M68HC08
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
For More Information On This Product
Sensorless Bldc Motor Control Using MC68HC908MR32
Designer Reference Manual Rev
Revision history
List of Sections
List of Sections
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
List of Figures
Title
List of Figures
List of Tables
List of Tables
Contents
Benefits of the Solution
Introduction
Application Functionality
Introduction
System Description
System Concept
System Description
System Specification
Software Specification
Software written in C language specifications are listed
Software parameter tuning to a customer motor
Software Specifications
Hardware and Drive Specifications
High-Voltage Hardware Set Specification
High Voltage Hardware Set Specifications
Motor -Brake Set
Low Voltage Evaluation Hardware Set Specifications
Low-Voltage Evaluation Hardware Set Specification
Low-Voltage Hardware Set Specification
Low Voltage Hardware Set Specifications
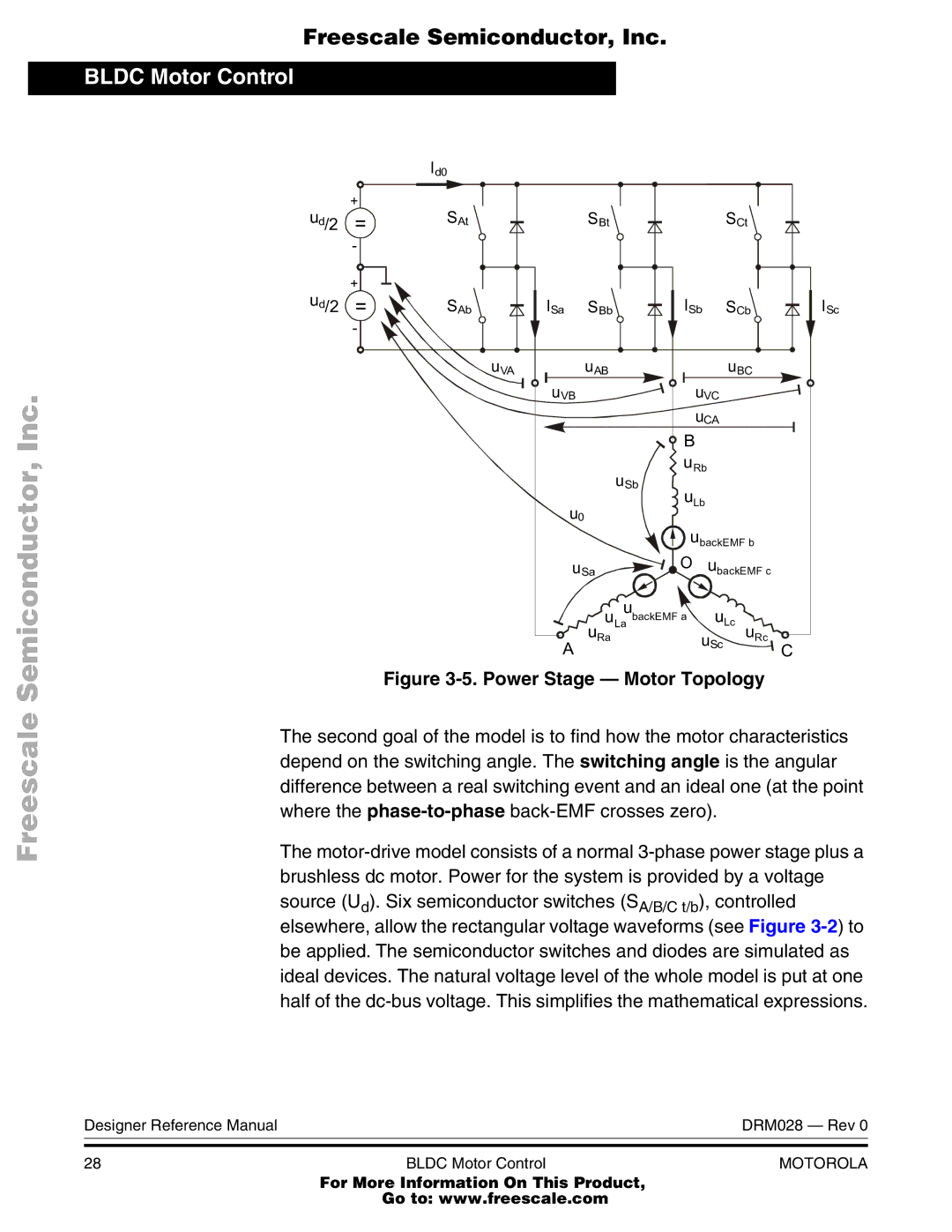
Brushless DC Motor Control Theory
Bldc Motor Control
Bldc Motor Targeted by This Application
Semiconductor, Inc
Bldc Motor Control Brushless DC Motor Control Theory
Bldc Motor Back EMF and Magnetic Flux
2 3-Phase Bldc Power Stage
Why Sensorless Control?
