AVR Robot Controller 1.1 Hardware Description
R/C servo output
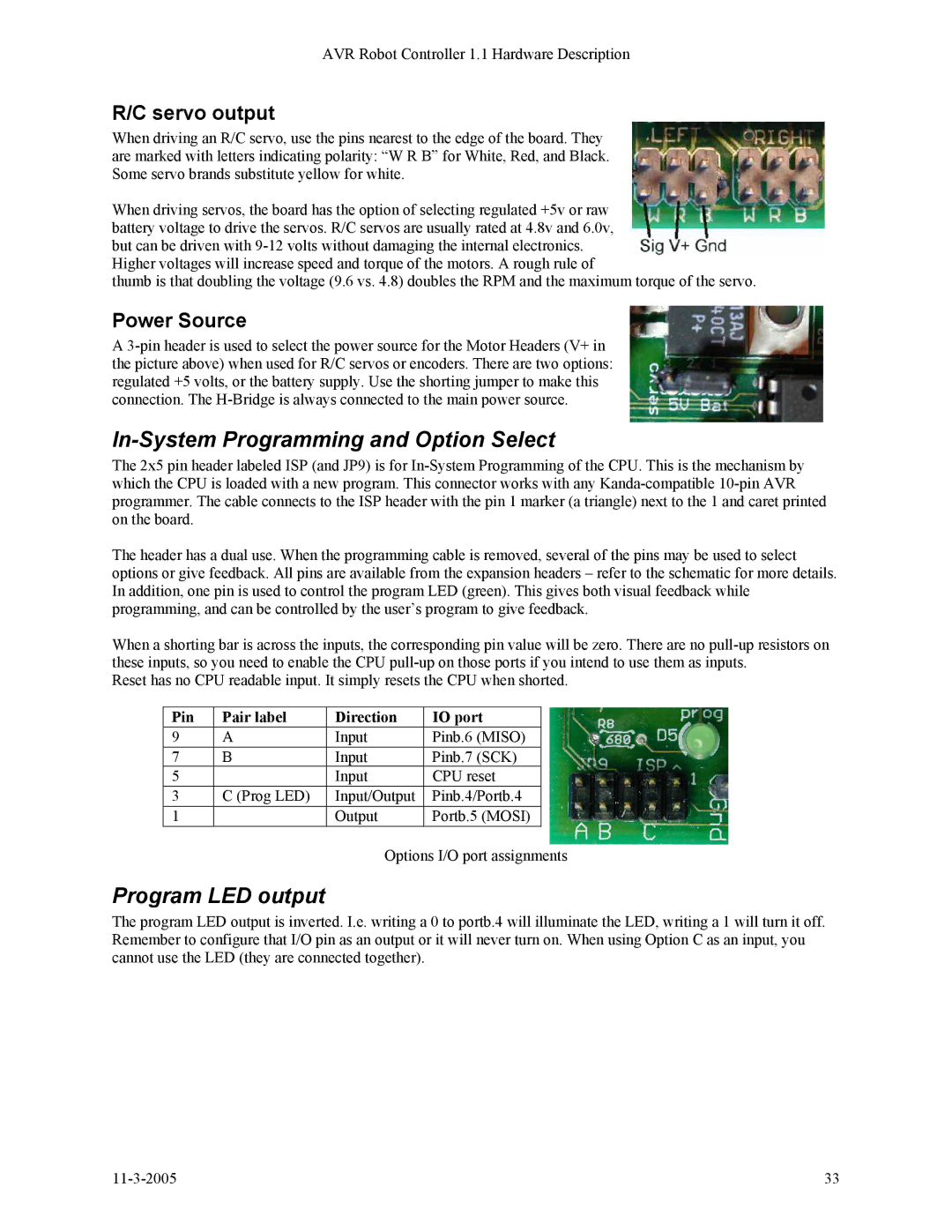
When driving an R/C servo, use the pins nearest to the edge of the board. They are marked with letters indicating polarity: “W R B” for White, Red, and Black. Some servo brands substitute yellow for white.
When driving servos, the board has the option of selecting regulated +5v or raw battery voltage to drive the servos. R/C servos are usually rated at 4.8v and 6.0v, but can be driven with
Higher voltages will increase speed and torque of the motors. A rough rule of
thumb is that doubling the voltage (9.6 vs. 4.8) doubles the RPM and the maximum torque of the servo.
Power Source
A
In-System Programming and Option Select
The 2x5 pin header labeled ISP (and JP9) is for
The header has a dual use. When the programming cable is removed, several of the pins may be used to select options or give feedback. All pins are available from the expansion headers – refer to the schematic for more details. In addition, one pin is used to control the program LED (green). This gives both visual feedback while programming, and can be controlled by the user’s program to give feedback.
When a shorting bar is across the inputs, the corresponding pin value will be zero. There are no
Reset has no CPU readable input. It simply resets the CPU when shorted.
Pin | Pair label | Direction | IO port |
9 | A | Input | Pinb.6 (MISO) |
7 | B | Input | Pinb.7 (SCK) |
5 |
| Input | CPU reset |
3 | C (Prog LED) | Input/Output | Pinb.4/Portb.4 |
1 |
| Output | Portb.5 (MOSI) |
Options I/O port assignments
Program LED output
The program LED output is inverted. I.e. writing a 0 to portb.4 will illuminate the LED, writing a 1 will turn it off. Remember to configure that I/O pin as an output or it will never turn on. When using Option C as an input, you cannot use the LED (they are connected together).
33 |