IBM TotalStorage DS8000 Series
Page
IBM TotalStorage DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
First Edition April
Contents
Page
Benefits of virtualization
Vi DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
Summary
Viii DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
Page
Page
Index
Xii DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
Copyright License
Dfsort
Trademarks
Team that wrote this redbook
Preface
Xvi DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
Preface
Xviii DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
Comments welcome
Become a published author
Xx DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
Part 1 Introduction
DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
Introduction to the DS8000 series
Overview of the DS8000 series
DS8000, a member of the TotalStorage DS family
Infrastructure Simplification
Business Continuity
DS8000 Base frame
Hardware overview
Storage system logical partitions LPARs
Storage capacity
Storage Hardware Management Console S-HMC for the DS8000
IBM Standby Capacity on Demand offering for the DS8000
Resiliency Family for Business Continuity
Supported environments
IBM TotalStorage Metro Mirror Synchronous Pprc
IBM TotalStorage FlashCopy
Three-site solution
Service and setup
Interoperability
IBM TotalStorage Global Mirror Asynchronous Pprc
DS8000 compared to ESS
Positioning
Common set of functions
Common management functions
IBM TotalStorage DS Command-Line Interface DS CLI
DS8000 compared to DS6000
IBM TotalStorage DS Storage Manager
DS Open application programming interface
Scalability and configuration flexibility
Future directions of storage system LPARs
Performance
Sequential Prefetching in Adaptive Replacement Cache Sarc
IBM TotalStorage Multipath Subsystem Device Driver SDD
Performance for zSeries
Summary
16 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
Part 2 Architecture
18 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
Components
Base frame
Frames
Rack operator panel
Expansion frame
Rack operator panel
Architecture
SAN fabric
Cache management
Server-based SMP design
Components
Randomseq
Processor complex
Components
Front view
Service processor and Spcn
Rear view
Processor memory
2 I/O enclosures
RIO-G
Device adapters
Disk subsystem
Rear view
DS8000 device adapter
Disk enclosures
DS8000 disk enclosure
Non-switched FC-AL drawbacks
11 DS8000 disk enclosure
Switched FC-AL advantages
12 Disk enclosure switched connections
DS8000 switched FC-AL implementation
Arrays and spares
Expansion
Arrays across loops
14 DS8000 switched loop layout
DDMs
Host adapters
AAL benefits
Control units and logical paths
Ficon and Fibre Channel protocol host adapters
Escon distances
Remote Mirror and Copy with Escon
Rack Power Control cards RPC
Power and cooling
Fibre Channel supported servers
Fibre Channel distances
Processor and I/O enclosure power supplies
Primary power supplies
Disk enclosure power and cooling
Battery backup assemblies
Ethernet switches
42 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
Storage system LPARs Logical partitions
Virtualization Engine technology
Introduction to logical partitioning
Partitioning concepts
Partitions
Logical partitioning Lpar
Building block
Physical partitioning Ppar
Dynamic logical partitioning
Software and hardware fault isolation
Micro-Partitioning
Virtual I/O
Server consolidation
Why Logically Partition?
