Ti20
Users Manual
|
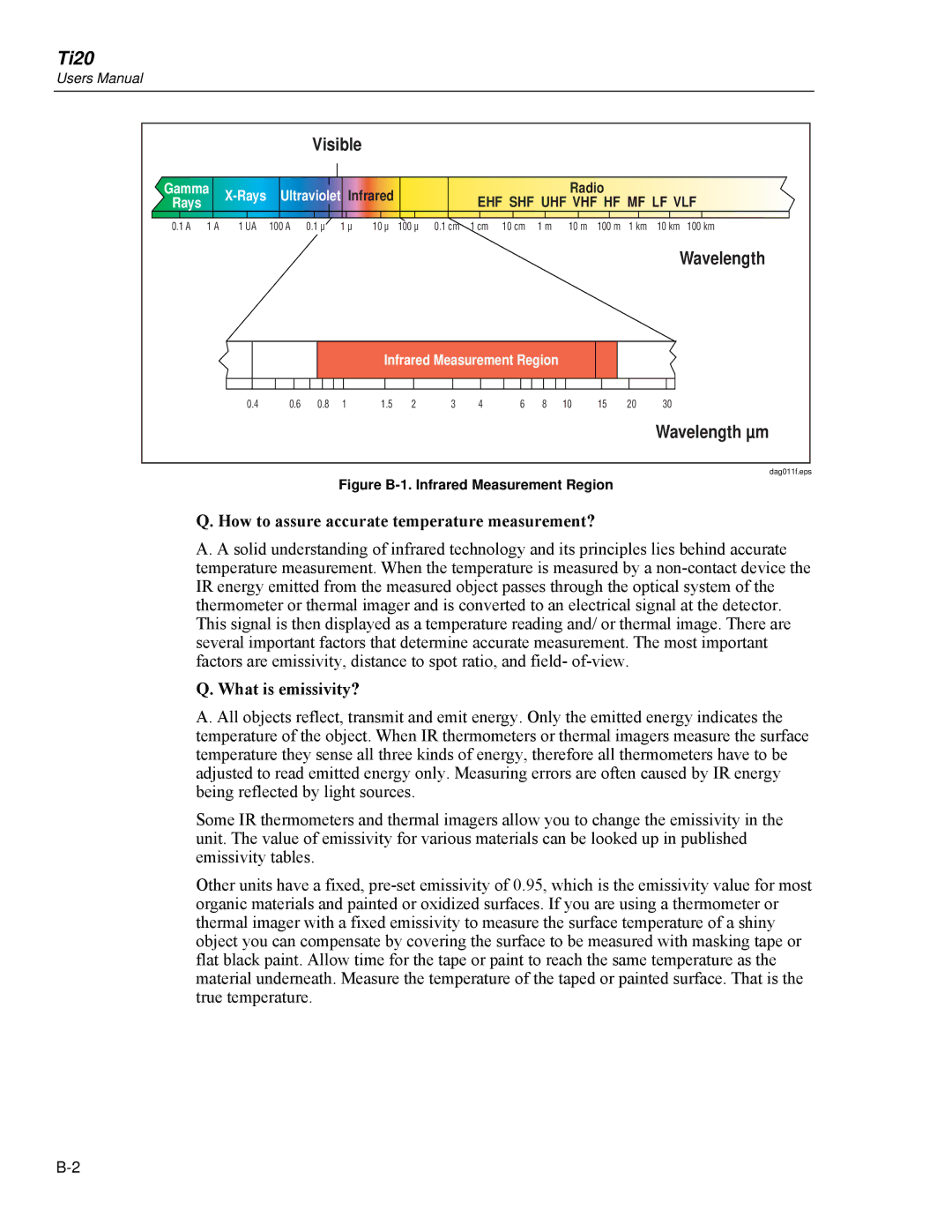
| Visible |
| |||
Gamma | Ultraviolet Infrared | Radio | ||||
Rays | EHF SHF UHF VHF HF MF LF VLF | |||||
|
|
|
| |||
0.1 A 1 A 1 UA | 100 A 0. |
| 1 µ 10 µ 100 µ 0.1 cm 1 cm 10 cm 1 m 10 m 100 m 1 km 10 km 100 km | |||
1 µ | ||||||
Wavelength
Infrared Measurement Region
0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 |
Wavelength µm
dag011f.eps
Figure B-1. Infrared Measurement Region
Q. How to assure accurate temperature measurement?
A. A solid understanding of infrared technology and its principles lies behind accurate temperature measurement. When the temperature is measured by a
Q. What is emissivity?
A. All objects reflect, transmit and emit energy. Only the emitted energy indicates the temperature of the object. When IR thermometers or thermal imagers measure the surface temperature they sense all three kinds of energy, therefore all thermometers have to be adjusted to read emitted energy only. Measuring errors are often caused by IR energy being reflected by light sources.
Some IR thermometers and thermal imagers allow you to change the emissivity in the unit. The value of emissivity for various materials can be looked up in published emissivity tables.
Other units have a fixed,