User’s Guide
Page
Contents
Contents
Basic Operation
Basic Digital Operation
Optimizing Performance
Custom Arb Waveform Generator
Custom Real Time I/Q Baseband
Awgn Waveform Generator
Contents
Xii
Documentation Overview
Key Reference
Signal Generator Models and Features
PSG Signal Generator Models
E8257D PSG Analog Signal Generator Features
E8267D PSG Vector Signal Generator Features
Options Firmware Upgrades
To Upgrade Firmware
GPIB/RS-232 LAN LAN Setup
Swept Signal
Modes of Operation
Continuous Wave
Analog Modulation
Digital Modulation
Standard E8267D Front Panel Diagram
Front Panel
Display
Softkeys
Knob
Amplitude
Trigger
Help
Hardkeys in Front Panel Menus Group
Mod On/Off
RF On/Off
Numeric Keypad
Incr Set
Arrow Keys
Hold
Preset
Line Power LED
Return
Contrast Decrease
Data
Input
Front Panel Display Diagram
Front Panel Display
Active Entry Area
Frequency Area
Annunciators
Interface
Error Message Area
Digital Modulation Annunciators
Amplitude Area
Text Area
Rear Panel
Standard E8267D Rear Panel
E8267D Option 1EM Rear Panel
Standard E8257D Rear Panel
E8257D Option 1EM Rear Panel
Event
Pattern Trig
Auxiliary I/O
Digital BUS
OUT
Bar OUT
GHz REF OUT Serial Prefixes =US4646/MY4646
AC Power Receptacle
Gpib
MHz EFC
ALC Hold Serial Prefixes =US4722/MY4722
Auxiliary Interface Connector
MHz
LAN
MHz OUT
Stop Sweep IN/OUT
RF OUT
EXT
Pulse Sync OUT
Symbol Sync
LF OUT
Basic Operation
Using Table Editors
Press Preset Sweep/List Configure List Sweep
Table Editor Softkeys
Modifying Table Items in the Data Fields
Configuring the RF Output
Configuring a Continuous Wave RF Output
Setting the RF Output Frequency
Setting the Frequency Reference and Frequency Offset
Setting the RF Output Amplitude
Press Frequency 700 MHz More 1 of 3 Freq Ref Set
Configuring a Swept RF Output
Setting the Amplitude Reference and Amplitude Offset
Activating Scalar Pulse in Sweep Configurations
Using Step Sweep
To Configure a Single Step Sweep
To Configure a Continuous Step Sweep
Using List Sweep
To Configure a Single List Sweep Using Step Sweep Data
To Edit List Sweep Points
To Configure a Single List Sweep
Press Edit Item 545 MHz
Press Insert Item -2.5 dBm
Press More 1 of 2 Sweep Trigger Trigger Key
To Configure a Continuous List Sweep
Using Ramp Sweep Option
Using Basic Ramp Sweep Functions
Equipment Setup
Press Frequency Freq CW
Press Freq Start
Using Markers
Marker Table Editor
Press Configure Ramp/Step Sweep
Press Turn Off Markers
Using Alternate Sweep
Press Alternate Sweep Off On to On
Configuring a Ramp Sweep for a Master/Slave Setup
Press Return Sweep Ampl
Basic Operation Configuring the RF Output
Master/Slave Equipment Setup
Modulating a Signal
Extending the Frequency Range
Turning On a Modulation Format
Applying a Modulation Format to the RF Output
To Turn RF Output Modulation On
To Turn RF Output Modulation Off
Using Data Storage Functions
Using the Memory Catalog
Storing Files to the Memory Catalog
Memory Catalog File Types and Associated Data
Using the Instrument State Registers
Viewing Stored Files in the Memory Catalog
Saving an Instrument State
Recalling an Instrument State
Deleting Registers and Sequences
Deleting a Specific Register within a Sequence
Using Security Functions
Deleting All Registers within a Sequence
Deleting All Sequences