Production and test environments
Application isolation
Increased flexibility of resource allocation
DS8000 and Lpar
Lpar and storage facility images
DS8300 Model 9A2 Lpar and storage facility image
2 DS8300 Lpar implementation
DS8300 Lpar resource allocation
Storage facility image hardware components
Processor and memory allocations
Storage Facility Image Processor complex
RIO-G interconnect separation
4 DS8300 Model 9A2 configuration options
Model conversion
DS8300 example configuration
Model conversions regarding Lpar functionality
Lpar security through Power Hypervisor Phyp
Lpar protection Power Hypervisor
Lpar and Copy Services
Remote mirroring
Lpar benefits
FlashCopy
Storage system LPARs Logical partitions
Example of storage facility images in the DS8300
Addressing capabilities with storage facility images
DS8300 addressing capabilities
60 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
RAS
Storage complex
Naming
Storage unit
Storage facility image
Processor complex
Processor complex RAS
Permanent monitoring
Reliability, availability, and serviceability
+1 redundancy
Memory reliability, fault tolerance, and integrity
Self-healing
Concurrent Maintenance
Fault masking
Hypervisor Storage image independence
Resource deallocation
RIO-G a self-healing interconnect
Server RAS
2 I/O enclosure
Metadata checks
Data flow
Server failover and failback
Normal data flow
Failover
Failback
NVS recovery after complete power loss
Single or multiple path
Host connection availability
Enclosure
Multi-pathing software
SAN/FICON/ESCON switches
ZSeries host connection
Open systems host connection
Disk path redundancy
Switched disk connections
RAID-10 overview
RAID-5 overview
RAID-5 theory
RAID-5 implementation in the DS8000
RAID-10 implementation in the DS8000
Spare creation
RAID-10 theory
Hot plugable DDMs
Predictive Failure Analysis PFA
Floating spares
Rack power control card RPC
Battery backup units
Disk scrubbing
Rack cooling fans
Power fluctuation protection
Building power loss
Power control of the DS8000
Emergency power off EPO
Installation process
Microcode updates
Different code versions across storage images
Management console
HMC considerations
Virtualization concepts
Storage system virtualization
Virtualization definition
Storage Facility virtualization
Abstraction layers for disk virtualization
Physical layer as the base for virtualization
Array sites
Array site
Arrays
Creation of an array
Ranks
Forming an FB rank with 1 GB extents
Extent pools
Server0
Fixed Block LUNs
Logical volumes
CKD volumes
Volume with
ISeries LUNs
Allocation and deletion of LUNs/CKD volumes
Logical subsystems LSS
DB2
Address groups
Volume access
Host attachment
Volume group
Summary of the virtualization hierarchy
11 Host attachments and volume groups
12 Virtualization hierarchy
Placement of data
Benefits of virtualization
13 Optimal placement of data
101
102 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
103
IBM TotalStorage DS8000 model overview and scalability
Model naming conventions
DS8000 highlights
2 DS8100 Model
3 DS8300 Models 922 and 9A2
Maximum configuration for the Model
IBM TotalStorage DS8000 model overview and scalability
Model comparison
Scalability for capacity
Designed for scalability
Large and scalable capacity
DS8000 model comparison
Adding DDMs
Scalability for performance
Future plan
Comparison of models for capacity
Linear-scalable architecture
Way I/O controllers
Benefit of the DS8000 for scalability
RIO-G
Model conversions
Model upgrades
114 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
115
Copy Services
Point-in-Time Copy FlashCopy
Introduction to Copy Services
Copy Services functions
Write to the source volume
Read from the source volume
Read from the target volume
Refresh target volume also known as Incremental FlashCopy
Point-in-Time Copy function authorization
FlashCopy options
No background copy option
Incremental FlashCopy
Data Set FlashCopy
Data Set FlashCopy
Multiple Relationship FlashCopy
Consistency Group FlashCopy
What is Consistency Group FlashCopy?
FlashCopy Source Volume FlashCopy Target Volume
FlashCopy to Pprc Primary Volume
Remote Mirror and Copy Peer-to-Peer Remote Copy
Inband Commands over Remote Mirror link
Persistent FlashCopy
Metro Mirror Synchronous Pprc
Metro Mirror
Global Copy PPRC-XD
Global Copy
Global Mirror Asynchronous Pprc
Global Mirror
How Global Mirror works
Global Mirror How it works
OS Global Mirror XRC
11 z/OS Global Mirror
Secondary server
12 z/OS Metro/Global Mirror
Comparison of the Remote Mirror and Copy functions
Global Copy PPRC-XD
What is data consistency?
What is a Consistency Group?
How does Consistency Group keep data consistency?
1st
LSS13
Storage Hardware Management Console S-HMC
Interfaces for Copy Services
DS Storage Manager Web-based interface
16 DS8000 Copy Services network components
DS Open application programming Interface API
DS Command-Line Interface DS CLI
Tip What is changed from the ESS CLI?
