S T E P 4
Color Correction - Histogram Setting
The data comprising an image contains a variety of brightness settings ranging from shadows to highlights. These settings are represented in
The method is applicable to
How to Interpret Histograms
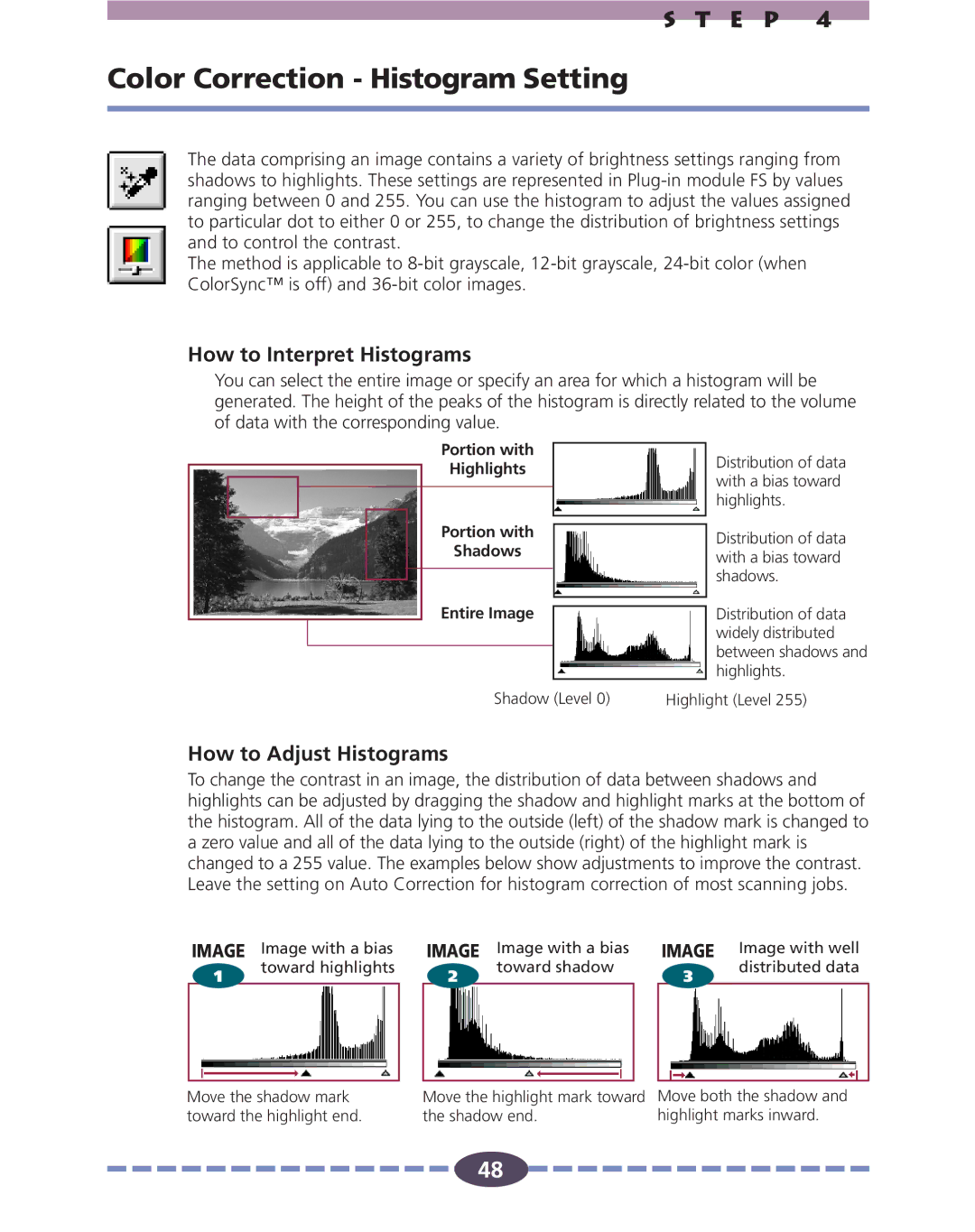
You can select the entire image or specify an area for which a histogram will be generated. The height of the peaks of the histogram is directly related to the volume of data with the corresponding value.
Portion with
Highlights
Portion with
Shadows
Entire Image
Distribution of data with a bias toward highlights.
Distribution of data with a bias toward shadows.
Distribution of data widely distributed between shadows and highlights.
Shadow (Level 0) | Highlight (Level 255) |
How to Adjust Histograms
To change the contrast in an image, the distribution of data between shadows and highlights can be adjusted by dragging the shadow and highlight marks at the bottom of the histogram. All of the data lying to the outside (left) of the shadow mark is changed to a zero value and all of the data lying to the outside (right) of the highlight mark is changed to a 255 value. The examples below show adjustments to improve the contrast. Leave the setting on Auto Correction for histogram correction of most scanning jobs.
IMAGE Image with a bias | IMAGE Image with a bias |
| IMAGE Image with well | ||||
1 | toward highlights | 2 | toward shadow | 3 | distributed data | ||
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Move the shadow mark | Move the highlight mark toward |
toward the highlight end. | the shadow end. |
Move both the shadow and highlight marks inward.
48
![]()
![]()
![]() 48
48![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()