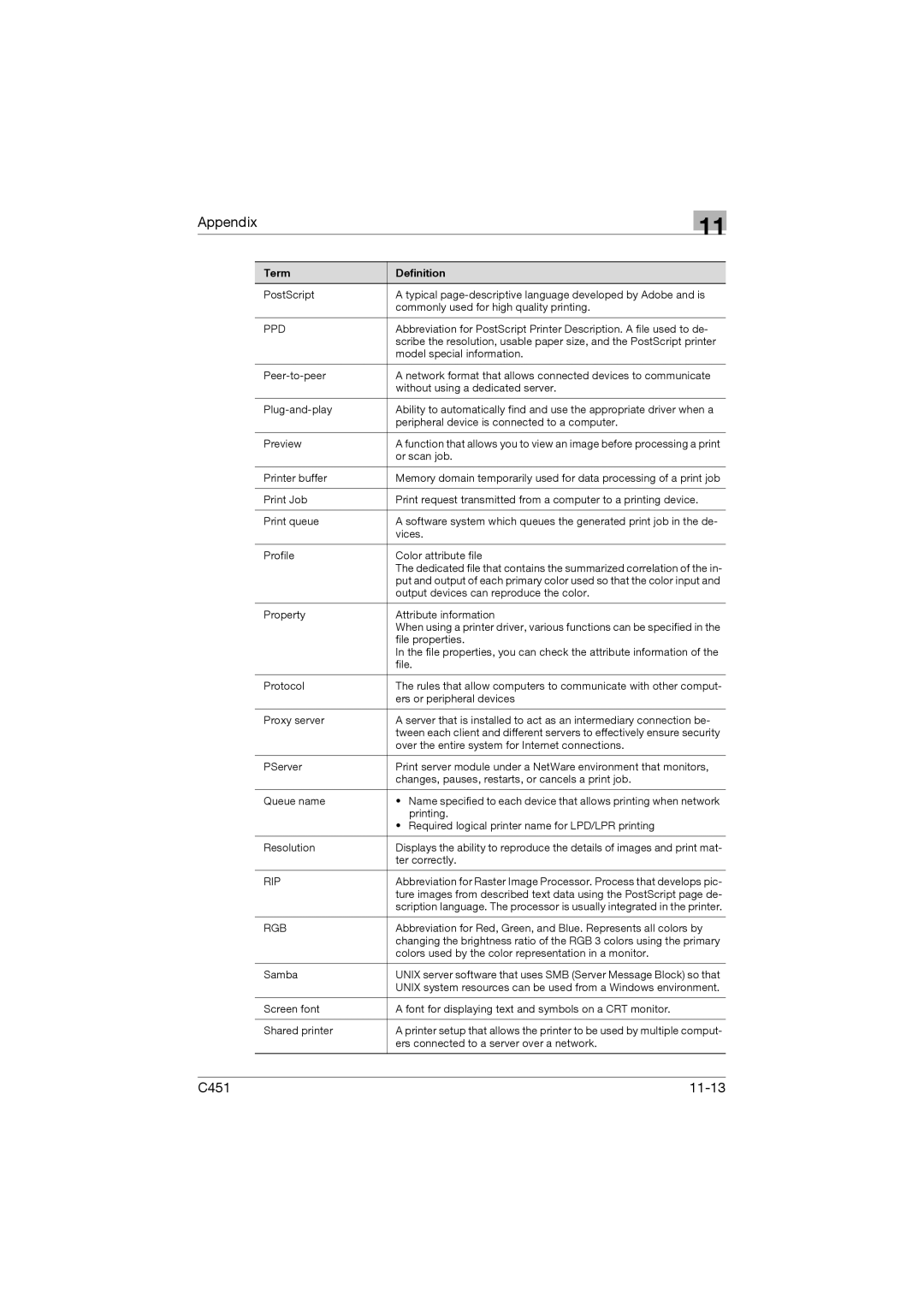
C451 specifications
Konica Minolta's C350, C451, C200, C300, and C353 models represent a significant leap in multifunctional printing technology aimed at enhancing productivity and efficiency in the workplace. These devices are designed to meet the diverse printing, copying, scanning, and faxing needs of businesses while providing high-quality output and advanced features.The Konica Minolta C350 is known for its compact size and exceptional versatility. It offers color printing at speeds of up to 35 pages per minute. With a maximum paper capacity of 3,600 sheets, users can manage larger print jobs without constant replenishment. The C350 is equipped with a user-friendly touchscreen interface, making navigation simple and intuitive. It supports various media types, allowing for flexibility in printing brochures, presentations, and everyday documents.
The Konica Minolta C451 builds on the strengths of the C350 by offering even higher speeds and improved functionality. It boasts a print speed of 45 pages per minute and enhanced color reproduction thanks to advanced imaging technologies. The C451 introduces enhanced security features, including secure printing and user authentication, which are critical for maintaining the confidentiality of sensitive documents.
The C200 model is aimed at smaller offices or workgroups needing reliable color printing without compromising performance. It can print up to 20 pages per minute and incorporates a flatbed scanner for quick and efficient digitization of documents. Its energy-saving mode and low noise levels make it ideal for environments where minimal disruption is essential.
The C300 version takes performance a step further with speeds of up to 30 pages per minute and an improved scanning capability. It offers advanced finishing options, including stapling, hole punching, and booklet making, making it a perfect choice for businesses that require professional quality documents on-demand.
Meanwhile, the C353 is a powerhouse, supporting high-volume printing needs with a speed of up to 35 pages per minute in both color and black-and-white. It combines high-quality printing with a range of advanced features such as mobile printing capabilities through AirPrint and Google Cloud Print, ensuring that users can print directly from their smartphones or tablets.
All these models utilize Konica Minolta's proprietary Simitri HD toner technology, which contributes to sharper images and vibrant colors while being environmentally friendly. Their robust design and push technology for automatic updates ensure that they remain in peak condition and secure.
In summary, the Konica Minolta C350, C451, C200, C300, and C353 models cater to various business needs with their outstanding features, reliable performance, and advanced technologies, making them a worthwhile investment for any organization looking to enhance its document workflow.