Chapter 4. Network Configuration
DMZ/LAN Configuration
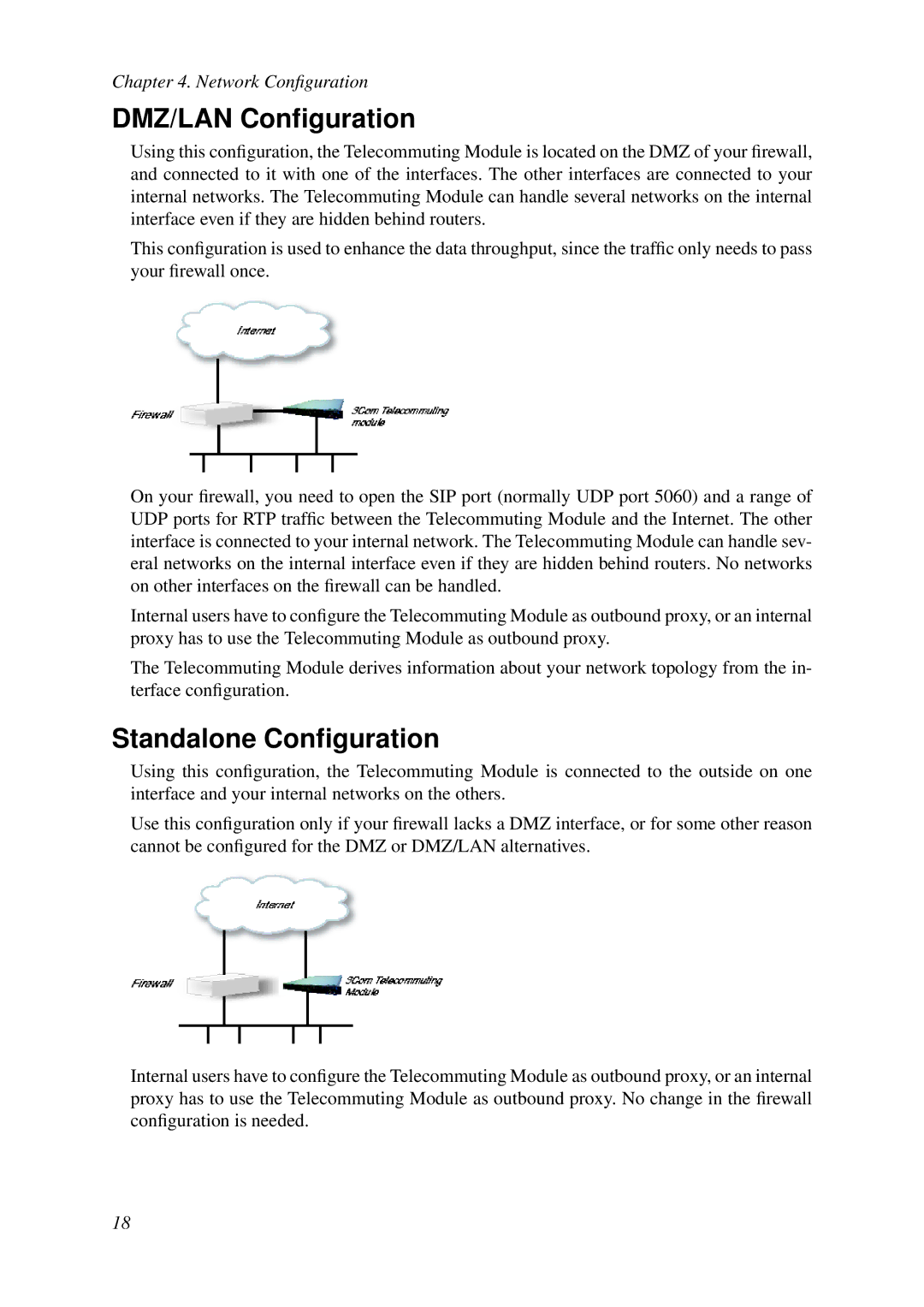
Using this configuration, the Telecommuting Module is located on the DMZ of your firewall, and connected to it with one of the interfaces. The other interfaces are connected to your internal networks. The Telecommuting Module can handle several networks on the internal interface even if they are hidden behind routers.
This configuration is used to enhance the data throughput, since the traffic only needs to pass your firewall once.
On your firewall, you need to open the SIP port (normally UDP port 5060) and a range of UDP ports for RTP traffic between the Telecommuting Module and the Internet. The other interface is connected to your internal network. The Telecommuting Module can handle sev- eral networks on the internal interface even if they are hidden behind routers. No networks on other interfaces on the firewall can be handled.
Internal users have to configure the Telecommuting Module as outbound proxy, or an internal proxy has to use the Telecommuting Module as outbound proxy.
The Telecommuting Module derives information about your network topology from the in- terface configuration.
Standalone Configuration
Using this configuration, the Telecommuting Module is connected to the outside on one interface and your internal networks on the others.
Use this configuration only if your firewall lacks a DMZ interface, or for some other reason cannot be configured for the DMZ or DMZ/LAN alternatives.
Internal users have to configure the Telecommuting Module as outbound proxy, or an internal proxy has to use the Telecommuting Module as outbound proxy. No change in the firewall configuration is needed.
18