Network Analyzer Save and Recall Functions
Understanding PSG Memory Types
Base Instrument Memory
Baseband Generator Memory Options 601
Base Instrument Memory
Purpose/Contents Data Input Method Remarks Type Size
Hard Disk Memory
Removing Sensitive Data from PSG Memory
Erase All
Erase and Overwrite All
Erase and Sanitize All
Using the Secure Mode
Setting the Secure Mode Level
Activating the Secure Mode
Processor Board
Hard Disk
Using the Secure Display
Enabling Options
Enabling a Software Option
Using the Web Server
Proceed With Reconfiguration Confirm Change
Perform the following steps to access the Web Server
Activating the Web Server
Signal Generator Web
Web Page Front Panel
Basic Digital Operation
Custom Modulation
Arbitrary ARB Waveform File Headers
Custom Arb Waveform Generator
Custom Real Time I/Q Baseband
Creating a File Header for a Modulation Format Waveform
Press ARB Setup Header Utilities
Modifying Header Information in a Modulation Format
Custom Digital Modulation Default Header Display
Description key, see 2 on
Also shows the softkey paths used in steps four through nine
ARB Setup Softkey Menu and Marker Utilities
Saved File Header Changes
Press Mode Dual ARB Select Waveform
Modifying Header Information
Viewing Header Information with the Dual ARB Player Off
Viewing Header Information for a Different Waveform File
Seq
Press Return Header Utilities
Waveform is selected saved header settings are applied
Playing a Waveform File that Contains a Header
Using the Dual ARB Waveform Player
Accessing the Dual ARB Player
Press Mode Dual ARB
Creating Waveform Segments
Press Mode Dual ARB Waveform Segments Load Store to Store
Building and Storing a Waveform Sequence
Press Rename Segment Editing Keys Clear Text
Press Done Inserting
Playing a Waveform
Editing a Waveform Sequence
Adding Real-Time Noise to a Dual ARB Waveform
Press Edit Repetitions 200 Enter
Configuring Awgn
Storing and Loading Waveform Segments
Storing Waveform Segments to Non-volatile Memory
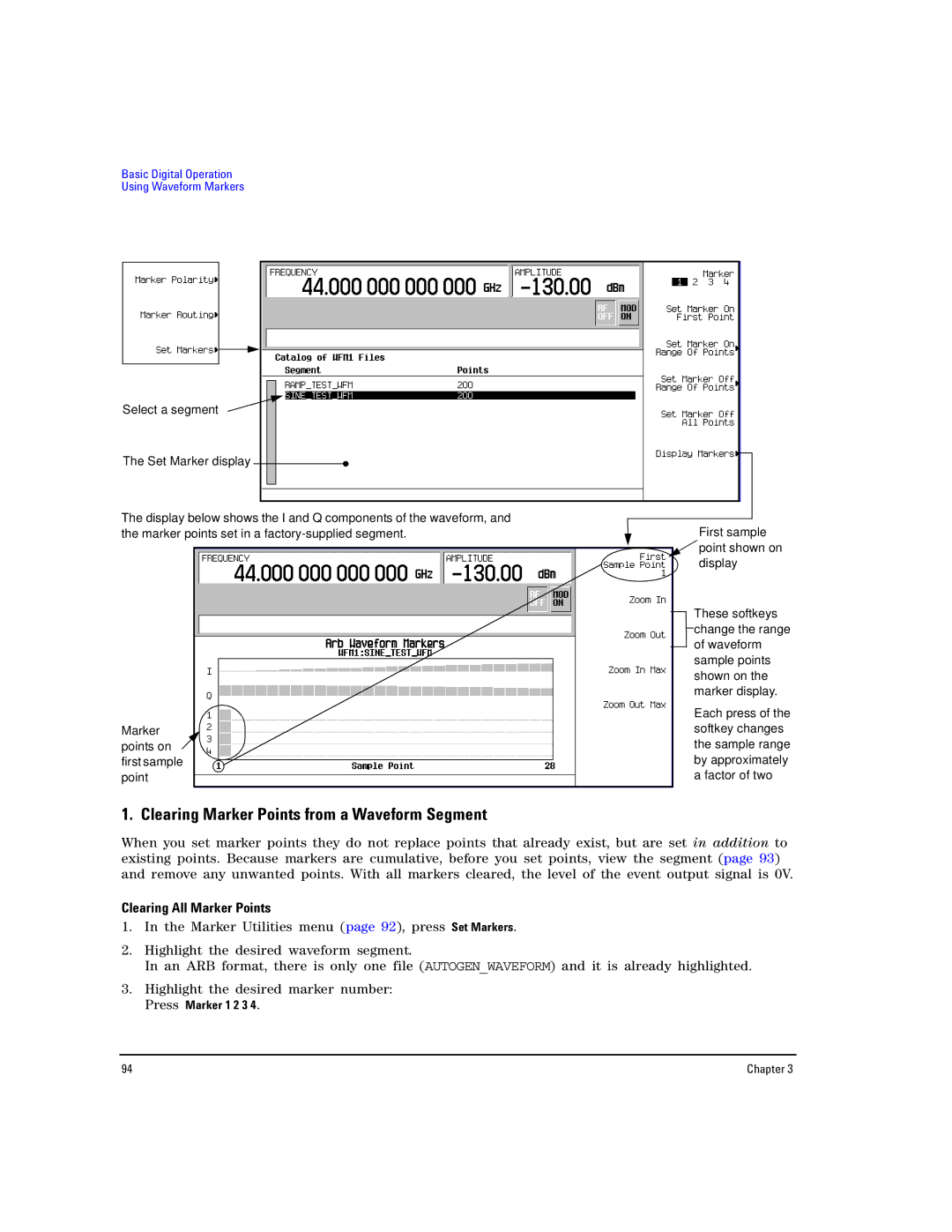
Using Waveform Markers
Renaming a Waveform Segment
Loading Waveform Segments from Non-volatile Memory
Press Load All From Nvwfm Memory
Waveform Marker Concepts
Marker File Generation
Marker Point Edit Requirements
Positive Marker File Bit N
Saving Marker Polarity and Routing Settings
Example of Correct Use
Accessing Marker Utilities
Viewing Waveform Segment Markers
Clearing Marker Points from a Waveform Segment
Clearing All Marker Points
Highlight the desired marker number Press Marker 1 2 3
Setting Marker Points in a Waveform Segment
Clearing a Range of Marker Points
Clearing a Single Marker Point
Placing a Marker Across a Range of Points
Placing a Marker on a Single Point
Placing Repetitively Spaced Markers
Controlling Markers in a Waveform Sequence Dual ARB Only
As You Create a Waveform Sequence
An Existing Waveform Sequence
Press Return Name And Store Enter
Viewing a Marker Pulse
Using the RF Blanking Marker Function
RF Signal
Setting Marker Polarity
Triggering Waveforms
Marker Utilities menu page 92, press Marker Polarity
Mode and Response
Source
Accessing Trigger Utilities
Setting the Polarity of an External Trigger
Using Gated Triggering
Gated Mode
Continuous, Single, or Segment Advance Modes
Press Select Waveform
