HP 10bII+ Financial Calculator User’s Guide
HP Part Number NW239-90001 Edition 1, May
Legal Notice
HP 10bII+ Financial Calculator
Keyboard Map Legend
Number
Table of Contents
Page
Page
III
At a Glance
JGD
Basics of Key Functions
Shift Keys
Boxed Key Functions
Percentages
Jj7V1
JV§4
Add 15% to
DDÃ
JVÀ
GG¼
Memory Keys
GV4
GG4
J7GV
JYÏ
JG\Í
DSÙ
Time Value of Money TVM
TVM What if
JyÌ
D7VÒ
How much can you borrow at a 9.5% interest rate?
Amortization
Jæjg
Amortize the 1 st through 24 th loan payments
Depreciation
Interest Rate Conversion
\½\«
Cash Flows, IRR/YR, NPV, and NFV
JÆG¤
Yy¤
Yj¤
GD¤
VG4
G7GgGJ
Date and Calendar
Bonds
Y7jVÔ
S7jVÎ
For more information on bond calculations, refer to , Bonds
Break-even
\h \«
\k \«
\T \«
\e \«
SÆJS¡
GÆV¡
YÆd¡
\T\«
17GV4
\5V
7VF
Probability
Trigonometric Functions
7SG
Find Sin θ =.62 in degrees. If RAD is displayed, press
Convert the results to radians using Pi
\aJg
At a Glance
Manual Conventions and Examples
Power On and Off
Getting Started
Displayed text
Item before the / is the alternate
Shift Keys
Simple Arithmetic Calculations
GY7jJ1SG7Yj4
JdPJG7Sg4
Operating Modes
S7dPV7DVa
Calculations in Chain Mode
1JJV7V4
7dJ4
Da\qgVA
Calculations in Algebraic Mode
Using Parentheses in Calculations
JG\n
Understanding the Display and Keyboard Cursor
JVy
AD4
Clearing the Calculator
Clear All
Annunciators
Clearing Messages
INV
Statistics Keys
Input Key
Swap Key
Same as pressing
Math Functions
Gd7GV\B
D7Vj1G7DS\b
One-Number Functions
Getting Started
J1SC
\5Y
JVc
7DVoR
YP\
A7SGoR
\5G
PY7V\2
Two-Number Functions
J7GVrc
17VdrC
In-line Functions
Gd\¨
Jj\¨
JjÆ
Gd1DD
Arithmetic with One-and Two-number Functions
-23below lists the two-number functions of the calculator
G7V\K
JGV\QD4
GG1JY\¨
VAJ7GV4
\Qv4
Last Answer
7JGVS4
\5D
YV7SP
Specifying Displayed Decimal Places
\54
Jaj4
\zyJG
D7gjSVYD
Messages
Business Percentage Keys
GV§
Business Percentages
Percent key
DJS7g4
JGV1j§
GdJ7j\¨
Jgpvæ
Margin and Markup Calculations
Gvvà
JdÀ
Margin Calculations
D7SÀ
Using Margin and Markup Together
JVÃ
V1Gª
Using Stored Numbers in Calculations
Using Constants
Number Storage and Storage Register Arithmetic
Example Calculate 10 + 10%, 11 + 10%, and 25 + 10%
J1J§ª
\QDª
Example Calculate 23
VV\¨DGª
Using the M Register
YV4
JY7GVm
Using Numbered Registers
Jjs
JS7dVm
VS7J1
YjV7S
\w7Y ADd7JV \wG
V7Y
G7V
YV7j \wD
\wPD
Picturing Financial Problems
How to approach a Financial Problem
Simple and Compound Interest
Signs of Cash Flows
Periods and Cash Flows
Simple Interest
Interest Rates
Compound Interest
