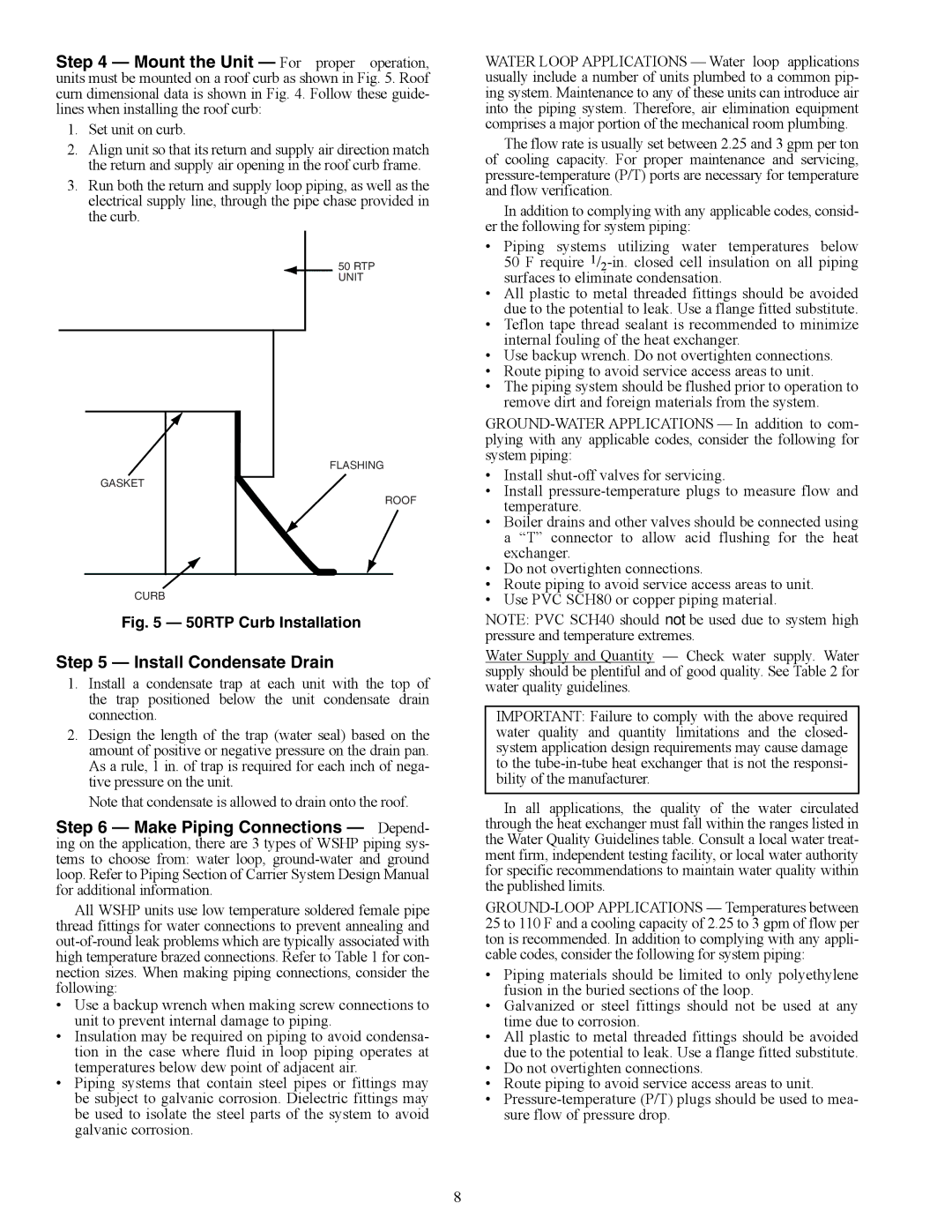
Step 4 — Mount the Unit — For proper operation, units must be mounted on a roof curb as shown in Fig. 5. Roof curn dimensional data is shown in Fig. 4. Follow these guide- lines when installing the roof curb:
1.Set unit on curb.
2.Align unit so that its return and supply air direction match the return and supply air opening in the roof curb frame.
3.Run both the return and supply loop piping, as well as the electrical supply line, through the pipe chase provided in the curb.
50 RTP
UNIT
FLASHING
GASKET
ROOF
CURB
Fig. 5 — 50RTP Curb Installation
Step 5 — Install Condensate Drain
1.Install a condensate trap at each unit with the top of the trap positioned below the unit condensate drain connection.
2.Design the length of the trap (water seal) based on the amount of positive or negative pressure on the drain pan. As a rule, 1 in. of trap is required for each inch of nega- tive pressure on the unit.
Note that condensate is allowed to drain onto the roof.
Step 6 — Make Piping Connections — Depend- ing on the application, there are 3 types of WSHP piping sys- tems to choose from: water loop,
All WSHP units use low temperature soldered female pipe thread fittings for water connections to prevent annealing and
•Use a backup wrench when making screw connections to unit to prevent internal damage to piping.
•Insulation may be required on piping to avoid condensa- tion in the case where fluid in loop piping operates at temperatures below dew point of adjacent air.
•Piping systems that contain steel pipes or fittings may be subject to galvanic corrosion. Dielectric fittings may be used to isolate the steel parts of the system to avoid galvanic corrosion.
WATER LOOP APPLICATIONS — Water loop applications usually include a number of units plumbed to a common pip- ing system. Maintenance to any of these units can introduce air into the piping system. Therefore, air elimination equipment comprises a major portion of the mechanical room plumbing.
The flow rate is usually set between 2.25 and 3 gpm per ton of cooling capacity. For proper maintenance and servicing,
In addition to complying with any applicable codes, consid- er the following for system piping:
•Piping systems utilizing water temperatures below 50 F require
•All plastic to metal threaded fittings should be avoided due to the potential to leak. Use a flange fitted substitute.
•Teflon tape thread sealant is recommended to minimize internal fouling of the heat exchanger.
•Use backup wrench. Do not overtighten connections.
•Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
•The piping system should be flushed prior to operation to remove dirt and foreign materials from the system.
•Install
•Install
•Boiler drains and other valves should be connected using a “T” connector to allow acid flushing for the heat exchanger.
•Do not overtighten connections.
•Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
•Use PVC SCH80 or copper piping material.
NOTE: PVC SCH40 should not be used due to system high pressure and temperature extremes.
Water Supply and Quantity — Check water supply. Water supply should be plentiful and of good quality. See Table 2 for water quality guidelines.
IMPORTANT: Failure to comply with the above required water quality and quantity limitations and the closed- system application design requirements may cause damage to the
In all applications, the quality of the water circulated through the heat exchanger must fall within the ranges listed in the Water Quality Guidelines table. Consult a local water treat- ment firm, independent testing facility, or local water authority for specific recommendations to maintain water quality within the published limits.
•Piping materials should be limited to only polyethylene fusion in the buried sections of the loop.
•Galvanized or steel fittings should not be used at any time due to corrosion.
•All plastic to metal threaded fittings should be avoided due to the potential to leak. Use a flange fitted substitute.
•Do not overtighten connections.
•Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
•
8