Power Stage Motor Topology
Stator Winding Equations
Indirect Back EMF Sensing
Same expressions can also be found for phase a and B
Phase Voltage Waveform
Effect of Mutual Inductance
Mutual Inductance Effect
Effect of Mutual Phase Capacitance
Detail of Mutual Inductance Effect
Mutual Capacitance Model
10. Distributed Back-EMF by Unbalanced Capacity Coupling
11. Balanced Capacity Coupling Back-EMF Sensing Circuit
Inc
Sensorless Commutation Control
Used Control Technique
Alignment Starting Back-EMF Acquisition Running
14. Commutation Control Stages
Alignment
15. Alignment
Running
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Running Commutation Time Calculation
Commutation time calculation is shown in Figure
Service of received back-EMF zero crossing
17. Bldc Commutation Time with Zero Crossing Sensing
Where
Starting Back-EMF Acquisition
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
18. Vectors of Magnetic Fields
19. Back-EMF at Start Up
Running Commutation Time Calculation, but the following
Starting Commutation Time Calculation
Computation coefficients are different
Speed Control
Application Control
PC Master Software
Communication with PC Master Software Specifications
PC Master Software Communication Commands
PC Master Software API Variables
Name Type Representing Description Range
MotorStatusDef, FailureDef
BIT6 Reserved
BIT2 Reserved
PerSpeedMAXRange and zero crossing period PerZCrosFltT2
SpeedRangeMaxRPM*PerSpeedMAXRange/PerZCrosFltT2
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
System Configuration and Documentation
Hardware Design
MC68HC908MR32 Control Board
For High-Voltage Hardware Set cofiguration
For Low-Voltage Evaluation Motor Hardware Set configuration
EVM Motor Board Phase Low Voltage EVM Bldc Motor
Low-Voltage Hardware Set configuration
Components will describe the individual boards
High-Voltage Hardware Set Configuration
High-Voltage Hardware System Configuration
Manual Motorola document order number
Described in MC68HC908MR32 Control Board User’s
See References
Low-Voltage Evaluation Motor Hardware Set Configuration
Low-Voltage Evaluation Motor Hardware System Configuration
Low-Voltage Hardware Set Configuration
System configuration for low-voltage hardware set is shown
Low-Voltage Hardware System Configuration
References
All HW Sets Components
1 MC68HC908MR32 Control Board
4shows a block diagram of the board’s circuitry
Electrical characteristics in -1apply to operation at 25C
1 3-Phase AC/BLDC High Voltage Power Stage
Electrical Characteristics of Control Board
High-Voltage Hardware Set Components
Phase AC High Voltage Power Stage
Electrical Characteristics of Power Stage
Optoisolation Board
Electrical Characteristics of the Optoisolation Board
Electrical Characteristics
Low-Voltage Evaluation Motor Hardware Set Components
3 3-phase Bldc High Voltage Motor with Motor Brake
EVM Motor Board
Electrical Characteristics of the EVM Motor Board
Electrical Characteristics of the EVM Motor Board
2 3-phase Low Voltage EVM Bldc Motor
Characteristics of the Bldc motor
1 3-Ph AC/BLDC Low Voltage Power Stage
Low-Voltage Hardware Set Components
Block Diagram
2 3-phase Bldc Low Voltage Motor with Motor Brake
Section
Data Flow Main Software Flowchart State Diagram
Software Design
Introduction
Data Flow
Important system variables are listed in Table
Software Variables and Defined Constants
Software Variables
Sys3Def
Start/Stop Switch Reading and Start/Stop Decision
Process Measurement
Main Data Flow Part1 Process Fault Control Fault Stop
Process Back, EMF Zero Crossing Sensing
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Main Data Flow Part 2 Alignment, Starting
Process Desired Speed Setting
Closed Loop Control System
Bldc Speed Control and Calculation
Processes Commutation and Zero Crossing Preset and Set
Process Alignment Control
Main Software Flowchart
Bldc Commutation and Zero Crossing Selection
Main Software Flowchart
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Main Software Flowchart Main Software Loop
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
State Diagram
Software Flowchart Interrupts
Application State Transitions
State diagram for this software is shown in Figure
Initialize MCU
Initialize Application
Stand-By
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Stand-by State
Align State
Starting Commutation Time Calculation
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
10. Back-EMF Acquisition
Set
Service of Commutation
Commutation Time Calculation
Running State
Service of Received Back-EMF Zero Crossing