Press Trigger Gated
Using Segment Advance Triggering
Press Trigger Segment Advance
Press Trigger Source Trigger Key
Using Waveform Clipping
How Power Peaks Develop
Chapter 109
How Peaks Cause Spectral Regrowth
How Clipping Reduces Peak-to-Average Power
Circular Clipping
Chapter 113
Configuring Circular Clipping
Configuring Rectangular Clipping
Press Return Return Clipping
Press Clip I To 80 %
Using Waveform Scaling
How DAC Over-Range Errors Occur
How Scaling Eliminates DAC Over-Range Errors
See
Scaling a Currently Playing Waveform Runtime Scaling
Scaling a Waveform File in Volatile Memory
Using the ALC
Selecting ALC Bandwidth
To Select an ALC Bandwidth
Yes ARB On
Using External Leveling
To Level with Detectors and Couplers/Splitters
Required Equipment
Connect the Equipment
Configure the Signal Generator
Determining the Leveled Output Power
External Leveling with Option 1E1 Signal Generators
Creating and Applying User Flatness Correction
To Level with a mm-Wave Source Module
Press Amplitude Set Atten 45 dB Press Set ALC Level 5 dBm
Configure the Power Meter
Creating a User Flatness Correction Array
Press Configure Step Array
Press Freq Start 1 GHz Press Freq Stop 10 GHz
Perform the User Flatness Correction
Performing the User Flatness Correction Manually
Press # of Points 10 Enter
Press Amplitude More 1 of 2 Ampl Offset
Press More 1 of 2 User Flatness Configure Cal Array
Recalling and Applying a User Flatness Correction Array
Press Load/Store Press Store to File
Press Return Return Flatness Off On to On
Returning the Signal Generator to Gpib Listener Mode
Press Load From Selected File Confirm Load From File
Press Return Flatness Off On to On
Chapter 129
130 Chapter
Chapter 131
Press Amplitude 0 dBm Press RF On/Off
Applying the User Flatness Correction Array
Press Return Return Flatness Off On
Adjusting Reference Oscillator Bandwidth Option UNR/UNX
When using the internal timebase reference
When using an external timebase reference
To Select the Reference Oscillator Bandwidth
To Restore Factory Default Settings
Internal Timebase 125 Hz External Timebase 25 Hz
136 Chapter
Analog Modulation
Analog Modulation Waveforms
Configuring AM Option UNT
Configuring FM Option UNT
Configuring ΦM Option UNT
To Activate FM
To Set the ΦM Deviation and Rate
DC Offset and External FM
Configuring Pulse Modulation Option UNU/UNW
To Activate ΦM
To Set the Pulse Period, Width, and Triggering
To Activate Pulse Modulation
Configuring the LF Output Option UNT
Configuring the Internal Modulation as the LF Output Source
Press FM Dev 75 kHz Press FM Rate 10 kHz
To Configure the LF Output with a Function Generator Source
Configuring the Low Frequency Output
Configuring the Function Generator as the LF Output Source
Configuring the Waveform
Working with Predefined Setups Modes
Overview
Working with User-Defined Setups Modes−Custom Arb Only
Modifying a Single-Carrier Nadc Setup
Press Mode Custom Arb Waveform Generator Setup Select
Custom Digital Mod State
Customizing a Multicarrier Setup
Press Return Digital Modulation Off On
Working with Filters
Recalling a User-Defined Custom Digital Modulation State
Enter
Using a Predefined FIR Filter
Selecting a Predefined FIR Filter
Filter Filter Alpha
Filter Select Gaussian
Using a User-Defined FIR Filter
