Chapter 5 | Configuring the Switch |
The Switch supports a common method of prioritizing layer 3/4 traffic to meet application requirements.. Traffic priorities can be specified in the IP header of a frame using the priority bits in the Type of Service (ToS) octet.. If priority bits are used, the ToS octet may contain six bits for Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) service.. When these services are enabled, the priorities are mapped to a Class of Service value by the Switch and the traffic then sent to the corresponding output queue.. Because different priority information may be contained in the traffic, the Switch maps priority values to the output queues in the following manner:
The precedence for priority mapping is DSCP Priority and then Default Port Priority..
To enable DSCP priority mapping, check the DSCP Priority Status Enabled checkbox..
Priority Status Enables the DSCP priority mapping.. (Enabled is the default setting..)
DSCP to CoS Maps Differentiated Services Code Point values to CoS values..
Click Save Settings to save the changes..
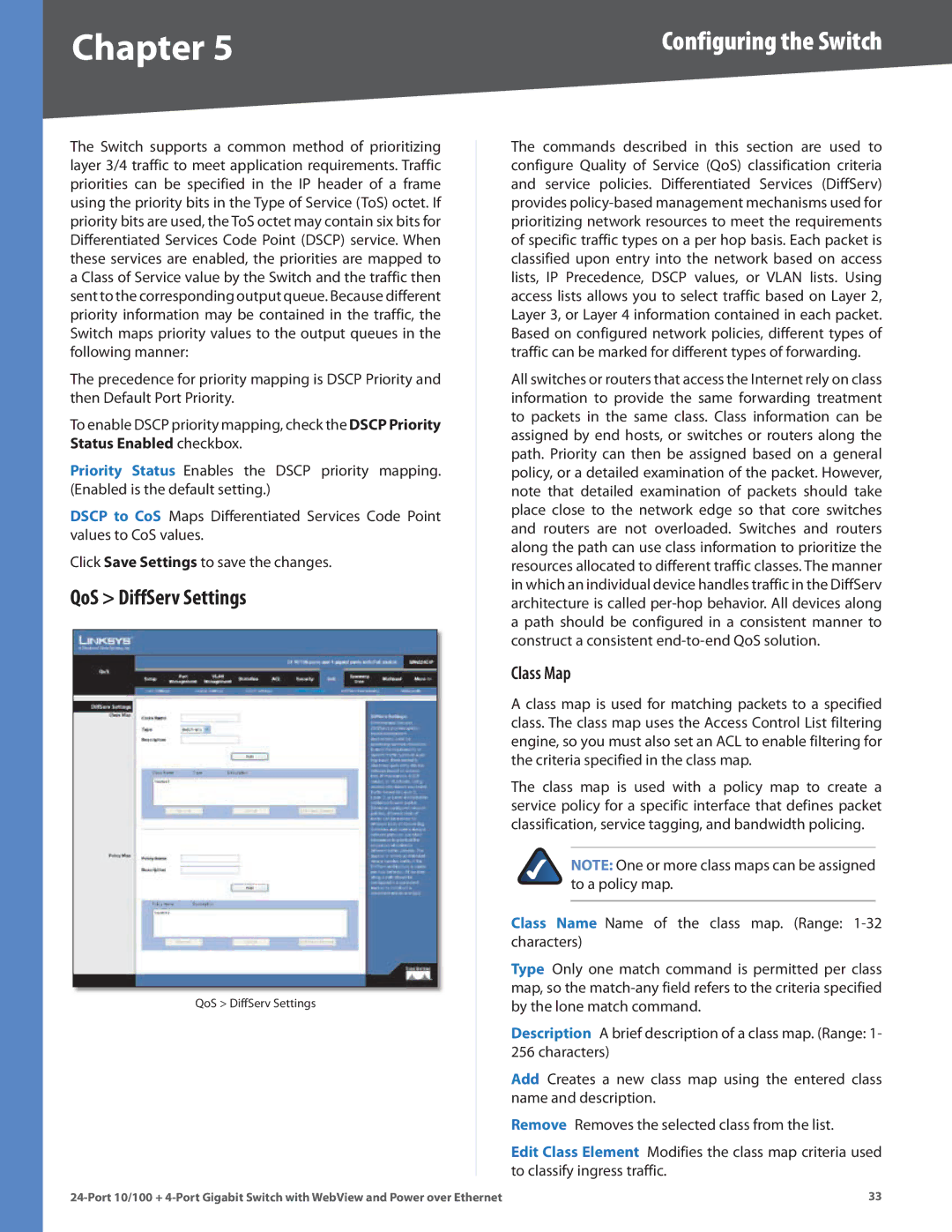
QoS > DiffServ Settings
QoS > DiffServ Settings
The commands described in this section are used to configure Quality of Service (QoS) classification criteria and service policies.. Differentiated Services (DiffServ) provides
All switches or routers that access the Internet rely on class information to provide the same forwarding treatment to packets in the same class.. Class information can be assigned by end hosts, or switches or routers along the path.. Priority can then be assigned based on a general policy, or a detailed examination of the packet.. However, note that detailed examination of packets should take place close to the network edge so that core switches and routers are not overloaded.. Switches and routers along the path can use class information to prioritize the resources allocated to different traffic classes.. The manner in which an individual device handles traffic in the DiffServ architecture is called
Class Map
A class map is used for matching packets to a specified class.. The class map uses the Access Control List filtering engine, so you must also set an ACL to enable filtering for the criteria specified in the class map..
The class map is used with a policy map to create a service policy for a specific interface that defines packet classification, service tagging, and bandwidth policing..
NOTE: One or more class maps can be assigned to a policy map..
Class Name Name of the class map.. (Range:
Type Only one match command is permitted per class map, so the
Description A brief description of a class map.. (Range: 1- 256 characters)
Add Creates a new class map using the entered class name and description..
Remove Removes the selected class from the list..
Edit Class Element Modifies the class map criteria used to classify ingress traffic..
33 |