Page
AN/USM-459 HEWLETT-PACKARD Model 5328A/E42 NSN
Page
TM 11-6625-2941-14 + P
I b l a n k
Page
Table of Contents
Installation
Model 5328A Table of Contents
Theory of Operation
L l
Table of Contents Section
Vll
Appendix A. References
List of Tables
Model 5328A List of Tables
List of Figures
Remote Controllable Programmable Input Block Diagram
Vii
F E T Y C O N S I D E R a T I O N S General
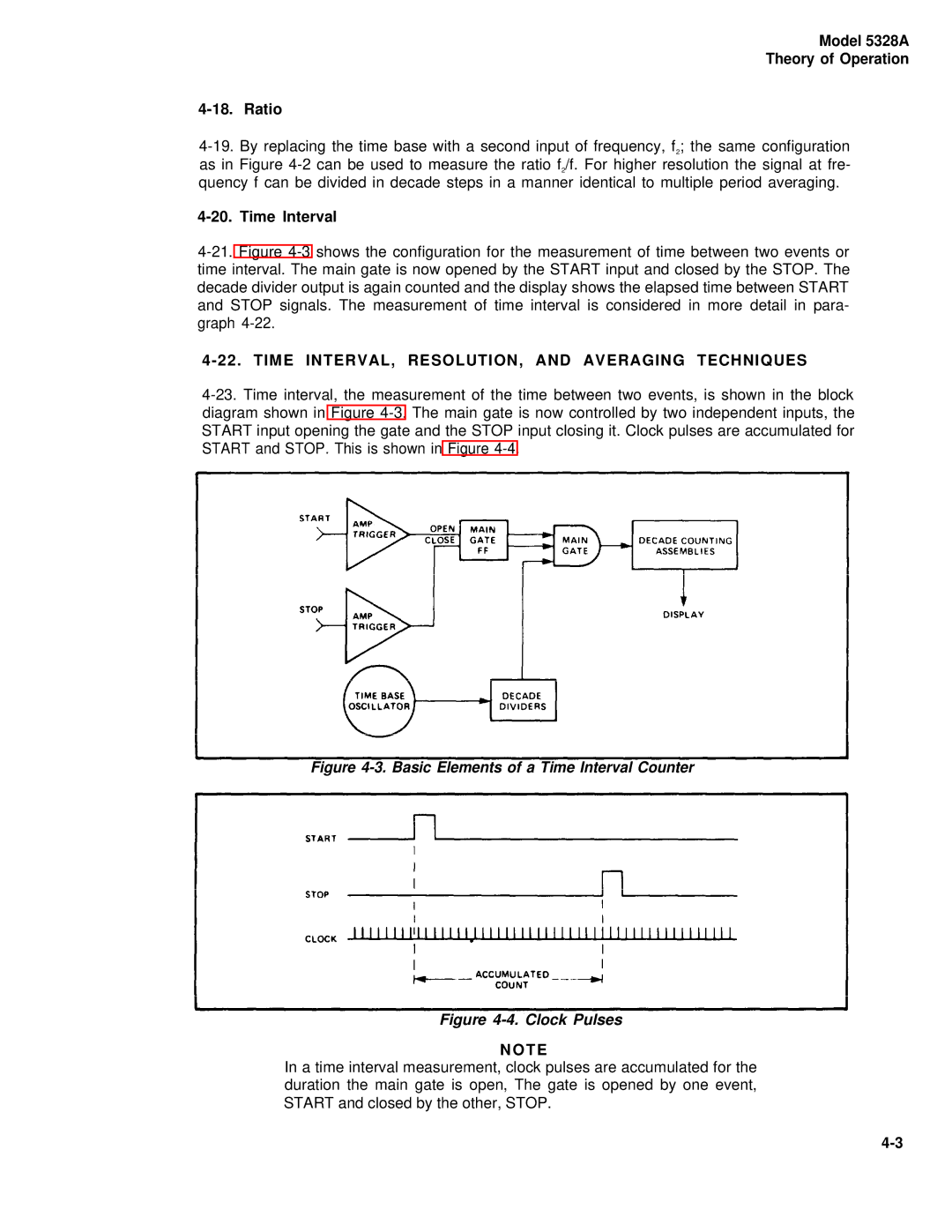
Model 5328A Safety Considerations
Service
Operation
Model 5328A Safety Considerations
Model 5328A General Information
Model 5328A 500 MHz Universal Frequency Counter
Indexes of Publications
Administrative Storage
Section O Introduction
Forms and Records
Page
Description
Model 5320A General Information
C T I O N N E R a L I N F O R M a T I O N Scope of Manual
Instrument Identification
Accessories Available
Equipment Supplied
5328A Counter Specifications
Programmable Operation Channels a and B
Trigger level 0 volts
A Counter Specifications
Channel C Time Base
Maximum Input 5 volts rms
Unpacking and Inspection
C T I O N I Installation
Preparation for USE
Rack Mounting
Operating Environment
Bench Operation
Packaging for Reshipment
Model 5328A Installation Other Packaging Methods
Storage
Page
E R a T O R S I N S T R U C T I O N S N T R O D U C T I O N
Model 5328A Operation C T I O N I l l
E R a T I O N
Frequency Measurements
Model 5328A Operation
Period Measurements
Time Interval Measurements
Deadtime
Ratio Measurements
Operating Controls
5328A Front Panel Operation Summary
A Front Panel Operation Summary
5328A Rear Panel Controls and Connectors
Function of CONTROLS, INDICATORS, INPUTS, and Outputs
Functions and Resolution Switch Settings
B Channel Signal Conditioning
Model 5328A Operation Input Channel Section
Slope Switch Settings
T E
Hysteresis Band of Trigger Levels
Model 5328A Operation Channel C Input
Channel Overload lndicator
External Frequency Standard Input
Setting Address Switches
Addresssing
Model 5320A Operation
Program Code Set
BUS Commands
Measurement Output Format
American Standard Code for Information Interchange Ascii
Program Examples
Model 5328A Operation
Page
Overall Description
Model 5328A Theory of Operation
C T I O N I E O R Y O F O P E R a T I O N
Basic Counter Operation
Period
Measuring Period
Model 5328A Theory of Operation Ratio
Time INTERVAL, RESOLUTION, and Averaging Techniques
Time Interval
Model 5328A Theory of Operation Resolution
Time Interval Averaging
Sources of Measurement Error
36.±1 Count Ambiguity
Time Base Error
Trigger Error
48.5328A Principles of Operation
Main Counter Section
Block Diagram
Hewlett-Packard Interface Bus HP-US Section
Input Section
2 . a 1 M O T H E R B O a R D
Decade Counting Assembly DCA
69.A3 Oscillator Support
83.A2 Power Supply
85.+5V Supply