Future Plans
Interoperability with ESS
140 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
141
Part 3 Planning and configuration
142 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
143
Installation planning
Delivery requirements
Packaged dimensions and weight for DS8000 models
General considerations
145
Installation site preparation
Floor and space requirements
Calculating space requirements
Installing on raised or nonraised floors
Meeting floor load requirements
Power control
Power requirements
DS8000 dimensions
147
Input voltage requirements
Power outlet requirements
Power consumption and environmental information
Power connector requirements
Environmental requirements
Fans and air intake areas
Cooling the storage complex
Host attachment
Attaching to open systems hosts
151
ESCON-attached S/390 and zSeries hosts
FICON-attached S/390 and zSeries hosts
SAN Fabric products
Where to get the updated information for host attachment
Host systems attachment
HMC network requirements
Network and SAN requirements
Channel extension technology products
153
SAN requirements
Remote power control requirements
Remote support connection requirements
155
156 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
157
Configuration planning
Storage Hardware Management Console S-HMC
Configuration planning overview
External S-HMC
S-HMC and Ethernet switches
DS Storage Manager
Remote services
HMC software components
Required ports
161
HMC network topology
163
Dial-up connection
Secure high-speed connection
Call home
Remote access
Security mechanism 1 Console must initiate session
HMC security considerations
Security mechanism 2 Public key encryption
165
HMC user management
Security mechanism 3 Login security
FTP Offload option
Licensed function indicators
Operating environment license OEL required feature
DS8000 licensed functions
167
Operating environment license feature codes
Optional features
Point-in-Time Copy function 2244 Model PTC
License scope for each DS8000 licensed function
Remote Mirror and Copy RMC feature codes
Point-in-Time Copy PTC feature codes
Remote Mirror and Copy functions 2244 Model RMC
Remote Mirror for z/OS 2244 Model RMZ
Remote Mirror for zSeries RMZ feature codes
Parallel Access Volumes 2244 Model PAV
Parallel Access Volumes PAV feature codes
Ordering licensed functions
User authorize to FlashCopy 25 TB of CKD data
171
Solution
173
Disk storage feature activation
Capacity planning
Logical configurations
Scenarios for managing licensing
Adding storage capacity to an existing licensed function
CKD RAID rank capacity
175
FB RAID rank capacity
Sparing rules
177
Sparing examples
Sparing Example 2 RAID-10
11 Sparing example 3 RAID-5 Different capacity, same RPM
179
IBM Standby Capacity on Demand Standby CoD
Sparing Example 4 RAID-5
181
Capacity and well-balanced configuration
DDM to DA Mapping -- 2-way
183
Data migration planning
Operating system mirroring
Basic commands
Software packages
Remote copy technologies
185
Migration services and appliances
6 z/OS data migration methods
15 Different data migration methods
Planning for performance
Disk Magic
Parallel Access Volumes z/OS only
Size of cache storage
Number of host ports/channels
Hot spot avoidance
189
DS Storage Manager logical configuration
Storage configuration terminology
Configuration hierarchy, terminology, and concepts
PSeries1 PSeries2
Arrays
Array sites
Ranks
Extent pools
Extent Pool
Volume groups
Logical volumes
Volume Group
Address groups
Host System C