Two Types of Financial Problems
Recognizing a TVM Problem
Recognizing a Cash Flow Problem
Cash flow diagram Borrower’s perspective
Cash flow diagram Investment in a mutual fund
Time Value of Money Calculations
Using the TVM Application
TVM Keys
Begin and End Modes
Loan Calculations
Jyva
Dpjgù
J7VÒ
JVÏ
DjVyÌ
1VÌ
1JV4
DDyÌ
J7VÒ
1JG4
JjGVÏ
GV\Ú
G7gÒ
1vÌ4
YgÙ
Savings Calculations
GyÏ
J7GÒ
GY\Í
GyÌ
JV\Ú
S7DÒ
YyÏ
Cash flow diagram Calculate the monthly lease payment
Lease Calculations
Cash flow diagram Calculate PV of the lease
JVÉ
1vÌy4
YjÙ
GYyÌ
Step Find the present value of the buy option
1p4
JVyÉ
Step Add the results of ’ ’ and ’ ’
To Amortize
Amort key on the HP 10bII+ allows you to calculate
J7jVÒ
JJ7VÒ
Jdægy
Jygvï
VYÆ
GVÆ
Amortize the 1st, 25th, and 54th payments
Investments With Different Compounding Periods
S7j\Ó
Interest Rate Conversions
First Bank
DS\Í
S7SV\Ó
S7SD\Ó
Compounding and Payment Periods Differ
DSV\Í
GVyÌ
Resetting the TVM Keys
Depreciation
Depreciation Keys
Item in the selected format
Inputs 5 for the expected useful life
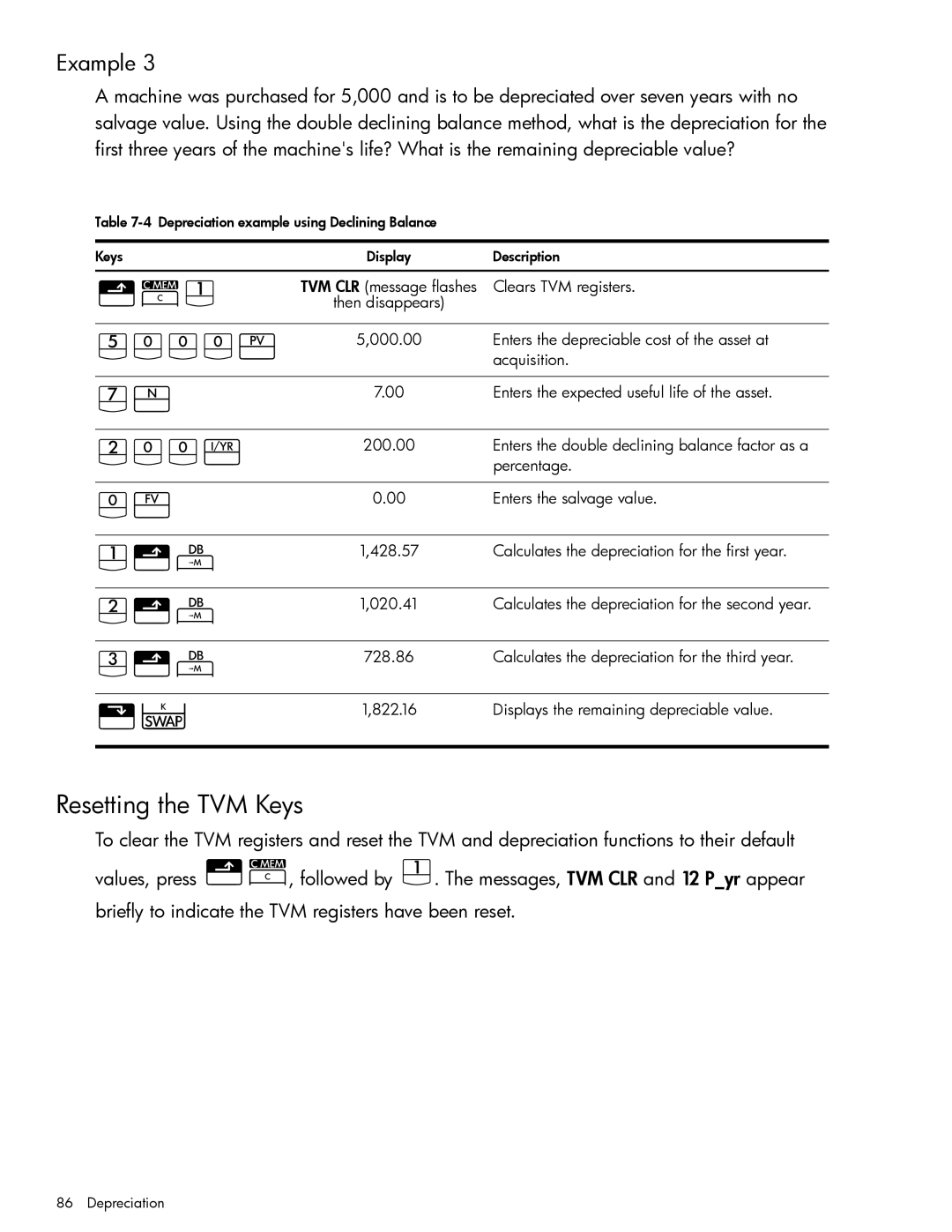
Depreciation example using Declining Balance Keys
How to Use the Cash Flow Application
Cash Flow Calculations
Clearing the Cash Flow Memory
Number1 ¤
Cash Flow Calculations
Gy¤
Vy¤
Calculating Internal Rate of Return
NPV and IRR/YR Discounting Cash Flows
JJjSV7Gd¤
AJG
Organizing Cash Flows
JJy¤
Initial cash flow and cash flow groups
Viewing and Editing Cash Flows
11GÆ
1JGyÆ1G
JVÆ1GÆ
Calculating Net Present Value and Net Future Value
VÆJ¤
ÆY¤
VÆG¤
JÆJ¤
JVÆJ¤
Æd¤
JVÒ
Cash flow diagram Calculates NPV
Automatic Storage of IRR/YR and NPV
Calendar Format
Calendar Formats and Date Calculations
Date Format
Using the Input key
Date Calculations and Number of Days
Date Calculation
\ÇJ4
To enter the data for this example using the Ækey
JG7JgGJJ
ÆJ\Ç
DJ7JGJ4
\5S
Y7SGJ\Ä
J7JjGJG
J7JjGJGÆ
Using the Ækey
S7YGJV\Ä
Bonds
Bond Keys
Y7GgGJ
JYË
S7YGG
V7VÎ
JJÑ
J7JVGG
Resetting the bond keys
Y7JVGJG
Break-even
Break-even Keys
Break-even example
Calculating the projected maximum fixed cost
Resetting the Break-even keys
\e\«
\k\«
\h\«
\Z\«
Clearing Statistical Data
Entering Statistical Data
Two-Variable Statistics and Weighted Mean
One-Variable Statistics
Viewing and Editing Statistical Data
DVÆVJV¡
DGÆYJV¡
YD\W\5G
DjÆSgV¡
YDÆJGD¡
YV\W
Summary of Statistical Calculations
D7V¡
Y7V¡
D7GV¡
D7jV¡
JjjÆgD¡
JdDÆd¡
JgGÆgJ¡
JgVÆjj¡
400
DÆJJ¡ VÆGGSV¡
GÆJY¡
JÆdG¡
VÆGgd¡
Weighted Mean
VJÆgg¡
VÆVY¡
VVÆDG¡
VJSÆdG¡
Factorial
Probability Calculations
Permutations
