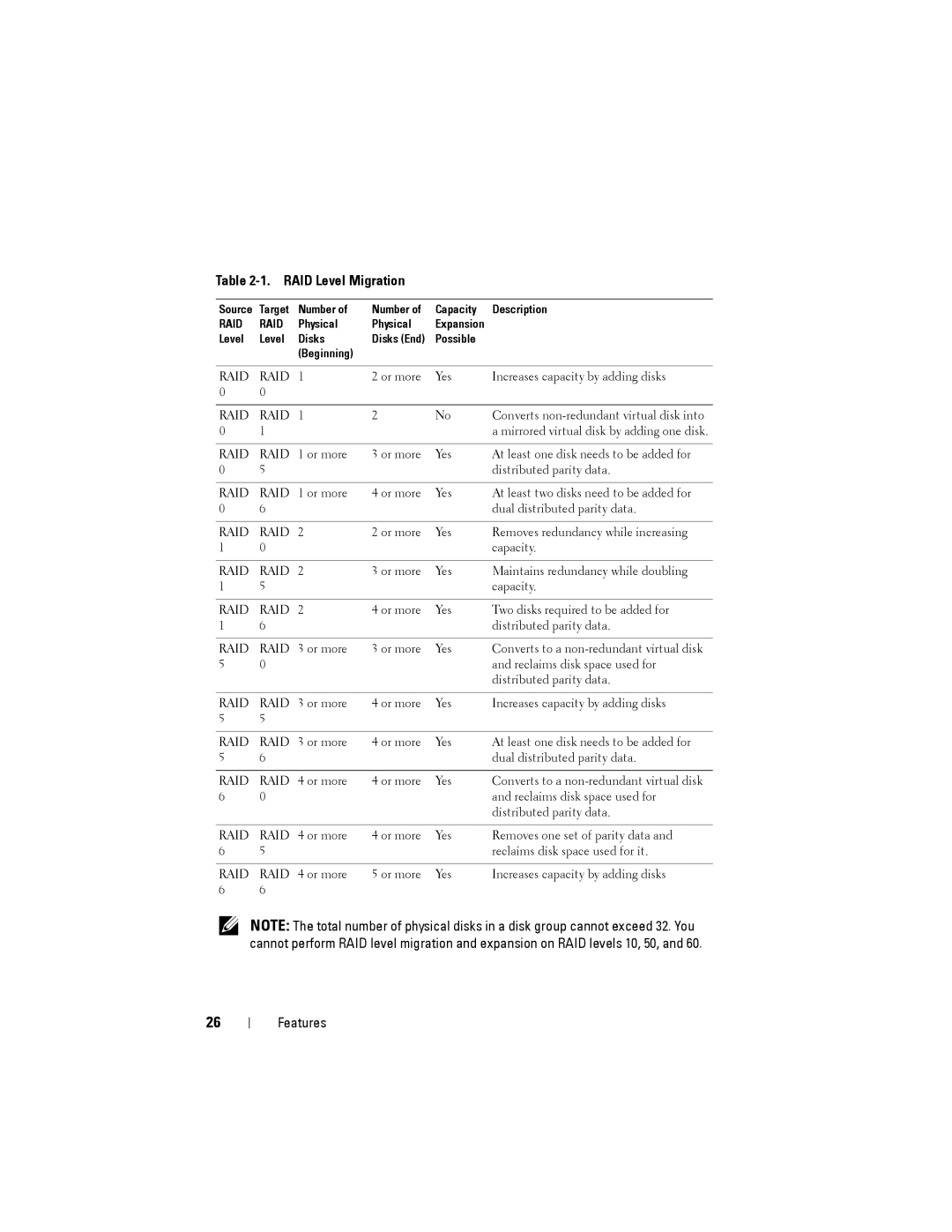
H310, H710, H710P, H810 specifications
Dell offers a range of storage controller technologies, notably the H810, H710, H710P, and H310, which cater to different enterprise needs. These controllers are designed to support various storage configurations, enhancing overall system performance and reliability.The Dell H810 is a high-performance PCIe 3.0 RAID controller that supports up to eight internal drives and is particularly suited for demanding workloads. It features advanced RAID levels including RAID 0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, and 60, providing flexibility for various data protection strategies. The H810 also supports up to 32TB of storage capacity, making it suitable for environments that require substantial data management capabilities.
The H710 is another powerful RAID controller, widely recognized for its balance of performance and cost-efficiency. It features 1GB of cache memory, which aids in accelerating read and write operations. The H710 supports the same RAID levels as the H810 and allows for up to 512MB of non-volatile memory. This ensures data integrity even in the event of a power failure, making it reliable for critical applications.
The H710P is an enhanced version of the H710, with a significant upgrade in its cache capabilities. It offers 2GB of battery-backed cache memory, further enhancing data processing speeds and improving responsiveness. The H710P is ideal for intensive workloads and virtualization, where rapid access to data is essential. This controller also includes features such as RAID storage pooling, intelligent data tiering, and support for multiple virtual disks.
Finally, the H310 is a cost-effective option for small to medium-sized businesses or those with less demanding storage requirements. It offers similar RAID support as the higher-end controllers but operates with a simpler architecture. The H310 features 512MB of cache, providing sufficient performance for regular workloads without the additional complexities of more advanced controllers.
In summary, Dell's H810, H710, H710P, and H310 storage controllers each serve distinct purposes, providing various features, technologies, and performance characteristics tailored to different business needs. From high-capacity storage solutions to user-friendly setups, Dell’s offerings ensure that organizations can efficiently manage their data storage requirements.