50CHAPTER 6: USING TRAFFIC PRIORITIZATION
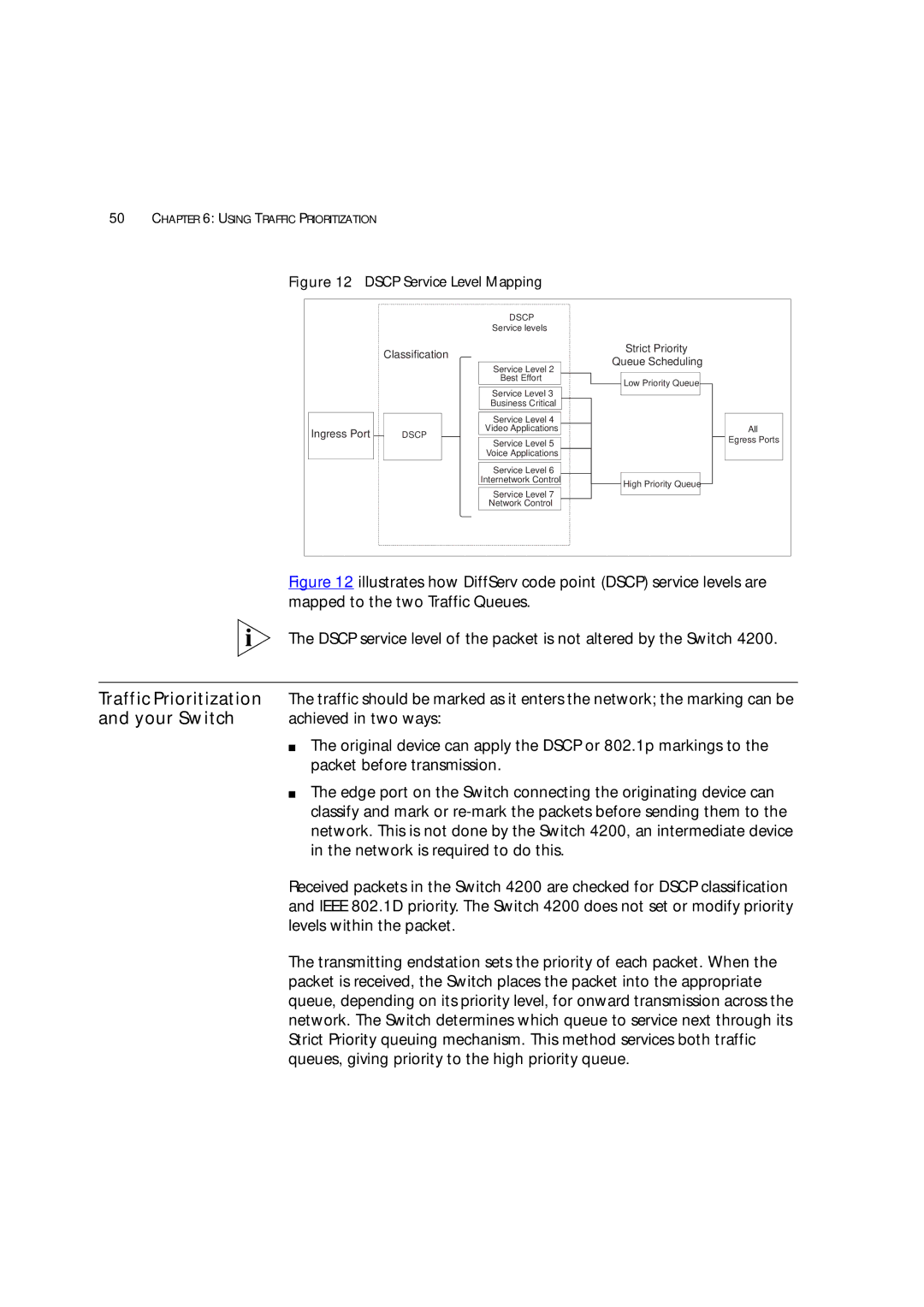
Figure 12 DSCP Service Level Mapping
Ingress Port
Classification
DSCP
DSCP
Service levels
Service Level 2
Best Effort
Service Level 3 Business Critical
Service Level 4
Video Applications
Service Level 5
Voice Applications
Service Level 6
Internetwork Control
Service Level 7
Network Control
Strict Priority
Queue Scheduling
![]() Low Priority Queue
Low Priority Queue
High Priority Queue
All
Egress Ports
| Figure 12 illustrates how DiffServ code point (DSCP) service levels are |
| mapped to the two Traffic Queues. |
| The DSCP service level of the packet is not altered by the Switch 4200. |
|
|
Traffic Prioritization | The traffic should be marked as it enters the network; the marking can be |
and your Switch | achieved in two ways: |
| ■ The original device can apply the DSCP or 802.1p markings to the |
| packet before transmission. |
| ■ The edge port on the Switch connecting the originating device can |
| classify and mark or |
| network. This is not done by the Switch 4200, an intermediate device |
| in the network is required to do this. |
| Received packets in the Switch 4200 are checked for DSCP classification |
| and IEEE 802.1D priority. The Switch 4200 does not set or modify priority |
| levels within the packet. |
| The transmitting endstation sets the priority of each packet. When the |
| packet is received, the Switch places the packet into the appropriate |
| queue, depending on its priority level, for onward transmission across the |
| network. The Switch determines which queue to service next through its |
| Strict Priority queuing mechanism. This method services both traffic |
| queues, giving priority to the high priority queue. |