Extent Pool
Extent Pool
Planning
Array layer
Raw or physical DDM layer
Array site layer
Logical volume layer
Logical Configuration flow
Rank layer
Extent pool layer
Connecting to the DS8000
Introducing the GUI and logical configuration panels
Welcome panel
10 Entering the URL using the TCP/IP address for the S-HMC
12 The Welcome panel
Real-time Manager configuration
Simulated Manager configuration
Copy Services
Log
Creating and defining the users and passwords
15 User administration panel
Using the help panels information center
17 View of the information center
Navigating the GUI
20 View of the Storage Complexes section
19 View of the storage complexes in the work area
21 Storage unit view of the pull-down
Radio buttons and check boxes
Configuring a storage complex
Logical configuration process
Configuring the storage unit
25 The General storage unit information panel
Configuration advancement steps
28 Specify I/O adapter configuration panel
29 Create host systems, screen
Configuring the logical host systems
31 View of the General host information panel
33 Define host ports panel, with updated host information
Click Apply assignment and OK
Creating arrays from array sites
36 The Definition method panel
38 The Add arrays to ranks panel with FB selected
Creating extent pools
39 The Definition method panel
Creating FB volumes from extents
41 The Select extent pool panel
42 The Define volume properties panel
Click Volume Groups
Creating volume groups
44 The Define volume group properties filled out
Click Host Systems
Deleting LUNs and recovering space in the extent pool
Assigning LUNs to the hosts
Click Volumes → zSeries
Creating CKD volumes
Creating CKD LCUs
Click Finish
Click Storage Units
Displaying the storage unit Wwnn
49 View of the Wwnn in the General panel
230 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
231
Functionality
Introduction
Supported environments
Installation methods
ESS Copy Services command flow using ESS Copy Services CLI
Command flow
TCP/IP ports
DS CLI command flow
Secure sockets
DS8000 split network
DS6000 command flow
ESS CLI co-existence
Command flow for the DS6000
CLI co-existence
Storage management
Single command mode
Command modes
Example 11-1 Using DS CLI via a single command
User security
Script mode
Interactive mode
Example 11-4 Using DS CLI in interactive mode
Example 11-3 Creating a DS CLI script
Lists all DS CLI commands with syntax information
Lists all available DS CLI commands
Syntax conventions
User assistance
Return codes
Example 11-8 Use of the help -lcommand
Man pages
DS CLI return codes
Example 11-10 Return code examples
Example 11-11 Example of a configuration script
Usage examples
Mixed device environments and migration
Which CLI to use based on what hardware you have installed
Migration tasks
DS CLI migration example
Determining the saved tasks to be migrated
Migration considerations
Collecting the task details
A portion of the tasks listed by using the GUI
Using the GUI to get the contents of a FlashCopy task
Converting the saved task to a DS CLI command
Converting a FlashCopy task to DS CLI
Example 11-14 Using interactive dscli mode without profiles
Procedure to create an encrypted password file
Using DS CLI commands via a single command or script
Setting up a profile
Creating a user ID for use only with ESS
Example 11-18 Establishing a FlashCopy with a single command
Issuing a DS CLI command and scripting it
Example 11-19 Creating an executable file
Example 11-20 Using script mode
