DOC. Version
EM78P809N
Elan Microelectronics Corporation
Contents
Specification Revision History
Bit Microcontroller
CPU
„ General purpose
Applications
Pin Assignment
OTP Programming Pins
Function Description
Functional Block Diagram
Tbktc
Operating Registers
R2/PC − Program Counter & Stack Address 02h
R1/TCC − Time Clock /Counter Address 01h
Bit 7 ~ Bit 6 RBS1 ~ RBS0 R-Register page select
R3/SR − Status Register Address 03h
Bit 5 Not used
RBS1 RBS0
General Purpose Register Bank Address 20H ~ 3FH
Bit 0 C Carry flag R4/RSR − RAM Select Register Address 04h
GRBS1 GRBS0
PORT6 − Port 6 I/O Data Register Address 06h
SIS = 0 Idle mode SIS = 1 Sleep mode
PORT7 Port 7 I/O Data Register Address 07h
PORT8 − Port 8 I/O Data Register Address 08h
TC4S = 1 Start
TC4CR Timer/Counter 4 Control Register Address 0Bh
TC4FF1 TC4FF0
TC4CK2 TC4CK1 TC4CK0
ISFR1 − Interrupt Status Flag Register 1 Address 0Eh
Bit Microcontroller TC4D − Timer 4 Data Buffer Address 0Ch
TC3CAP =
Bit 7 TC3CAP Software capture control
TC3S = 1 Start
TC3CAP TC3S TC3CK1 TC3CK0 TC3M
TC2M = 1 Window mode
TC3DB − Timer 3 Data Buffer B Address 07h
Bit 7 ~ Bit 6 ADD1 ~ ADD0 AD low 2-bit data buffer
TC2S = 1 Start
Adcr − AD Control Register Address 0Bh
TC2DH − Timer 2 Data Buffer High Byte Address 09h
TC2DL − Timer 2 Data Buffer Low Byte Address 0Ah
Bit 7 ~ Bit 0 ADE7 ~ ADE0 AD input pin enable control
Bit 3 ADP AD power control
Adic − AD Input Pin Control Address 0Ch
Addh − AD High 8-bit Data Buffer Address 0Dh
TEN = 0 Disable TEN = 1 Enable
Bit 7 TEN Keytone enable control
Bit 3 Tbten Time Base Timer Enable Control
Bit Microcontroller Tbktc − TBT/Keytone Control Address 0Eh
Uinven = 0 Disable TXD and RXD port inverse output
Bit 3 Uinven Enable Uart TXD and RXD port inverse output
Uinven = 1 Enable TXD and RXD port inverse output
Bit 4 ~ Bit 2 BRATE2 ~ BRATE1 Transmit Baud Rate Select
Even = 0 Odd parity Even = 1 Even parity
Bit 5 PRE Enable parity addition
Bit Microcontroller URS − Uart Status Register Address 07h
EDS = 0 Rising edge EDS = 1 Falling edge
Bit 2 EDS Data shift out edge select
SMP Dcol BRS2 BRS1
EDS Dord WBE
SPIC2 − SPI Control Register 2 Address 06h
Transfer Mode
Spid SPI Data Buffer Address 07h
SPID7 SPID6 SPID5 SPID4 SPID3 SPID2 SPID1 SPID0
PLC1 Pull Low Control Register 1 Address 0Bh
PLE7x = 1 Disable P7x pull low
PHC2 − Pull High Control Register 2 Address 0Ch
PLC2 − Pull Low Control 2 Address 0Dh
Accumulator
Special Purpose Registers
Control Register
Bit 7 Wdto WDT output select
Intcr − INT Control Register Address 0Bh
Bit Microcontroller IOC6 ~ IOC9 − I/O Port Control Register
Bit 2 Reserved
INT1ES = 0 Rising edge INT1ES = 1 Falling edge
External Interrupt
INT Pin Secondary Enable Condition Function Pin
Adoscr − AD Offset Control Register Address 0Ch
Edge
Uerrie Urie Utie Tbie EXIE1 TCIE0
IMR2 − Interrupt Mask Register 2 Address 0Fh