High Speed Multiplexer, Main Gate, and 1st Decade
89.A4 Function Selector
Arming Multiplexer and Arming FF
103.A16 Display Assembly
An Example of Operation
Remote Controllable Programmable Input Block Diagram
Examples
5328A Input Circuit Program Code Set
Function
117.A19 Switch Control Board
Remote Controllable Programmable Input Schematic Theory
122.A12 Amplifier Board
127.A10 Synchronizer Board
Model 5328A Theory of Operation
147.A11 DAC Board
156.A8 Channel C Input
HP Interface BUS Theory
HP-IB A15 Interface Operation
Talk Mode
Bus Command Mode
Listen Mode
Model 5328A Theory of Operation Overall Operation
Model 5328A Theory of Operation
10.ASM Oscillator Timing Diagram
C T I O N I N T E N a N C E
Assembly Designations
Assembly Connection Identification
Test Equipment
Preventive Maintenance
Model 5328A Maintenance Recommended Test Equipment
Preventive Maintenance
Repair Printed Circuit Component Replacement
Model 5328A Maintenance Inspection
Cleaning
Performance Test
Setup
Sensitivity Channel a Specification
Performance Test
Sensitivity Channel B Specification
Model 5328A Maintenance Performance Test
Setup HP 8840A
SENSITIVITY-Channel C Specification
Signal Generator HP 5328A Channel C
Ratio B/A, or C/A Specification
Time Interval and Time Interval Average
GATE/MARKER OUT and Sample Rate Setup
Remote Programming Test Setup
Performance Test
Performance Test
Atten X10 Test
Tab/e 5-4. Performance Test
Atten X1 Test
Atten X100 Test
Remote Trigger Level Test Setup
Performance Test
Performance Test
Page
Test Description Results Pass Fail
Performance Check Test Card
17A
Page
GATE/MARKER OUT and Sample Rate Remote Programming
5328A Date
Test Description Results Pass Fail Ratio B/A
17B
Page
Adjustments
Sensitivity Adjustments
Model 5328A Maintenance
Model 5328A Maintenance
DAC Adjustment Equipment Connections
DAC Adjustment oscilloscope readout and adjustment locations
Troubleshooting Aids
Model 5328A Maintenance Adjustment of A3 Oscillator Support
7 . Troubleshooting
Extender Board
A3 Jittler Adjustment
Model 5328A Maintenance IC Troubleshooting
Function Signals
5IC Troubleshooting, A1 Motherboard
IC Troubleshooting, A1 Motherboard
IC Troubleshooting, A1 Motherboard
LC Troubleshooting, A1 Motherboard 5328A Functional Signals
HP-IB Verification Using the HP9825A
System Configuration
Sample Printout
Program Listing
Program Listing
Program Listing
8A. Program Description
8B. Program Description
Step Test Counter Display Readout
8C. HP-IR Bus Commands
5328A A15 Qualifiers and Signal Mnemonics
Signal Source Description
A A15 Qualifiers and Signal Mnemonics
Outputs
10.A12 Relay Operation
Troubleshooting Input Channels
11.Relay Control Logic
Model 5328A Maintenance
Model 5328A Maintenance
Page
60Display Assembly Removal and Replacement