Restoring Default FIR Filter Parameters
Press Display Impulse Response
Press Load/Store Store To File
150 Chpater
Press Mirror Table
Press Return Display Impulse Response
Press Return Load/Store Store To File
Working with Symbol Rates
To Set a Symbol Rate
To Restore the Default Symbol Rate Custom Real Time I/Q Only
Working with Modulation Types
To Select a Predefined Modulation Type
To Use a User-Defined Modulation Type Real Time I/Q Only
Press More 2 of 2 Display I/Q Map
Press More 1 of 2 Load/Store Store To File
Editing Keys Clear Text
Symbol Data Value
Press More 2
Press .235702 Enter, then .235702 Enter
Edit Keys Clear Text
Differential Wideband IQ Option
Single-Ended Wideband IQ Option 015 Dis
Press I/Q Path Wide Ext Rear Inputs
Configuring Hardware
Press Mode Custom Arb Waveform Generator
Setting for an External or Internal Reference
Setting the External Frequency
Press Ext Delay Time 100 msec
To Set the ARB Reference
Custom Arb Waveform Generator Configuring Hardware
Selecting a Predefined Real Time Modulation Setup
Custom Real Time I/Q Baseband
Deselecting a Predefined Real Time Modulation Setup
Working with Data Patterns
Using a Predefined Data Pattern
Using a User-Defined Data Pattern
Selecting a Predefined PN Sequence Data Pattern
Selecting a Predefined Fixed 4-bit Data Pattern
168 Chapter
Press Mode Custom Real Time I/Q Baseband Data User File
Modifying an Existing Data Pattern User File
Press More 1 of 2 Rename Editing Keys Clear Text
Press Edit File
Press Goto 4 C Enter
Using an Externally Supplied Data Pattern
To Apply Bit Errors to an Existing Data Pattern User File
Press Apply Bit Errors Press Bit Errors 5 Enter
Press Mode Custom Real Time I/Q Baseband Data Ext
Configuring the Burst Rise and Fall Parameters
Using User-Defined Burst Shape Curves
To Create and Store User-Defined Burst Shape Curves
Press More 1 of 2 Display Burst Shape
To Set the BBG Reference
Press Select File
Press Return Custom Off On
To Adjust the I/Q Scaling
To Set the BBG Data Clock to External or Internal
Press Ext BBG Ref Freq
Working with Phase Polarity
To Set Phase Polarity to Normal or Inverted
Working with Differential Data Encoding
Understanding Differential Encoding
Differential Data Encoding
Transmittedbiti= databiti 1 ⊕ databiti
How Differential Encoding Works
Example
Using Differential Encoding
1st Symbol 5th Symbol
1st
Configuring User-Defined I/Q Modulation
Accessing the Differential State Map Editor
Press Configure Differential Encoding
Map QAM 4QAM
Editing the Differential State Map
Press Return Differential Encoding Off On
Multitone Waveform Generator
Creating, Viewing, and Optimizing Multitone Waveforms
To Create a Custom Multitone Waveform
Press Multitone Off On to On
To View a Multitone Waveform
To Edit the Multitone Setup Table
Press Apply Multitone
To Minimize Carrier Feedthrough
Tone Carrier
Intermodulation Carrier Distortion
To Determine Peak to Average Characteristics
Tone Minimized Carrier
Ccdf Plot with Fixed Phase Set
Ccdf Plot with Random Phase Set
Peak Power
194 Chapter
Two-Tone Waveform Generator
Creating, Viewing, and Modifying Two-Tone Waveforms
To Create a Two-Tone Waveform
To View a Two-Tone Waveform
Two-Tone Channels Intermodulation Carrier Distortion
Carrier Feedthrough Distortion
