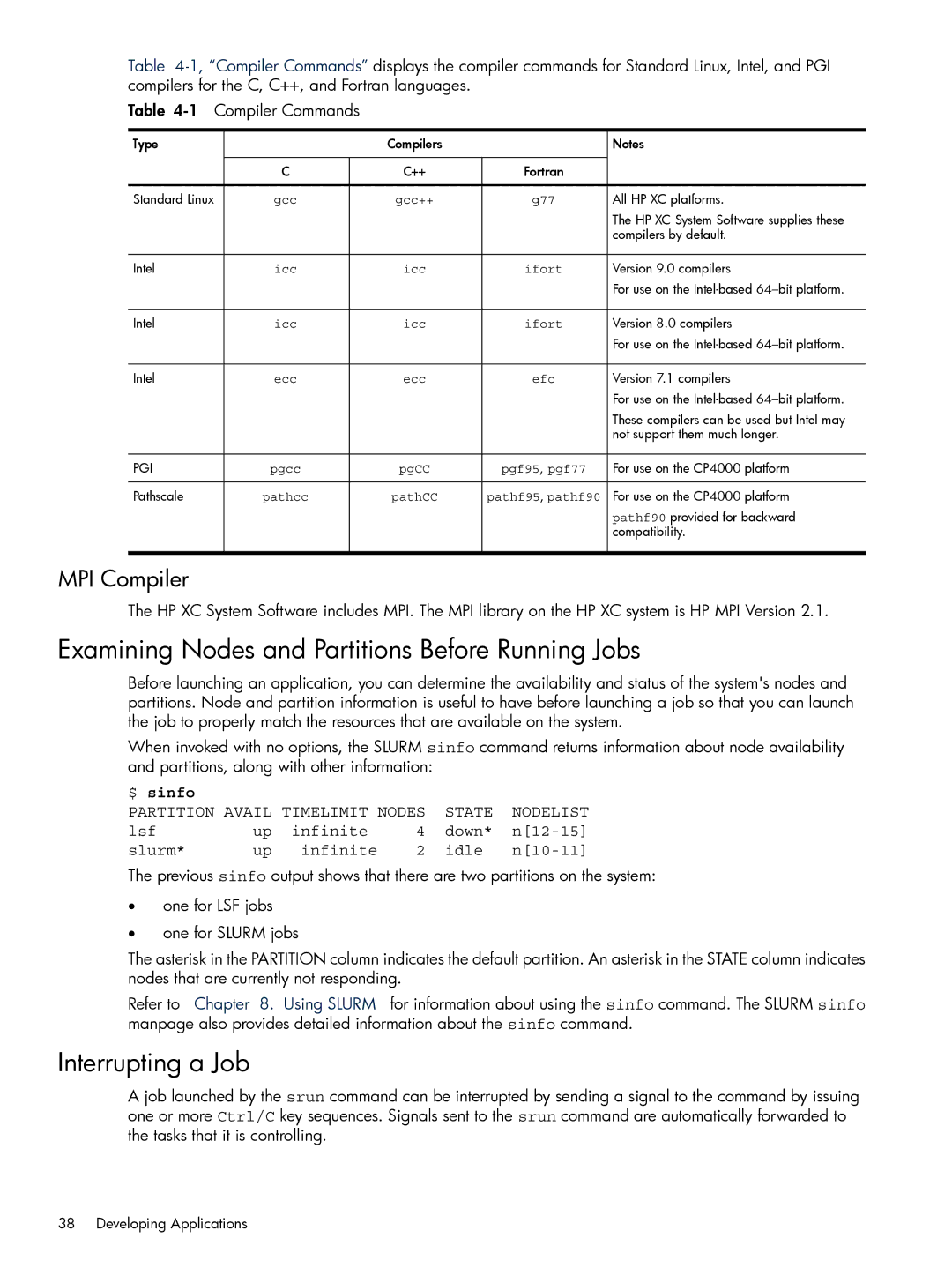
Table
Table
Type |
| Compilers |
| Notes |
| C | C++ | Fortran |
|
Standard Linux | gcc | gcc++ | g77 | All HP XC platforms. |
|
|
|
| The HP XC System Software supplies these |
|
|
|
| compilers by default. |
Intel | icc | icc | ifort | Version 9.0 compilers |
|
|
|
| For use on the |
Intel | icc | icc | ifort | Version 8.0 compilers |
|
|
|
| For use on the |
Intel | ecc | ecc | efc | Version 7.1 compilers |
|
|
|
| For use on the |
|
|
|
| These compilers can be used but Intel may |
|
|
|
| not support them much longer. |
PGI | pgcc | pgCC | pgf95, pgf77 | For use on the CP4000 platform |
Pathscale | pathcc | pathCC | pathf95, pathf90 | For use on the CP4000 platform |
|
|
|
| pathf90 provided for backward |
|
|
|
| compatibility. |
MPI Compiler
The HP XC System Software includes MPI. The MPI library on the HP XC system is HP MPI Version 2.1.
Examining Nodes and Partitions Before Running Jobs
Before launching an application, you can determine the availability and status of the system's nodes and partitions. Node and partition information is useful to have before launching a job so that you can launch the job to properly match the resources that are available on the system.
When invoked with no options, the SLURM sinfo command returns information about node availability and partitions, along with other information:
$ sinfo |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PARTITION AVAIL TIMELIMIT | NODES | STATE | NODELIST | |||
lsf | up | infinite |
| 4 | down* |
|
slurm* | up | infinite | 2 | idle |
| |
The previous sinfo output shows that there are two partitions on the system:
•one for LSF jobs
•one for SLURM jobs
The asterisk in the PARTITION column indicates the default partition. An asterisk in the STATE column indicates nodes that are currently not responding.
Refer to Chapter 8. Using SLURM for information about using the sinfo command. The SLURM sinfo manpage also provides detailed information about the sinfo command.
Interrupting a Job
A job launched by the srun command can be interrupted by sending a signal to the command by issuing one or more Ctrl/C key sequences. Signals sent to the srun command are automatically forwarded to the tasks that it is controlling.
38 Developing Applications