Explained in 5.5.5 Back-EMF Acquisition State
Over Current
11. Running State
12. Stop State Fault State
Stop State
Implementation Notes
See Figure
Software Files
Software files and structure are described in section
Bldc Commutation and Zero Crossing Selection
Preset Bldc Commutation and Bemf Zero Crossing Selection
Set Bldc Commutation and Bemf Zero Crossing Selection
Bldc Speed Control and Calculation
Desired Speed Calculation
PWM Duty Cycle
PWMValMax = DUTYPWMMAX*MCPWMMODULUS
Timers
Timer
Function TIMACh3Int
Designer Reference Manual DRM028 Rev 108 Software Design
User Guide
Application Suitability Guide
Minimal Application Speed
Motor’s nominal speed
Voltage Closed Loop
Maximal Application Speed
Motor Suitability
Mutual Inductance
Designer Reference Manual DRM028 Rev 112 User Guide
Hardware Configuration
Application Hardware and Software Configuration
Hardware setups are shown in -1, -2,
High-Voltage Hardware Set Configuration
Low-Voltage Evaluation Motor Hardware Set Configuration
Low-Voltage Hardware Set Configuration
Controller Board Settings
EVM board settings are the same for all hardware platforms
EVM Board Settings
Software Setup
Application HC08 Software Files
\bldczerocros08MR32\sources\bldc08.c, main program
Application PC Master Software Control Files
Build
Software Execution
Execute from Evaluation Board
When the software is built, the S-record file
Execute from Pre-programmed MCU
Bldczerocros08mr32MMDS.sx is generated
Application Control
Manual Operating Mode
PC Master Software Remote Operating Mode
PC Master Software Control Window
For More Information On This Product
Tuning for Customer Motor
User Guide Tuning for Customer Motor
Follow-up for Software Customizing to Customer Motor
Follow-up for Advanced Software Customizing
To have PC master software installed on your PC computer
Start the PC master software parameters tuning application
11. PC Master Software Parameters Tuning Control Window
Software Parameters Setting Follow-up
Labels in the File const.h
Software Customizing to Power Stage
Parameters File Selection
\bldczerocros08MR32\sources\constcustlv.h, definitions for
Example of Software Customizing to Hardware
Current Setting Hardware Customizing
Voltage Setting Hardware Customizing
Range 0,infinity
Example of Software Customizing to Hardware
Modified maximal measurable voltage is 55 V, so set
Software Customizing to Motor Voltage and Current Settings
Maximal and Minimal Voltage Limits Setting
Detailed description starts here
Range 0,VOLTRANGEMAX
Maximal and Minimal Current Limits Setting
Range 0,CURRENTRANGEMAXA
Current during alignment state before motor starts Α
Alignment Current and Current Regulator Setting
Range 0,8
Set constcustx.h
Parameters Tuning with PC Master Software Project File
From Evaluation Board
12. PC Master Software Current Parameters Tuning Window
Designer Reference Manual DRM028 Rev 142 User Guide
MUSTCHANGEEXPERnn in file constcustx.h
Commutation Parameters
Commutation time period to discharge coil current ∝s
Start-up Constants and Maximal Commutation Period
Maximal commutation period limit ∝s
Start-up Period
Range -128,127
Alignment Current and Current Regulator Setting 6.5.4.3
Constcustx.h
Constcustx.h Set #define Percmtstartus in constcustx.h
Ensure Percmtstartus =PERCMTMAXUS /2
#define Speedpiregigain
Constcustx.h file
13. PC Master Software Start Parameters Tuning Window
Number of commutations per motor revolution
Software Customizing to Motor Speed Control Setting
Range 0,255
Minimal speed of the drive rpm
Maximal speed range rpm
Range 0,SPEEDRANGEMAXRPM
Speedminrpm = 0.07 to 0.5SPEEDMAXRPM
User Guide 153
Execute from Evaluation Board
Remote Operating Mode
Set PC master software control mode and start motor see
Start motor see Application Control and PC Master Software
PWM Frequency and Current Sampling Period Setting
For the PWM frequency setting, follow the label
PWM frequency setting is provided by
PWM Frequency
PWM period = Periodpwmus = SETPERPWM*2 EQ
PWM Frequency Setting
Current Sampling Period
Conclusion Software Parameters Setting and Tuning
CANCHANGEPERCURSAMPn in const.h file
PERCST1US = Periodpwmus * Setpercs ∝s
Current Sampling Instant
User Guide 159
Designer Reference Manual DRM028 Rev 160 User Guide
Appendix A. References
Motor using MC68HC705MC4 document order number
AN1627, Motorola
Appendix B. Glossary
SG40N
Glossary
Serial communications interface module SCI a module that
Designer Reference Manual DRM028 Rev 166 Glossary
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
HOW to Reach US USA/EUROPE/LOCATIONS not Listed

![]()