TK-260G/270G
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
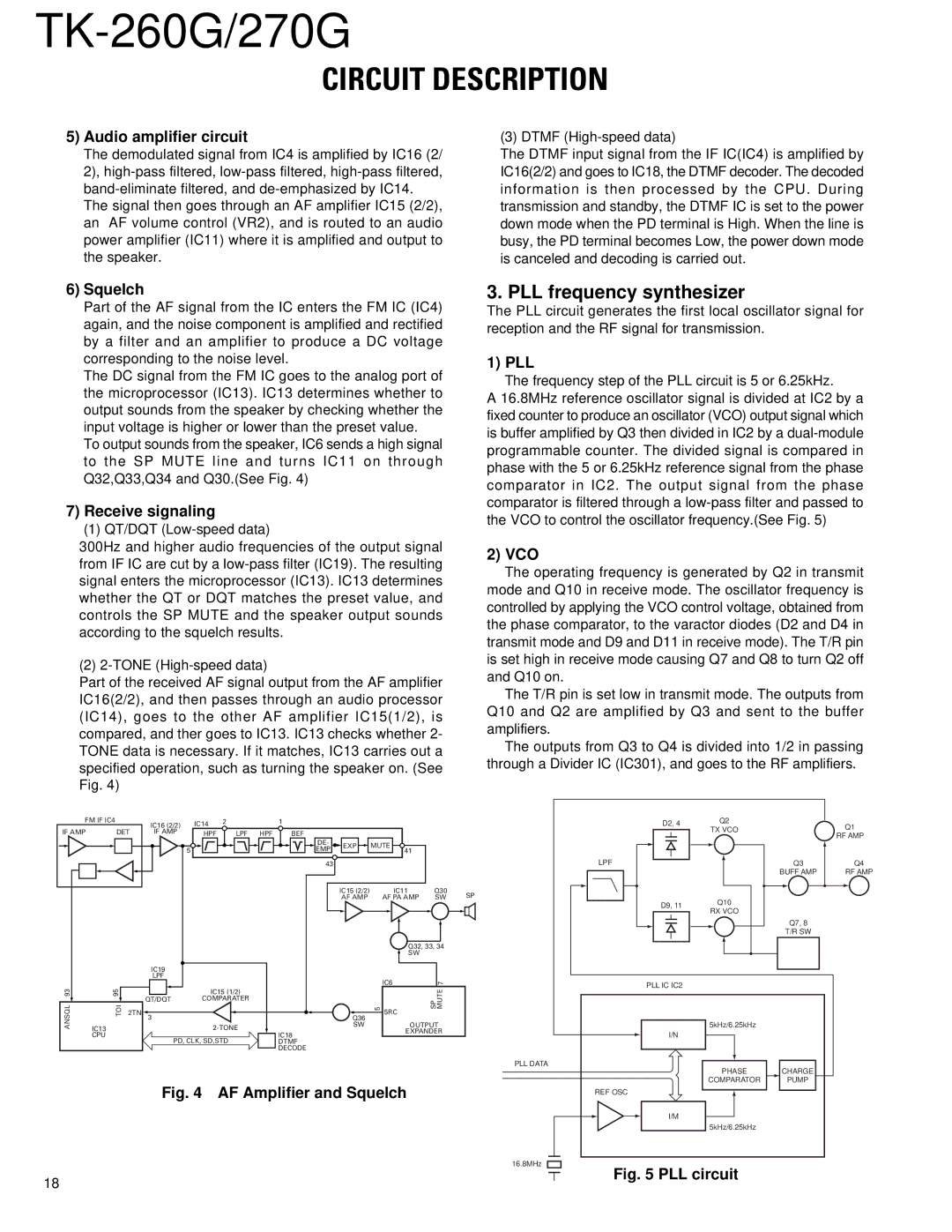
5)Audio amplifier circuit
The demodulated signal from IC4 is amplified by IC16 (2/ 2),
The signal then goes through an AF amplifier IC15 (2/2), an AF volume control (VR2), and is routed to an audio power amplifier (IC11) where it is amplified and output to the speaker.
