White Paper ⏐ Issue: October 2006 ⏐ Integration of BX600 SB9 Switches in Cisco Networks | Page 15 / 47 |
2.4.2Recommended Solution
As discussed earlier, there are a number of different combinations of STP protocols that can be selected when integrating SB9 switches into Cisco networks. Although using MSTP between the Cisco and the SB9 would be the best solution, it will not be discussed further in this paper because MSTP is so very unusual in Cisco networks. If you were to run MSTP (802.1s) on the SB9 switches while using STP or RSTP at the Cisco switches, MSTP would fall back to RSTP and STP respectively.
The resulting and possible solutions are shown in Table 4.
|
|
|
| SB9 Switch |
|
|
| ||
|
|
| 802.1D |
| 802.1w |
| No STP | ||
Cisco | PVST+ |
| Ok* |
| Ok |
|
| Ok |
|
RAPID- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Switch |
| with restrictions |
| with restrictions |
|
|
|
| |
PVST |
|
|
|
| Ok |
| |||
|
| (Problems with TCN) |
| (Problems with TCN) |
|
|
| ||
Table 4 : Possible STP combinations when using VLAN Trunks
* SB9 firmware >1.14 required
The recommended solution when running STP over VLAN trunks between Cisco and SB9 switches is to disable STP completely at the SB9 and run the STP or RSTP protocol at the Cisco switches (see Figure 4 and Figure 7).
When the SB9 is connected to Cisco switches without VLAN trunks, the preferred solution is RSTP, because this would lead to the shortest failover times.
Caution: | In order to avoid loops in the network, please be sure that the VLAN configuration on both uplinks is |
| the same. Misconfiguration may lead to unidirectional links and to network loops! |
|
|
Caution: | There is a significant difference between disabling STP on the SB9 globally and for each interface: |
| If STP is disabled for one interface BPDUs are neither sent nor bridged. This behavior may lead to |
| network loops. |
| When STP is disabled globally BPDUs are bridged. This is needed in the recommended scenarios. |
|
|
Caution: | When running STP on an SB9 it is important to enable STP at all ports, especially when creating port- |
| channels: this is not the default and must be enabled manually. |
2.4.3Configuration with VLAN Trunks
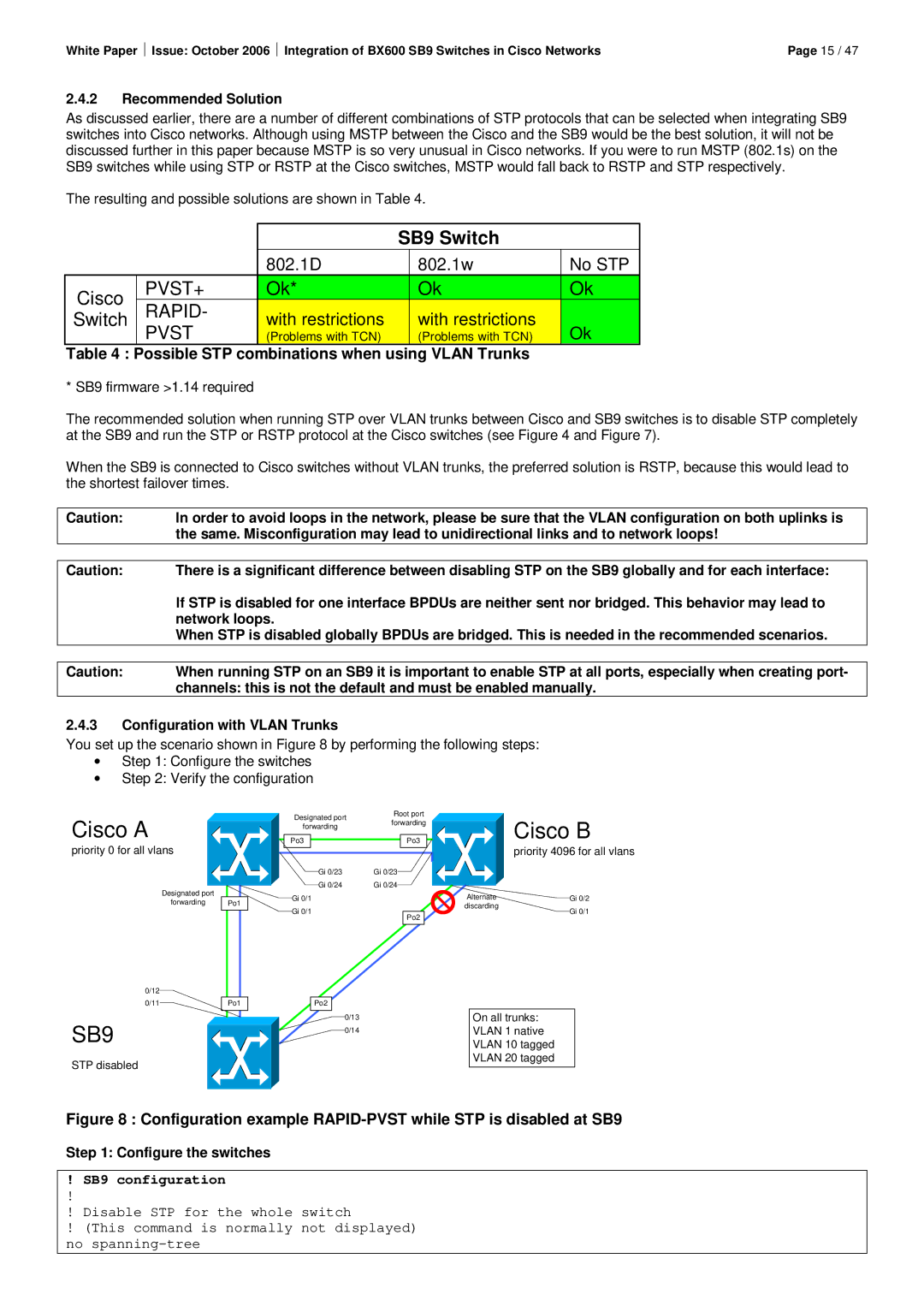
You set up the scenario shown in Figure 8 by performing the following steps:
∙Step 1: Configure the switches
∙Step 2: Verify the configuration
Cisco A
priority 0 for all vlans
Designated port
forwarding Po1
0/12
0/11![]() Po1
Po1
SB9
STP disabled
Designated port | Root port |
| ||
forwarding |
| |||
forwarding |
| |||
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
Po3 |
|
| Po3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Gi 0/23 | Gi 0/23 |
| |
| Gi 0/24 | Gi 0/24 |
| |
Gi 0/1 |
|
|
| |
Gi 0/1 |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Po2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Po2
0/13
0/14
Cisco B
priority 4096 for all vlans
Alternate | Gi 0/2 |
discarding | Gi 0/1 |
|
On all trunks:
VLAN 1 native
VLAN 10 tagged
VLAN 20 tagged
Figure 8 : Configuration example RAPID-PVST while STP is disabled at SB9
Step 1: Configure the switches
!SB9 configuration
!Disable STP for the whole switch
!(This command is normally not displayed) no