Registers for CPU operation mode
CPU Operation Mode
Rbank Register Bank bits 7, 6 of R3, R/W Read/Write
Rbank
Normal
Mode Switching Control
Operation Mode
Registers for AD Converter Circuit
AD Converter
→ Don’t care → Interrupt request flag will be recorded
Conversion Time
ADC Data Register
Sampling Time
Max. Frequency Max. Conversion Rate per Bit
Time Base Timer and Keytone Generator
ADCK10
Tone Output Pin Timing Chart
Rbank Address Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit
Uart Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
Registers for Uart Circuit
Data Format in Uart
Uart Mode
Receiving
Transmitting
Registers for the SPI Circuit
SPI Serial Peripheral Interface
Baud Rate Generator
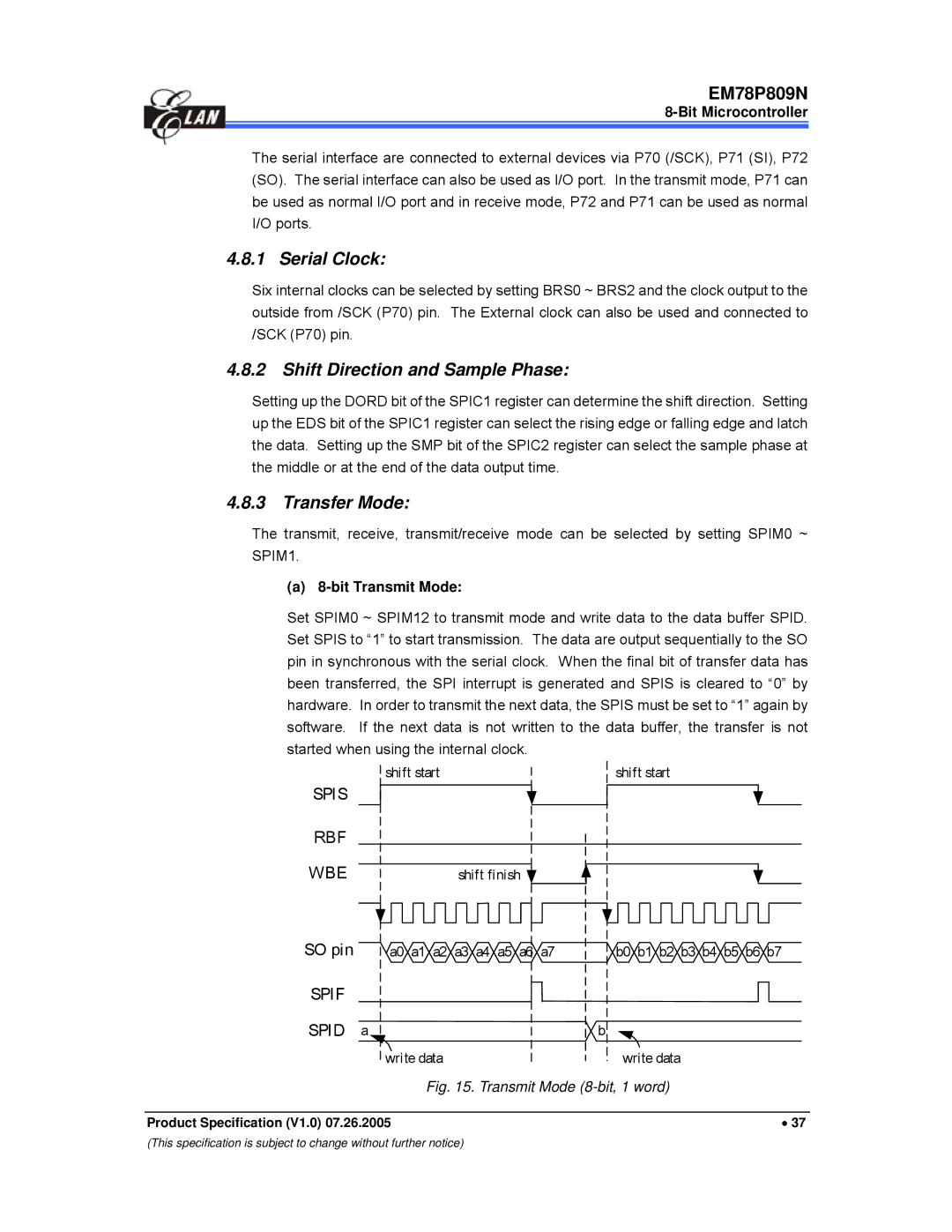
Transfer Mode
Shift Direction and Sample Phase
Bit Transmit Mode
Serial Clock
Bit Transmit/Receive Mode
Bit Microcontroller Bit Receive Mode
Multiple Device Connect /SS
SCK pin
Rbank Address Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit
Timer/Counter
Registers for Timer/Counter 2 Circuit
Window Mode
Timer Mode
Counter Mode
Registers for Timer/Counter 3 Circuit
Window Mode Timing Chart
Configuration of Timer/Counter3
Capture mode
TCIF4
Registers for Timer 4 Circuit
TCR4
PDO Mode
TC4 Interrupt
PWM Mode
12 TCC/WDT & Prescaler
13 I/O Ports
Reset and Wake-up
Reset
All interrupt
Wake-up from Sleep Mode
Wake-up from Idle mode
Summary of the Initialized Values for Registers
Address Name Reset Type Bit
SCR
Bit Microcontroller Register Bank
TC2D9 TC2D8
Register Bank
Reset Type
Previous value before reset
Status of RST, T, and P of Status Register
Bit Microcontroller General Purpose Registers
Interrupt
Controller Reset Block Diagram
Oscillator Modes
Oscillator
Crystal Oscillator/Ceramic Resonators Crystal
Summary of Maximum Operating Speeds
EM78P809N
Oscillator Type Frequency Mode C1 pF C2 pF
Ext. Clock
740
Crystal/Resonator-Parallel Mode Circuit
External RC Oscillator Mode
Code Option Register
Enwdtb = 0 Enable Enwdtb = 1 Disable
Code Option Register Word
For design reference only
External Power-on Reset Circuit
Power-on Considerations
Customer ID Register
Cyes = 0 One cycle Cyes = 1 Two cycles
Vdd
Residue-Voltage Protection
EM78P809N Rin
Vdd EM78P809N
Vdd 40KR2
Instruction Set
DEC
Binary Instruction Hex Mnemonic Operation Status Affected
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Condition Min Typ Max Unit
Recommended Operating Conditions
Vss =
Typical value is based on characterization results at 25C
DC Electrical Characteristics
Ta= 25 C, VDD= 5.0V ± 5%, VSS=
Ta= 25 C, VDD= 3.0V ± 5%, VSS=
Varef
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
AC Electrical Characteristic
Ta=- 40C ~ 85 C, VDD=5V ± 5%, VSS=0V
= selected prescaler ratio
AC Test Input/Output Waveform
Timing Diagram
Pin Count Package Size
Package Types
OTP MCU
Contents III
EM78P809N