Introduction
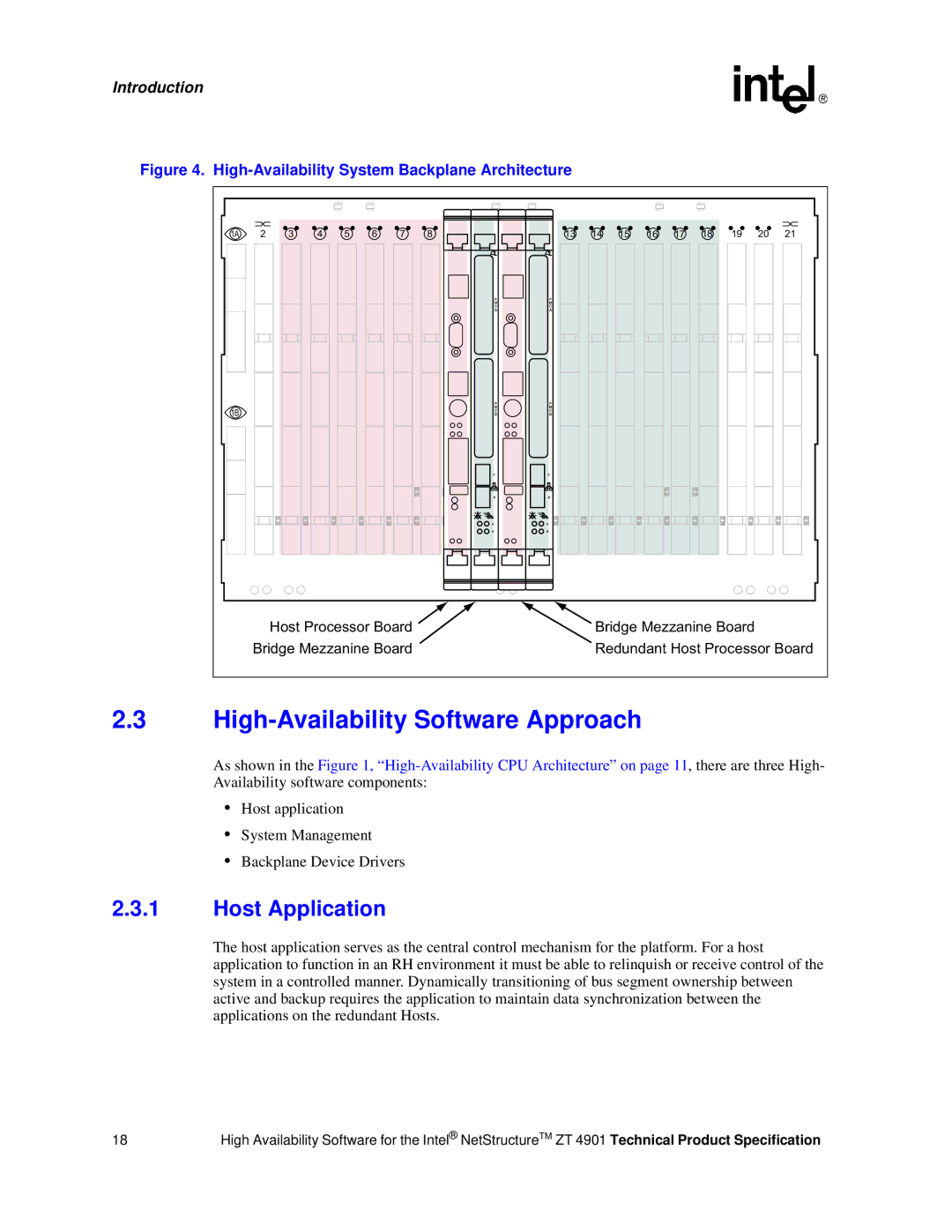
Figure 4. High-Availability System Backplane Architecture
1A | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
1B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Host Processor Board |
|
| Bridge Mezzanine Board |
|
| |||||||||
| Bridge Mezzanine Board |
|
| Redundant Host Processor Board | ||||||||||||
2.3High-Availability Software Approach
As shown in the Figure 1,
•Host application
•System Management
•Backplane Device Drivers
2.3.1Host Application
The host application serves as the central control mechanism for the platform. For a host application to function in an RH environment it must be able to relinquish or receive control of the system in a controlled manner. Dynamically transitioning of bus segment ownership between active and backup requires the application to maintain data synchronization between the applications on the redundant Hosts.
18 | High Availability Software for the Intel® NetStructureTM ZT 4901 Technical Product Specification |