To access the redundant ROM, set S1, S5, and S6 to on.
When the system maintenance switch position 6 is set to the On position, the system is prepared to erase all system configuration settings from both CMOS and NVRAM.
![]() CAUTION: Clearing CMOS and/or NVRAM deletes configuration information. Be sure to properly configure the server or data loss could occur.
CAUTION: Clearing CMOS and/or NVRAM deletes configuration information. Be sure to properly configure the server or data loss could occur.
NMI functionality
An NMI crash dump enables administrators to create crash dump files when a system is hung and not responding to traditional debug mechanisms.
Crash dump log analysis is an essential part of diagnosing reliability problems, such as hangs in operating systems, device drivers, and applications. Many crashes freeze a system, and the only available action for administrators is to cycle the system power. Resetting the system erases any information that could support problem analysis, but the NMI feature preserves that information by performing a memory dump before a hard reset.
To force the OS to invoke the NMI handler and generate a crash dump log, the administrator can use the iLO Virtual NMI feature.
For more information, see the white paper on the HP website (http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/ support/SupportManual/c00797875/c00797875.pdf).
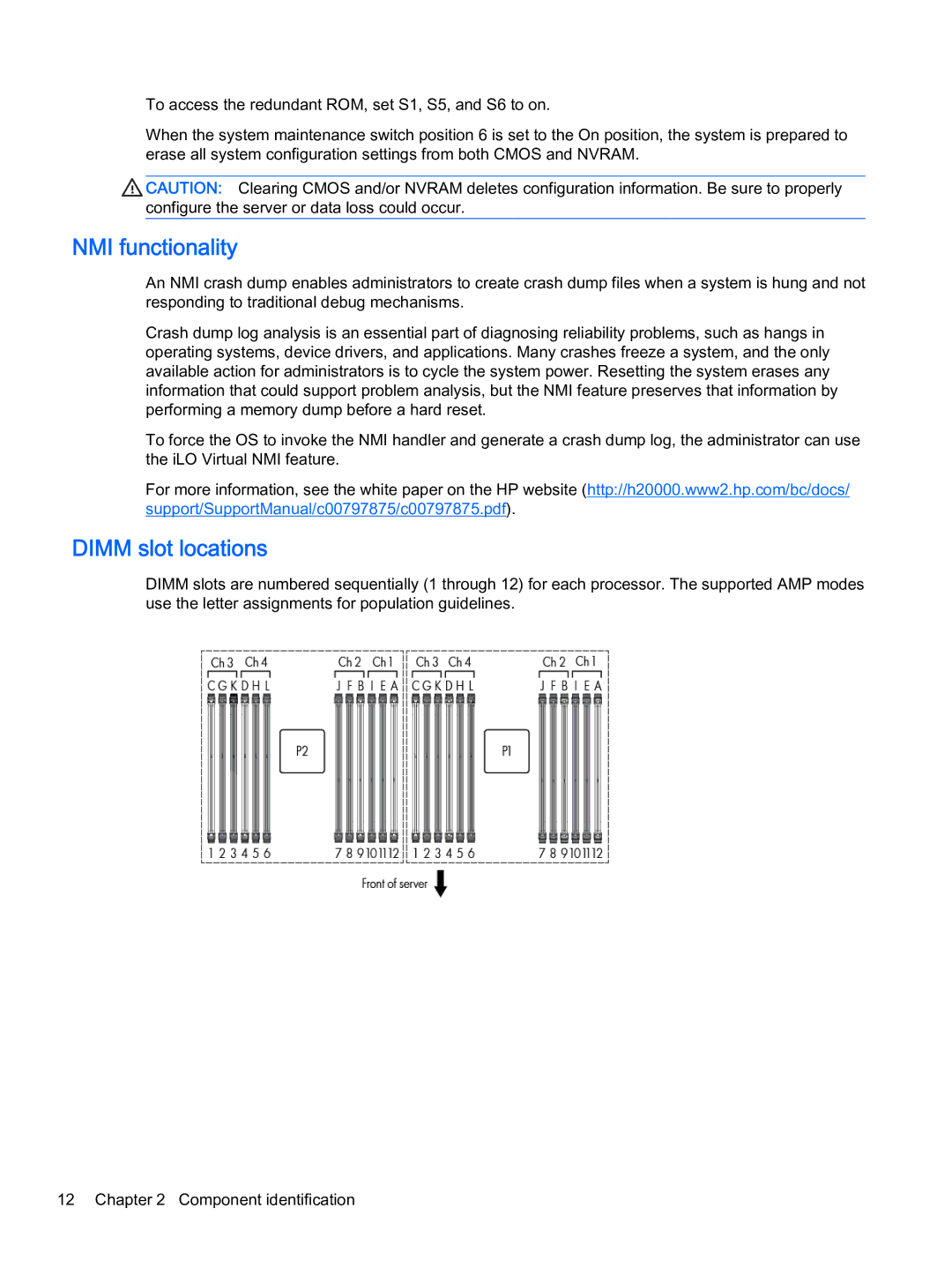
DIMM slot locations
DIMM slots are numbered sequentially (1 through 12) for each processor. The supported AMP modes use the letter assignments for population guidelines.
12 Chapter 2 Component identification