High Availability CompactPCI Device Drivers
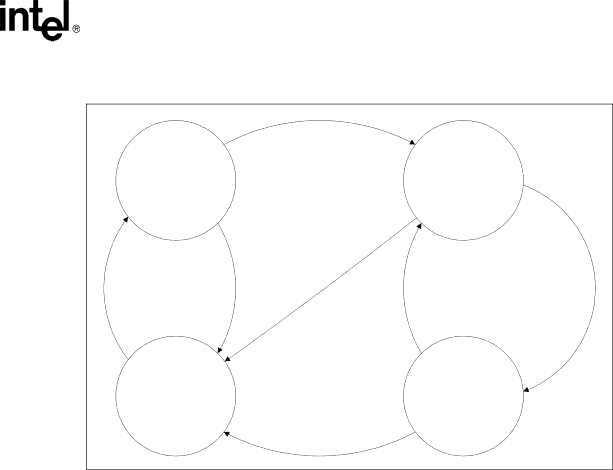
Figure 6. Multi-Stated Driver Flowchart
|
| AddDevice |
| |
Driver | Device |
| ||
Not Loaded | Suspended |
| ||
|
| RemoveDevice / |
| |
Find |
| SurpriseRemoval |
| |
Device |
|
| ||
Suitable | StopDevice | StartDevice | ||
Removed | ||||
Driver |
|
| ||
|
|
| ||
Device Not | Device |
| ||
Present | Running |
| ||
|
| RemoveDevice / |
| |
|
| SurpriseRemoval |
| |
5.1.2Adding High-Availability Functionality
Operating in a Redundant Host architecture places additional responsibilities on device drivers beyond those issues required to function in a normal Hot Swap environment. This section covers particular issues that a Redundant Host device driver designer needs to be aware of when implementing their design.
The Redundant Host architecture leverages the Hot Swap driver interface to enable
Additional measures need to be taken to protect against inadvertent backplane interrupts and bus- mastering activities by devices on the segment in question. These additional measures are completely transparent operations to the device drivers since the Hot Swap Manager in the kernel handles them. All a device driver needs to be concerned with is being able to gracefully suspend and resume interaction with the device or devices it controls.
Each operating system that supports Hot Swap does so in a unique way. The specific function callbacks, number of callbacks, and level of control vary between operating system implementations. However, all Hot Swap implementations are based on the stated driver model described in Section 5.1.1, “Device Driver States” on page 32. The driver states can be classified into the following generic functions:
High Availability Software for the Intel® NetStructureTM ZT 4901 Technical Product Specification | 33 |
