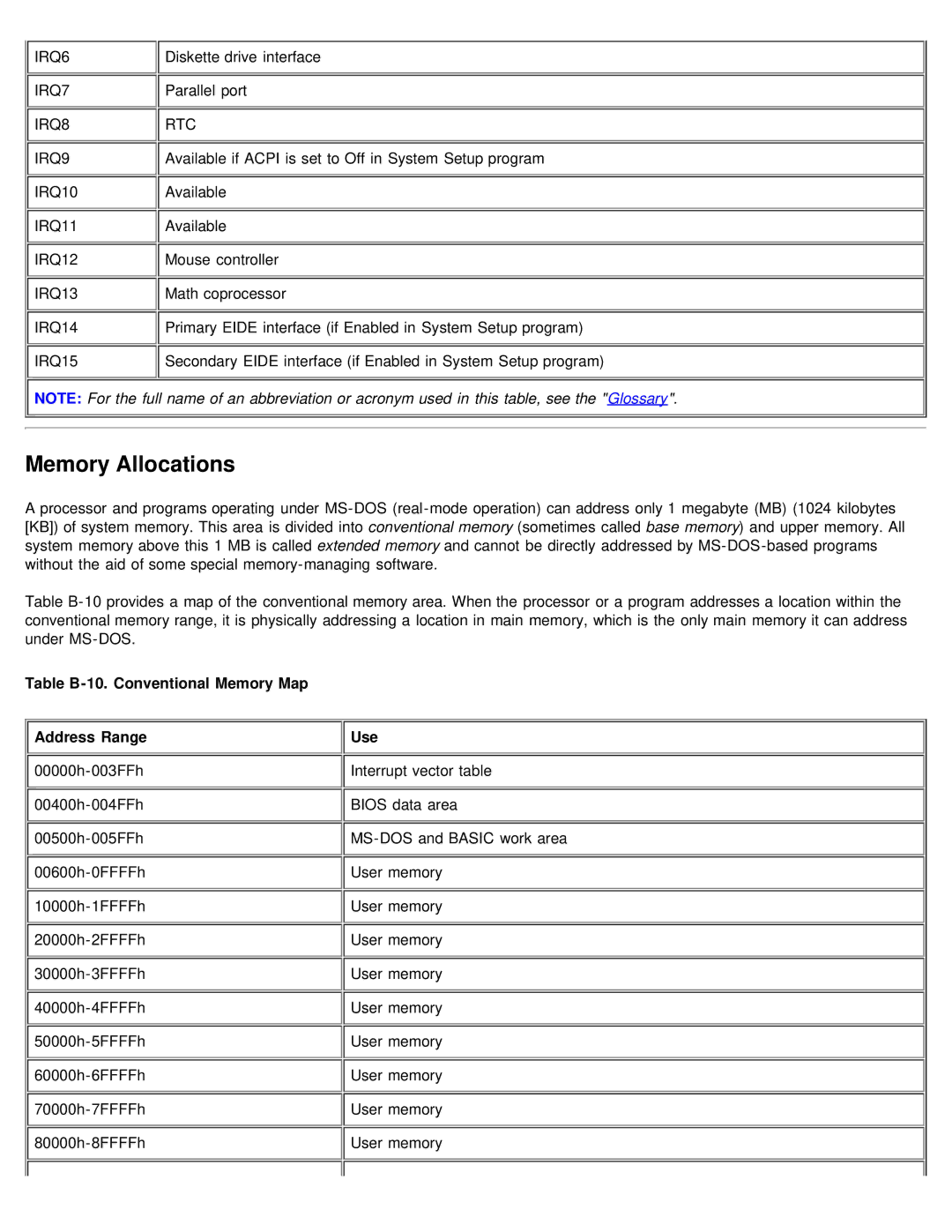
IRQ6 | Diskette drive interface |
IRQ7 | Parallel port |
IRQ8 | RTC |
IRQ9 | Available if ACPI is set to Off in System Setup program |
IRQ10 | Available |
IRQ11 | Available |
IRQ12 | Mouse controller |
IRQ13 | Math coprocessor |
IRQ14 | Primary EIDE interface (if Enabled in System Setup program) |
IRQ15 | Secondary EIDE interface (if Enabled in System Setup program) |
![]() NOTE: For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this table, see the "Glossary".
NOTE: For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this table, see the "Glossary".
Memory Allocations
A processor and programs operating under
Table
Table |
| |
| Address Range | Use |
| ||
| Interrupt vector table | |
| BIOS data area | |
| ||
| User memory | |
| User memory | |
| User memory | |
| User memory | |
| User memory | |
| User memory | |
| User memory | |
| User memory | |
| User memory | |
|
|
|