252 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
253
Performance considerations
New and enhanced functions
What is the challenge?
Speed gap between server and disk storage
255
Where do we start?
SSA backend interconnection
Switch from Escon to Ficon ports
Arrays across loops
Pprc over Fibre Channel links
How does the DS8000 address the challenge?
Fibre Channel switched disk interconnection at the back end
FC-AL shortcomings
How the DS8000 series overcomes FC-AL shortcomings
Memory
259
New four-port host adapters
Fibre Channel device adapter
261
POWER5 Heart of the DS8000 dual cluster design
RIO-G Interconnect
263
RIO-G Interconnect
Vertical growth and scalability
Performance and sizing considerations for open systems
Data placement in the DS8000
Workload characteristics
Cache size considerations for open systems
265
266 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
LVM striping
267
Stripe size
Subsystem Device Driver SDD Dynamic I/O load-balancing
Determining where to attach the host
Determining the number of paths to a LUN
269
Performance and sizing considerations for z/OS
Connect to zSeries hosts
12 DS8100 frontend connectivity example partial view
Performance potential in z/OS environments
271
Appropriate DS8000 size in z/OS environments
Processor memory size considerations for z/OS environments
Or zSeries channel consolidation
273
Disk array sizing considerations for z/OS environments
Configure one extent pool for each single rank
Configuration recommendations for z/OS
275
Minimize the number of extent pools
Plan for a reasonable number of extent pools
Extent pool0 Extent pool1
15 Mix of extent pools
277
278 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
279
280 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
281
ZSeries software enhancements
Scalability support
Software enhancements for the DS8000
13.2 z/OS enhancements
Read availability mask support
Large Volume Support LVS
Benefits of the scalability enhancements
283
Read control unit and device recognition for DS8000
Initial Program Load IPL enhancements
13.2.5 DS8000 definition to host software
285
New performance statistics
Listdata Count
Listdata Counts report of DS8000
287
Listdata Status
289
Resource Management Facility RMF
13.4 z/VSE enhancements
13.3 z/VM enhancements
Migration considerations
Coexistence considerations
291
TPF enhancements
292 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
293
Data migration in zSeries environments
Consolidate storage subsystems
Define migration objectives in z/OS environments
295
Consolidate logical volumes
Considerations for new logical volume size
Example 14-1 Data Classes with EF attribute
Dynamic Parallel Access Volumes required for large volumes
297
Keep source and target volume size at the current size
Physical migration with DFSMSdss and other storage software
Data migration based on physical migration
Summary of data migration objectives
299
Software- and hardware-based data migration
Data migration with Piper for z/OS
Piper hardware
301
Data migration with z/OS Global Mirror
Bridge from Escon to Ficon with Metro/Global Copy
Hardware- or microcode-based migration
303
Data migration with Metro Mirror or Global Copy
Pprcopy DDNAMEDD02 Query
Example 14-3 All data is replicated
305
Example 14-5 All data is replicated
491
307
Data Set Services Utility
Data migration based on logical migration
System utilities
Hierarchical Storage Manager, DFSMShsm
SMS Storage Groups migration source environment