To Change the Alignment of a Two-Tone Waveform
Main Marker Minimized Carrier Feedthrough Delta Marker
Two-Tone
Frequency
Intermodulation Distortion Carrier Frequency
Configuring the Awgn Generator
Configuring the RF Output
Arb Waveform Generator Awgn
Real Time I/Q Baseband Awgn
Generating the Waveform
N5102A Digital Signal Interface Module
Clock Timing
Clock and Sample Rates
Data Setup Menu for a Parallel Port Configuration
Maximum Clock Rates
Least significant bit Most significant bit
Serial Port Configuration Clock Rates
Output Serial Clock Rates
Input Serial Clock Rates
Output Parallel and Parallel Interleaved Clock Rates
Input Parallel and Parallel Interleaved Clock Rates
Clock Source
Common Frequency Reference
PSG Frequency Reference Connections
Baseband GEN REF
Internally Generated Clock Device DUT Supplied Clock
Clock Timing for Parallel Data
Clock Per Sample
Clocks Per Sample
Clock Timing for Parallel Interleaved Data
214 Chapter
Clock Timing for Phase and Skew Adjustments
Clock Timing for Serial Data
Connecting the Clock Source and the Device Under Test
Clock to the device is in the ribbon
Output Mode
Input Mode
Data Types
Operating the N5102A Module in Output Mode
Setting up the Signal Generator Baseband Data
Accessing the N5102A Module User Interface
Maximum Sample Rate for Selected Filter
First-Level Softkey Menu
Selecting the Output Direction
Selecting the Data Parameters
Data Setup Menu Location
Chapter 223
Configuring the Clock Signal
Press the Gain, Offset & Scaling softkey
Chapter 225
If External or Device is Selected
Clocks Per Sample softkey
Clock Source Settings and Connectors
Operating the N5102A Module in Input Mode
Generating Digital Data
Selecting the Input Direction
230 Chapter
Press the Clock Setup softkey, as shown
232 Chapter
Chapter 233
234 Chapter
Chapter 235
Using Agilent Millimeter-Wave Source Modules
Millimeter-Wave Source Modules
Digital Data
Setting Up the External Source Module
Setup for E8257D PSG without Option 1EA
Configuring the Signal Generator
Turn on the signal generator’s line power
Using Other Source Modules
Chapter 241
Toggle the OEM Source Off On softkey to On
RF Output Power Problems
No RF Output Power when Playing a Waveform File
RF Output Power too Low
Power Supply has Shut Down
Signal Loss While Working with a Mixer
Amplitude More 1 of 2 Ampl Offset 0 dB
Effects of Reverse Power on ALC
Mixer
Signal Loss While Working with a Spectrum Analyzer
Reverse Power Solution
Setting ALC Off Mode
Setting Power Search Mode
Press Do Power Search
No Modulation at the RF Output
Sweep Problems
Cannot Turn Off Sweep Mode
Sweep Appears to be Stalled
Incorrect List Sweep Dwell Time
Data Storage Problems
Press Configure Step Sweep
List Sweep Information is Missing from a Recalled Register
Press Recall 99 Enter
Cannot Turn Off Help Mode
Signal Generator Locks Up
Fail-Safe Recovery Sequence
Press Utility Instrument Info/Help Mode
Error Messages
Characteristic Front Panel Display Error Queue
Error Message File
Error Message Format
Error Message Types
Contacting Agilent Sales and Service Offices
Returning a Signal Generator to Agilent Technologies
254 Chapter
Index
Awgn ARB
Custom 143-163,165-184 formats
FAQ
Auxiliary Interface 27 Gpib
260 Index
Index 261
262 Index
Scpi
264 Index
Index 265
266 Index