Scanning Channels
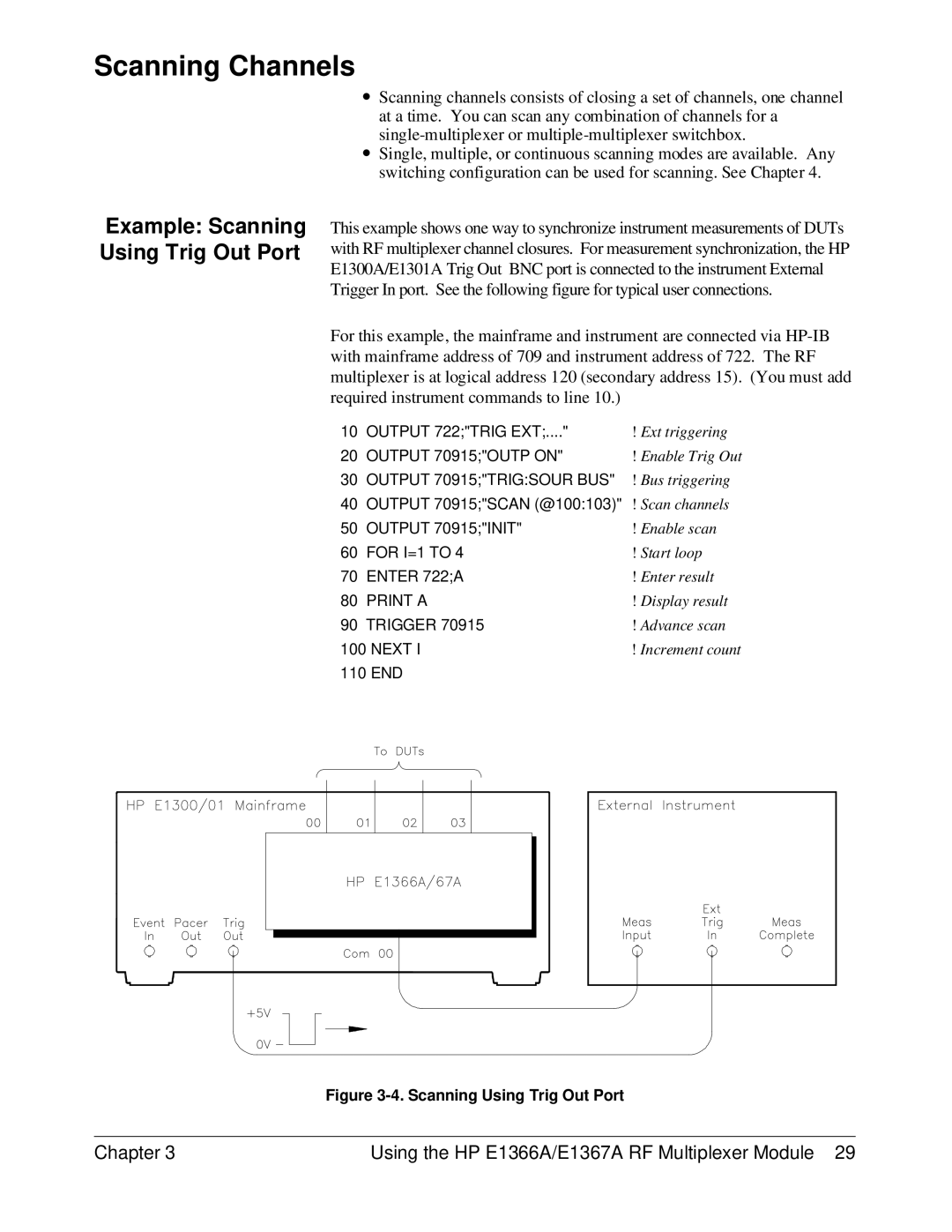
Example: Scanning Using Trig Out Port
∙Scanning channels consists of closing a set of channels, one channel at a time. You can scan any combination of channels for a
∙Single, multiple, or continuous scanning modes are available. Any switching configuration can be used for scanning. See Chapter 4.
This example shows one way to synchronize instrument measurements of DUTs with RF multiplexer channel closures. For measurement synchronization, the HP E1300A/E1301A Trig Out BNC port is connected to the instrument External Trigger In port. See the following figure for typical user connections.
For this example, the mainframe and instrument are connected via
10 | OUTPUT 722;"TRIG EXT;...." | ! Ext triggering |
20 | OUTPUT 70915;"OUTP ON" | ! Enable Trig Out |
30 | OUTPUT 70915;"TRIG:SOUR BUS" | ! Bus triggering |
40 | OUTPUT 70915;"SCAN (@100:103)" | ! Scan channels |
50 | OUTPUT 70915;"INIT" | ! Enable scan |
60 | FOR I=1 TO 4 | ! Start loop |
70 | ENTER 722;A | ! Enter result |
80 | PRINT A | ! Display result |
90 | TRIGGER 70915 | ! Advance scan |
100 NEXT I | ! Increment count | |
110 END |
| |
Figure 3-4. Scanning Using Trig Out Port
Chapter 3 | Using the HP E1366A/E1367A RF Multiplexer Module 29 |