309
Storage Group Application Selection
Example 14-8 Select SMS storage group in Scds
311
Alter Volume Statuses Pool Copy Pool Backup only
ALL Volumes Altered
Example 14-12 Confirmation about SMS volume status change
313
Combine physical and logical data migration
315
14.5 z/VM and VSE/ESA data migration
Summary of data migration
316 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
317
318 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
319
Open systems support and software
Supported operating systems and servers
Where to look for updated and detailed information
Open systems support
IBM HBA Search Tool
DS8000 Interoperability Matrix
DS8000 Host Systems Attachment Guide
TotalStorage Proven program
Platform and operating system vendors’ pages
Differences to the ESS
Emulex Corporation
Atto
Additional supported configurations RPQ
Boot support
Subsystem Device Driver
DS CLI
Other multipathing solutions
IBM TotalStorage Productivity Center
IBM TotalStorage Productivity Center
MDM main panel
Sample Device Manager view
Device Manager
Sample screenshot of TPC for Disk
TPC for Disk
TPC for Replication
Global Mirror Utility
Enterprise Remote Copy Management Facility eRCMF
332 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
333
Data migration in the open Systems environment
Tor
Host operating system-based migration
Comparison of migration methods
Copy raw devices
Basic copy commands
Online copy and synchronization with rsync
Migration using volume management software
Migration using LVM mirroring
Backup and restore
Subsystem-based data migration
Migration using backup and restore
Combination of Metro Mirror and Global Copy
Metro Mirror and Global Copy
Piper migration
IBM Piper migration
Other migration applications
IBM migration services
343
Appendix A. Open systems operating systems specifics
DS8000 Host Systems Attachment Guide
Data placement considerations
Planning
Capacity planning considerations
Example A-1 AIX iostat output
Unix performance monitoring tools
Iostat
Example A-2 SUN Solaris iostat output
System Activity Report SAR
Example A-3 SAR Sample Output
Vmstat
AIX host attachment scripts
Other publications
Finding the World Wide Port Names
Example A-4 Finding Fibre Channel adapter WWN
Useful SDD commands
Determine the installed SDD level
Managing multiple paths
Subsystem device driver SDD
Multipath I/O Mpio
Example A-7 lsvpcfg command
Example A-8 lspath command result
Determine the installed Sddpcm level
Useful Mpio commands
AIX access methods for I/O
LVM configuration
LVM striping
LVM mirroring
AIX on IBM iSeries
Boot device support
Direct I/O
Concurrent I/O
Iostat
Monitoring I/O performance
Filemon
Example A-9 Filemon output file
IBM Mpio FC
Linux
Implementing Linux with IBM Disk Storage
Existing reference material
Linux with zSeries and ESS Essentials
Getting Started with zSeries Fibre Channel Protocol
Table A-1 Major numbers and special device files
Important Linux issues
Some Linux Scsi basics
Example A-10 Create new special device files for Scsi disks
Missing device files
Scsi device assignment changes
Managing multiple paths
Limited number of Scsi devices
Fibre Channel disks discovered before internal Scsi disks
RedHat Enterprise Linux RH-EL multiple LUN support
Example A-13 SCSi disks attached at system start time
Adding FC disks dynamically
Example A-12 Sample /etc/modules.conf
Gaps in the LUN sequence
Linux on IBM iSeries
Example A-16 Sample /proc/scsi/scsi file
Troubleshooting and monitoring