V9D4
VD4
VÆD
VÆD9
YG\w6
Advanced Probability Distributions
J7jyF
Normal Lower Tail Probability
7GVoF
Inverse of Normal Lower Tail Probability
GÆJ7gSyI
GIJ7gSy4
Students T Probability Lower Tail
GSÆ7VoI
GSoI7V4
Inverse of Student’s t Probability Lower Tail
Y1J4
Conversions from Lower Tail
J7GyF
PG4
Returns desired value of z
Statistical Calculations
Additional Examples
Setting a Sales Price
\qJ1\q GaJ4
Business Applications
DÆJDS¡
JÆJ¡
GÆJJGJ¡
YÆJSjV¡ VÆGVd¡
\qDA
Gpdspj
\q\qJ AG\n
YVsPJ§
AJPJ4
Jg§
YVjG7gy
Yield of a Discounted or Premium Mortgage
G7VÒ
VÙAYGÙ
JdyÏ
Annual Percentage Rate for a Loan With Fees
JGÒ
JSÏ
AG§Ï
AD§Ï
YV\Ǥ4
AJGP
JSaDP
1YVÏ
PvÙ4
Jgvï
D7VÒ
Jjvï
ÉD\Ú
JG\Ó
JDÏ
Canadian Mortgages
DVVVyÌ
JJ7GÒ
What if … TVM Calculations
VÏ4
GS\Í
PvÙ1
Savings
Stores effective rate as annual
Jyyù
Gains That Go Untaxed Until Withdrawal
PJV§4
DVÙ
Yòìï
Cash Flow Examples
G7JjVAGg
DyÌ
Wrap-Around Mortgages
Cash flow diagram Wrap-around mortgage
GGVJ7GG
GG\¥
DVy¤
VÌyAjVY
VÌy¤
Installing Batteries
Power and Batteries
Low Power Annunciator
Appendix a Batteries and Answers to Common Questions
Calculator won’t turn on
Determining if the Calculator Requires Service
Resetting the calculator
Erasing the calculator’s memory
See Determining If the Calculator Requires Service
Answers to Common Questions
Environmental Limits
IRR/YR Calculations
Appendix B More About Calculations
Equations
Amortization
Payment Mode Factor S = 0 for End mode 1 for Begin mode
Time Value of Money TVM
Interest Rate Conversions
Cash-Flow Calculations
Bonds
For more than one coupon period to redemption
Depreciation
Statistics
Forecasting
Cashflow memory was cleared
Appendix C Messages
Memory has been erased Ch
Tvm registers were cleared
Bond registers were cleared
Statistical memory and registers were cleared
Limited Hardware Warranty Period
Warranty, Regulatory, and Contact Information
HP Limited Hardware Warranty and Customer Care
Replacing the Batteries
General Terms
Exclusions
Modifications
Avis Canadien
Canadian Notice
European Union Regulatory Notice
Germany
Perchlorate Material special handling may apply
Customer Care Contact Information
香港特別行
ไทย
Tobago Tunisia Turkey Türkiye Turks 01-800-711-2884
Warranty, Regulatory, and Contact Information
Warranty, Regulatory, and Contact Information
Chain mode
Advance payments Algebraic mode
Battery
Error messages Factorial
Keyboard
In-line functions Interest
Interest rate conversions Investments
Keys
Modes
Trigonometric functions Troubleshooting
Warranty
Operating modes Parentheses