(3) DTMF
The DTMF input signal from the IF IC(IC4) is amplified by IC16(2/2) and goes to IC18, the DTMF decoder. The decoded information is then processed by the CPU. During transmission and standby, the DTMF IC is set to the power down mode when the PD terminal is High. When the line is busy, the PD terminal becomes Low, the power down mode is canceled and decoding is carried out.
6)Squelch
Part of the AF signal from the IC enters the FM IC (IC4) again, and the noise component is amplified and rectified by a filter and an amplifier to produce a DC voltage corresponding to the noise level.
The DC signal from the FM IC goes to the analog port of the microprocessor (IC13). IC13 determines whether to output sounds from the speaker by checking whether the input voltage is higher or lower than the preset value.
To output sounds from the speaker, IC6 sends a high signal to the SP MUTE line and turns IC11 on through Q32,Q33,Q34 and Q30.(See Fig. 4)
7)Receive signaling
(1) QT/DQT
300Hz and higher audio frequencies of the output signal from IF IC are cut by a
(2)
Part of the received AF signal output from the AF amplifier IC16(2/2), and then passes through an audio processor (IC14), goes to the other AF amplifier IC15(1/2), is compared, and ther goes to IC13. IC13 checks whether 2- TONE data is necessary. If it matches, IC13 carries out a specified operation, such as turning the speaker on. (See Fig. 4)
3. PLL frequency synthesizer
The PLL circuit generates the first local oscillator signal for reception and the RF signal for transmission.
1) PLL
The frequency step of the PLL circuit is 5 or 6.25kHz.
A 16.8MHz reference oscillator signal is divided at IC2 by a fixed counter to produce an oscillator (VCO) output signal which is buffer amplified by Q3 then divided in IC2 by a
2)VCO
The operating frequency is generated by Q2 in transmit
mode and Q10 in receive mode. The oscillator frequency is controlled by applying the VCO control voltage, obtained from the phase comparator, to the varactor diodes (D2 and D4 in transmit mode and D9 and D11 in receive mode). The T/R pin is set high in receive mode causing Q7 and Q8 to turn Q2 off and Q10 on.
The T/R pin is set low in transmit mode. The outputs from Q10 and Q2 are amplified by Q3 and sent to the buffer amplifiers.
The outputs from Q3 to Q4 is divided into 1/2 in passing through a Divider IC (IC301), and goes to the RF amplifiers.
FM IF IC4 |
| IC16 (2/2) | IC14 | 2 |
|
IF AMP | DET | IF AMP | HPF | LPF | HPF |
|
|
| 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| IC19 |
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
| LPF |
|
| ||
93 | 95 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| IC15 (1/2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
| QT/DQT |
| COMPARATER | |||
ANSQL | TOI | 2TN | 3 |
|
|
| |||
| IC13 |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
| CPU |
|
|
|
|
| PD, CLK, SD,STD | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1
BEF
IC18
DTMF DECODE
| DE- |
|
| EXP |
|
|
| MUTE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| EMP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 41 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| 43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| IC15 (2/2) |
|
|
| IC11 |
| Q30 |
| SP | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
| AF AMP |
| AF PA AMP |
| SW |
| ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Q32, 33, 34 |
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| IC6 |
| 7 |
|
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 5 | 5RC |
| SP MUTE |
|
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
| Q36 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
| SW |
|
|
|
|
|
| OUTPUT |
|
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| EXPANDER |
|
|
|
| ||||||
D2, 4 | Q2 |
| Q1 |
TX VCO |
| ||
|
| ||
|
| RF AMP | |
|
|
| |
LPF |
| Q3 | Q4 |
|
| BUFF AMP | RF AMP |
D9, 11 | Q10 |
|
|
RX VCO |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| Q7, 8 |
|
|
| T/R SW |
|
PLL IC IC2 |
|
|
|
| 5kHz/6.25kHz |
|
|
I/N |
|
|
|
PLL DATA | PHASE | CHARGE |
|
|
| ||
| COMPARATOR | PUMP |
|
Fig. 4 AF Amplifier and Squelch
REF OSC |
16.8MHz
18
I/M
5kHz/6.25kHz