/proc pseudo file system
Example A-17 Sample /proc/scsi/qla2300/x
Performance monitoring with iostat
Generic Scsi tools
SDD for Windows
HBA and operating system settings
Microsoft Windows 2000/2003
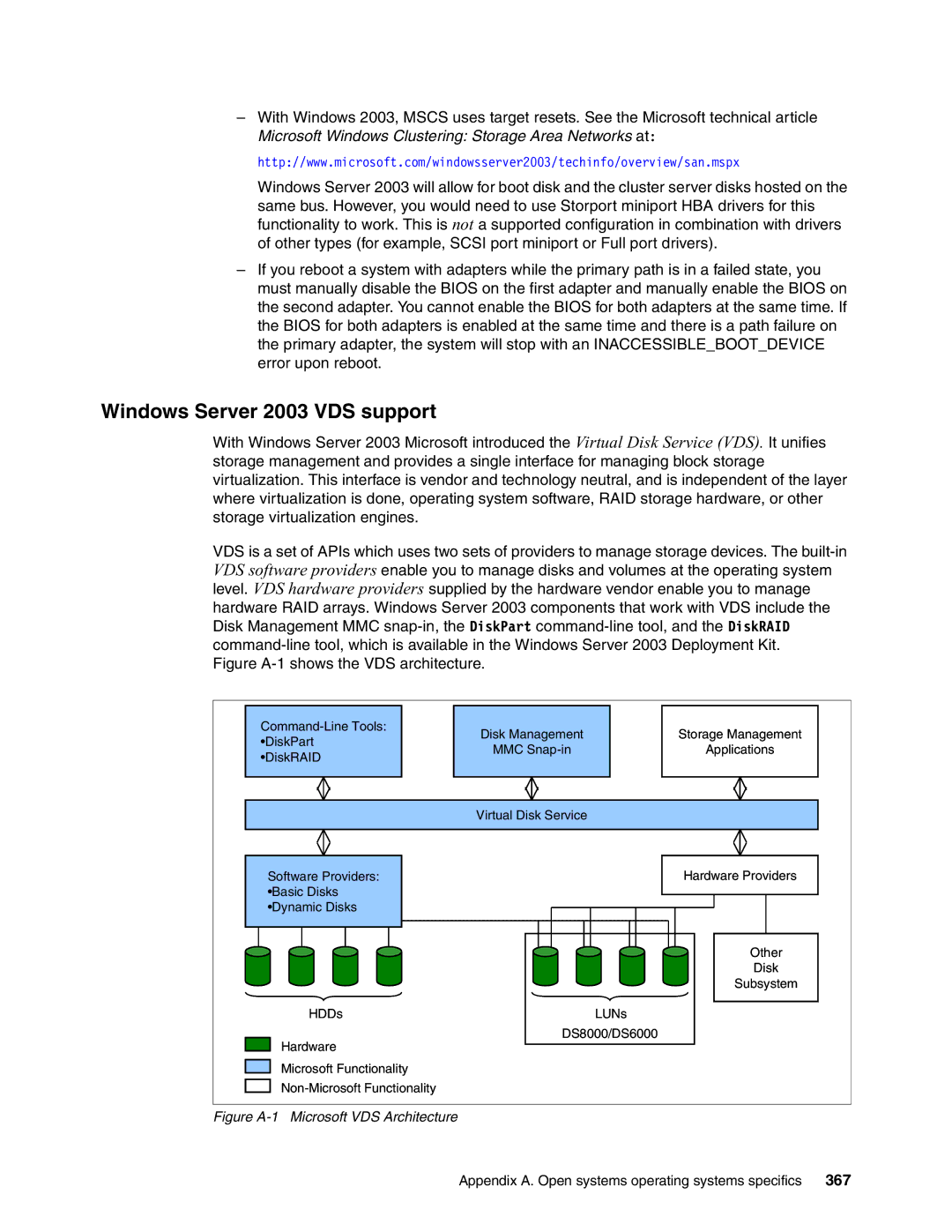
Figure A-1 Microsoft VDS Architecture
Windows Server 2003 VDS support
Volume Shadow Copy Service
FC port configuration
HP OpenVMS
Geographically Dispersed Sites
Configurations
Volume configuration
OpenVMS volume shadowing
Command Console LUN
Appendix A. Open systems operating systems specifics
372 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
373
Appendix B. Using DS8000 with iSeries
Table B-1 OS/400 logical volume sizes
Logical volume sizes
Supported environment
Hardware
Changing LUN protection
Protected versus unprotected volumes
Using 5250 interface
Adding volumes to iSeries configuration
Figure B-3 Work with Disk Configuration menu
Figure B-5 Confirm Add Units
Adding volumes to an Independent Auxiliary Storage Pool
Figure B-7 iSeries Navigator Signon to iSeries window
Figure B-9 SST Signon
Figure B-11 New disk pool welcome
Figure B-13 Confirm disk pool configuration
Figure B-15 Choose the disks to add to the Disk Pool
Figure B-17 New Disk Pool Summary
Figure B-20 New Disk Pool shown on iSeries Navigator
Avoiding single points of failure
Multipath
Figure B-22 Single points of failure
Configuring multipath
Figure B-24 Example of multipath with iSeries
Adding multipath volumes to iSeries using 5250 interface
Figure B-25 Adding multipath volumes to an ASP
Figure B-27 Adding a multipath volume
Adding volumes to iSeries using iSeries Navigator
Figure B-28 New Disk Pool shown on iSeries Navigator
Figure B-30 Example of multipath logical units
Managing multipath volumes using iSeries Navigator
Appendix B. Using DS8000 with iSeries
Figure B-32 Multipath logical unit properties
Figure B-33 Multipath connections
Multipath rules for multiple iSeries systems or partitions
Changing from single path to multipath
Sizing guidelines
Cache
Planning for arrays and DDMs
Table B-2 Capacity per I/O Adapter
Number of iSeries Fibre Channel adapters
Size and number of LUNs
Table B-3 Disk operations per second per RAID rank
Recommended number of ranks
Sharing ranks between iSeries and other servers
Migration
Connecting via SAN switches
OS/400 mirroring
Metro Mirror and Global Copy
OS/400 data migration
Figure B-35 Using Metro Mirror to migrate from ESS to DS8000
Figure B-36 Ending allocation for existing disk units
Remote Mirror and Copy
Copy Services for iSeries
FlashCopy
AIX on IBM iSeries
ISeries toolkit for Copy Services
Linux on IBM iSeries
406 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
407
Appendix C. Service and support offerings
IBM service offerings
IBM Web sites for service offerings
IBM Implementation Services for TotalStorage disk systems
IBM Implementation Services for TotalStorage Copy Functions
Enterprise Remote Copy Management Facility eRCMF
IBM Geographically Dispersed Parallel Sysplex Gdps
IBM eServer iSeries Copy Services
IBM Operational Support Services Support Line
Appendix C. Service and support offerings
412 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
413
IBM Redbooks
Other publications
Online resources
Help from IBM
How to get IBM Redbooks
416 DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
417
Index
DS CLI
OEL
Escon Ficon
RH-EL
BBU
Spcn
VSE
IBM TotalStorage DS8000 Series Concepts and Architecture
Page
Page
IBM TotalStorage DS8000 Series Concepts Architecture