Removal and Replacement Instructions
Instrument Cover Removal
Model 5328A Maintenance
10. Assembly Flowchart Sheet 1
10. Assembly Flowchart Sheet 2
10. Assembly Flowchart Sheet 3
11.Local Troubleshooting Flowchart Sheet 1
11. Address Switch Troubleshooting Flowchart
12. Address Switch Troubleshooting Flowchart
C T I O N V P L a C E a B L E P a R T S
Model 5328A Replaceable Parts
R D E R I N G I N F O R M a T I O N
Model 5328A Replaceable Parts
Component Parts and Materials
HP Part Number Organization
Prefix Component/Part/Material
Factory Selected Parts
Part Number to National Stock Number Cross Reference Index
Mother Main BOARD, Series
DIODE-SWITCHING 80V 200MA 2NS DO-35
DIODE-SWITCHING 30V 50MA 2NS DO-35
Not Assigned
IC Cntr TTL Decd Synchro POS-EDGE-TRIG
SWITCH-SL DPDT-NS Submin .5A 125VAC PC
NETWORK-RES 9-ON-SIP .15-PIN-SPCG
IC SCHMITT-TRIG TTL Nand Quad 2-INP
CONNECTOR-PC Edge 15-CONT/ROW 2-ROWS
CONNECTOR-SGL Xont PIN .04-IN-BSC-32 RND
CONNECTOR-PC Edge 18-CONT/ROW 2-ROWS
ASSEMBLY,POWER Supply Series
Fuse 2A 250V FAST-BLO 1.25X.25 UL IEC
Connector 3-PIN F
Crystal Oscillator Assembly
Inductorfxd 300UH AT 5A DC
CONNECTOR-RF SMC FEM Unmtd 50-OHM
DIODE-SWITCHING 30V 50MA 2NS D0-35
Cable ASSEMBLY, Oscillator
CONNECTOR-RF BNC FEM SGL-HOLE-RR 50-OHM
CAPACITOR-FXD 15PF +-5% 500VDC Mica
CAPACITOR-FXD 800PF +-1% 300VDC Mica
CAPACITOR-FXD 60PF +-5% 300VDC Mica
NETWORK-RES 9-PIN 81P .15-PIN-SPCG
Channel Input Series
Connector ASSEMBLY, BNC
Connector ASSEMBLY,SMC
CAPACITOR-FXD 68UF+-20% 6VDC TA
RESISTOR-TRMR 10K 10% C SIDE-ADJ 1-TRN
Resisto
CABLE, Overload Indicator
Cable ASSEMBLY, Frequency C
Cable ASSEMBLY, Test
CONNECTOR-SGL Cont SKT RND
CONNECTOR-SGL Cont PIN .04-IN-BSC-8Z NRD
SWITCH-SL DPDT-NS Mintr 1A 125VAC PC
CONNECTOR-SGL Cont PIN .04-IN-SBC-8Z RND
CONNECTOR-SGL Cont PIN .04-IN-BSC-SZ RND
Transistor J-FET N-CHAN D-MODE SI
DIODE-SWITCHING 15V 50MA 750PS DO-7
DIODE-SWITCHING 15V 50MA 750PS D0-7
Transistor J-FET P-CHAN D-MODE SI
Cable ASSEMBLY, RF/A & B Input
CONNECTOR-SGL Cont PIN .04-IN-BSC-8Z RND
CONNECTOR-SGL Cont PIN .04-IN-BSC-8Z RNS
CONNECTOR-RF FEM SGL-HOLE-RR 50-OHM
CAPACITOR-FXD 470PF +-20% 500VDC CER
DIODE-SWITCHING 30V 50MA 2NA DO-35
CAPACITOR-FXD 10UF+-20% 25VDC TA
CAPACITOR-FXD 3.3PF +-.25PF 500VDC CER
IC Gate ECL EXCL-OR/NOR TPL 1-INP
RESISTOR-TRMR 100 10% C SIDE-ADJ 1=TRN
RESISTOR-TRMR 100 10% C SIDE-ADJ 1-TRN
IC Comparator 16-DIP-C
CAPACITOR-FXD 33UF+-10% 10VDC TA
Connector 24-PIN F Microribbon
SWITCH-SL 7-1A-NS DIP-NS DIP-SLIDE-ASSY .1A
NETWORK-RES 10-PIN-SIP .1-PIN-SPCG
DIODE-SWITCHING 30V 50MA 2NS DO.35
Cable ASSEMBLY, HP-IB Single
Display Assembly
IC LCH TTL L D-TYPE 4-BIT
CONNECTOR-SGL Cont PIN 1.143MM3BSC-SZ SQ
SWITCH-TGL Submin Dpdt NS 2A 250VAC PC
SWITCH-PB Dpdt MOM .02A 20VAC
CONNECTOR-PC Edge 24-CONT/ROW 2-ROWS
