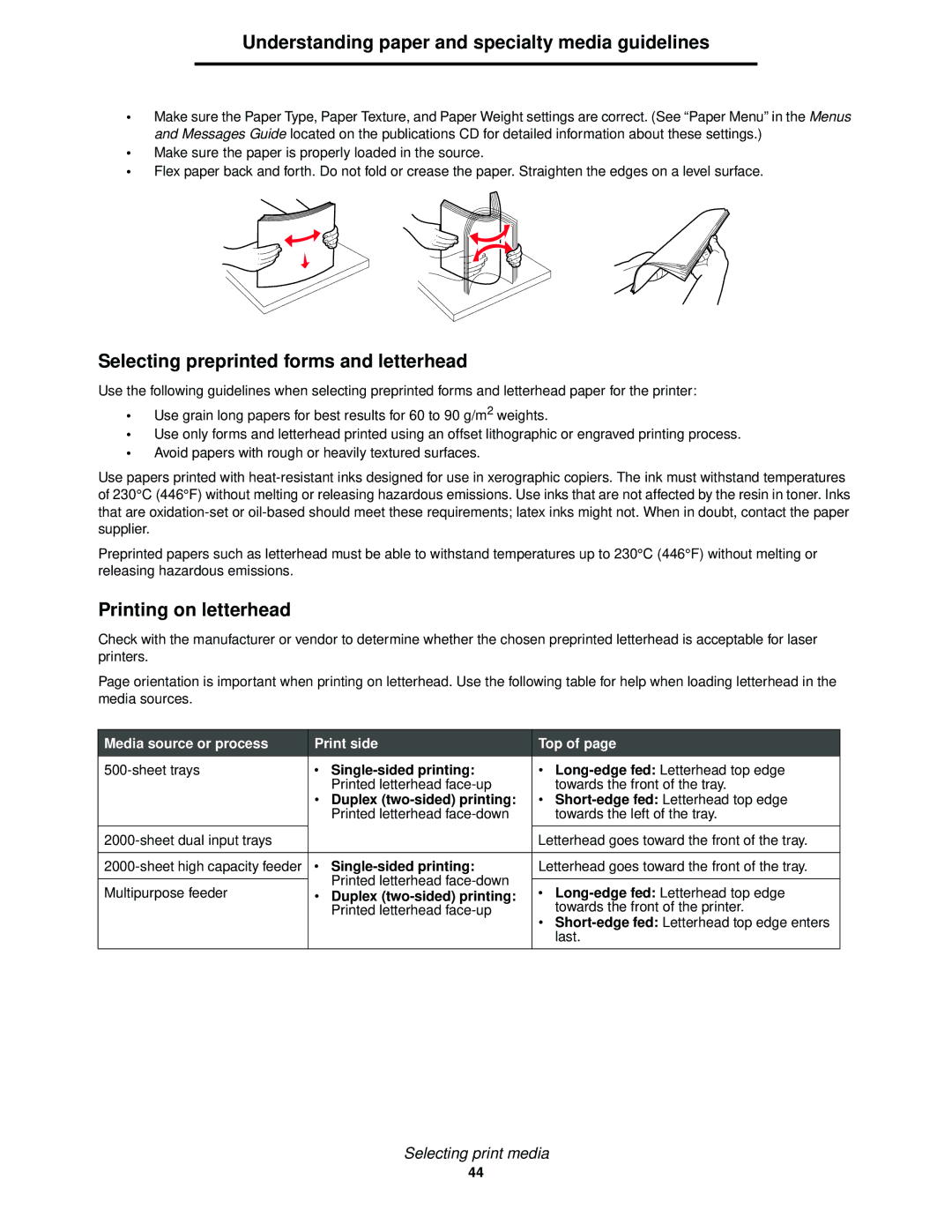
1585 (MT 4539) specifications
The IBM 1585, also known as the MT 4539, is a significant model in the line of IBM's automatic data processing systems. Introduced in the early 1980s, the IBM 1585 was primarily designed for data management tasks, catering to businesses that required efficient solutions for their growing data needs.At its core, the IBM 1585 incorporated robust features that made it highly effective for numerous applications. Primarily, it was designed for data entry and processing, significantly enhancing productivity through automation. Its advanced input/output capabilities supported various peripheral devices that were essential in data handling, allowing users to connect printers, scanners, and storage devices with ease.
One notable characteristic of the IBM 1585 was its architecture, which supported multitasking and real-time processing. This enabled users to run multiple applications simultaneously without a significant drop in performance. The system's processing power was driven by the IBM proprietary processor technology, which ensured fast computation and responsiveness, vital for time-sensitive operations.
Furthermore, the IBM 1585 showcased innovative technologies that were ahead of its time. It included support for a graphical user interface, making it more accessible for users who were transitioning from command-line interfaces. This feature not only enhanced user experience but also made training new employees more efficient.
Another key feature was its excellent compatibility with various software applications, especially those tailored for business management, accounting, and statistical analysis. The extensibility of the IBM 1585 allowed organizations to customize their setup to meet specific operational demands.
Additionally, the IBM 1585 emphasized security and data integrity, incorporating measures to protect sensitive information. This focus on security was particularly relevant for businesses managing confidential data, as robust access controls and encryption features were part of the system’s design.
In summary, the IBM 1585 (MT 4539) was a pioneering computing platform, featuring advanced data processing capabilities, multitasking architecture, user-friendly graphical interface, and strong compatibility with various applications. Its introduction marked a significant step in the evolution of business computing, reflecting IBM’s commitment to meeting the demands of a rapidly changing technological landscape.