Cable ASSEMBLY,OVERLOAD
SWITCH-SL DP3T-NS Mintr .5A 125VAC/DC PC
LED, Indicator
A19 Miscellaneous
CONNECTOR-RF BNC FEM SGL-HOLE-FR 50-OHM
FAN and Control Module Assembly
SWITCH-SL DPDT-NS STD 1.5A 250VAC
Cover Assembly
Manufacturers Code list
73899 5910-00-983-2623
0757-0280 28480 5905-00-853-8190
2100-1738 28480 5905-00-256-8993
Page
C T I O N V I N U a L C H a N G E S
Model 5328A Manual Changes
Manual Changes Sheet
N U a L D E S C R I P T I O N
Change Date July 7
Manual Changes Model 5328A/H42
Page
H E M a T I C D I a G R a M S
Schematic Diagram Symbols and Reference Designators
Identification Markings on Printed Circuit Boards
Aoro
Model 5328A Schematic Diagrams
Assembly Locations and Component Locators
Identifies
Schematic Diagram Notes
ARM
Signal Mnemonics
Mnemonic Description
DVM
RL IC ANN
Htbo
RL IA
Lddca
RL3 Hdvm
OSC
RL5 TIO
5328A Front View
5328A Top View
5328A Bottom View
Page
A1 Motherboard
7.A1 Mother board Assembly
7.A1 Motherboard Assembly
7.A1 Motherboard Assembly
A1 Motherboard Schematic and Components Sheet 1
A1 Motherboard Schematic and Components Sheet 2
A2 Power Supply Block Diagram
A2 Power Supply Schematic and Components
10.A3/A3A1 Oscillator Support Schematic and Components
10.A3/A3A1 Oscillator Support Schematic and Components
11.A4 Function Selector Block Diagram
12.A4 Function Selector Assembly
12.A4 Function Selector Schematic and Components
13. A8 Channel C Block Diagram
14.A8 Channel CSchematic and Components
15.A10 Synchronizer Block Diagram
16.A10 Synchronizer Schematic and Components
17. A11 Digital-to-Analog Converter Block Diagram
18.A11 Digital-to-Analog Converter Schematic and Components
19. A12 A-B Channel Block Diagram
20.A12 A-B Channel Schematic and Components
21.A15 HP-IB Interface Block Diagram
22.A15 HP-IB Interface Schematic and Components
22.A15 HP-IB Interface Schemaatic and Components
23.A16 Display Block Diagram
Page
24.A16 Display Schematic and Components
25.A19 Switch/Attenuator Schematic and Components
Appendix a References
Page
General
P E N D I X B M P O N E N T S O F E N D I T E M L I S T
Section I. Introduction Scope
Explanation of Columns
Counter Electronic Digital Readout
Power Cord Inside Cover
Cover Assembly Inside Cover
Extender Board Inside Cover
Section Basic Issue Items Illustration National
Page
Section l. Introduction General
Maintenance Function
P E N D I X D I N T E N a N C E a L L O C a T I O N
Column Entries
Tool and Test Equipment Requirements Sec Ill
Remarks Sec
Electronic Counter AN/USM-459
Power Supply PP-7547/U HP 6113A Voltmeter HP
Signal Generator SG-1112V1/U
Signal Generator HP 608 CR
Repair KIT Printed Wiring Board MK-772/U
Section IV. Remarks
Page
By Order of the Secretary of the Army
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
PIN