TH-D7A
Features
Thank YOU
Models Covered by this Manual
One or more of the following statements may be applicable
Precautions
Contents
System Ctcss
Scan
Functions
Microphone Control
SKY Command 2 TH-D7A only
Wireless Remote Control TH-D7A only
Maintenance
Optional Accessories
KEY+ Power on
Supplied Accessories
Conventions Followed in this Manual
KEY2
Latch, then slide the battery pack back
Preparation
Insert the charger AC plug into an AC wall outlet
Installing the Hand STRAP/ Belt Hook
Installing the Antenna
Batteries
PB-39 NiCd PB-38 NiCd
Installing Alkaline Batteries
10 2 Insert four AA LR6 alkaline batteries
Alkaline
Connecting with a Cigarette Lighter Socket
Connecting with a Regulated Power Supply
First QSO
Adjusting Volume
Switching Power ON/OFF
Operating Basics
Selecting a Band
Press OK to complete the setting
Adjusting Squelch
Press F, Moni
Press UP/ DWN to select from 6 squelch levels
Selecting lower transmit power is a wise method to
When you finish speaking, release the PTT switch
Reduce battery consumption, if communication is still
Reliable. You can program a different power for band
Getting Acquainted
Indicators
Band a & B
Cursor Keys
UP/ DWN keys
OK key
VFO mode
Function Select mode
Memory Recall mode
Menu mode
Packet mode
Full Duplex mode
Commands to the built-in TNC from a personal computer
Press TNC twice to select. In this mode, you can send
Keypad Direct Entry
Quick Reference Guide
1 s
Key Operation Function
Ctcss ON/ OFF
VFO F
Menu SET-UP
Menu Access
Level Selections Default
Menu Configuration
Level Selections
Radio AUX
Aprs
OFF
Sstv
SKY
CMD
Offset Programming Flow
Operating Through Repeaters
Press UP/ DWN to select the appropriate offset Frequency
Programming Offset
Following methods to bring the transmit frequency
Within the band limits
Press F, 1 to switch the Tone function on or OFF
Press UP/ DWN to select the appropriate tone frequency
67.0 97.4 136.5 192.8
A. and Canada versions
Automatic Repeater Offset
Press REV 1 s to switch the function on
Press REV to switch the Reverse function on or 13 OFF
Reverse Function
Automatic Simplex Check ASC
Tone FREQ. ID
CHANNEL?
Memory Channels
Parameter
Ctcss on
Press PTT+OK
Press UP/ DWN to select the desired memory channel Press OK
Recalling a Memory Channel
Press MR+ Power on
Clearing a Memory Channel
Press UP/ DWN to select the desired memory Channel
Naming a Memory Channel
Press UP/ DWN to select the first digit
Repeat steps 3 and 4 to enter up to 8 digits
Call Channel TH-D7A only
Press VFO
Press PTT+CALL
Channel Display
MEMORY-TO-VFO Transfer
Press F+ Power on
Partial or Full RESET?
VHF Band Defaults Version VFO Freq Tone
UHF Band Defaults
Scan
This transceiver provides the following types of scans
Scan Type Scan Range
Carrier-Operated mode
Time-Operated mode
Seek mode
Selecting Scan Resume Method
Memory Scan
VFO Scan
Press VFO 1 s
Press MR 1 s
To quit MHz Scan, press ESC
MHz Scan
Program Scan
Select the desired frequency as the lower limit
Press F, MR
CALL/VFO Scan TH-D7A only
CALL/MEMORY Scan TH-D7A only
Recall the desired memory channel
Selecting a Ctcss Frequency
Continuous Tone Coded Squelch System Ctcss
Press F, 4 to select F-4 Ctcss Freq
Press UP/ DWN to select the appropriate Ctcss frequency
Press F, 3 to switch the Ctcss function on or
Using Ctcss
Ctcss FREQ. ID
OFF
Dual Tone MULTI-FREQUENCY Dtmf Functions
Manual Dialing
Freq. Hz 1209 1336 1477 1633
Automatic Dialer
Press UP/ DWN to select a character
Press OK
Press PTT+MENU
Transmitting a Stored Dtmf Number
Microphone Control
Direct Frequency Entry
Auxiliary Functions
Data is accepted for the digits entered and 0 is
Programmed for the digits not yet entered
Programmable VFO
Changing Frequency Step Size
Press F, ENT to switch Tone Alert on or OFF
Tone Alert
Beep ON/OFF
Adjusting Display Contrast
Adjusting Volume Balance
Lamp Function
Blanking a Band Display
Battery Saver
Automatic Power OFF APO
Transceiver Lock
POWER-ON Message
13 3 Press UP/ DWN to select a character
15 4 Press OK
Switching TX Deviation TH-D7E only
Switching AM/FM Mode TH-D7A only
TX Inhibit
Advanced Intercept Point AIP
Reference material for starting packet operation should
Packet Operation
Be available at any store that handles Amateur Radio
Equipment
Command mode
Connecting with a Personal Computer
Converse mode
Operating TNC
Following steps should guide you to a good start
Preparation Flow
Packet operation. The shaded steps indicate operations
On your personal computer. First connect
Full Duplex
Selecting Data Band
Band only
Both Bands
DX Packetclusters Monitor
Comment Press List to restore the frequency display
SLOW-SCAN Television Sstv with VC-H1
Entering Call SIGN/ MESSAGE/ RSV
20 3 Press UP/ DWN to select a character
22 4 Press OK
Selecting Color for Call SIGN/ MESSAGE/ RSV
Executing Superimposition
Power is on
VC-H1 Control
VC-H1
Automatic PACKET/ Position Reporting System
Operation Flow
Receiving Aprs Data
Indicator Meaning What is Included?
New Aprs Duplicate
KEY
Press List
Accessing Received Aprs Data
12 2 Press UP/ DWN to select the desired station
18 3 Press OK
Temperature
11 3 Press UP/ DWN to select a character
Programming a Call Sign
13 4 Press OK
15 5 Repeat steps 3 and 4 to enter up to 9 digits
Selecting Your Station Icon
Press OK Press Menu to exit Menu mode
Press UP/ DWN to select from 15 icons plus Others
Kenwood Sstv
Press Menu to enter Menu mode
Entering LATITUDE/ Longitude Data
Press 2, 3 to select 2-3 My Pos
Press UP/ DWN to select the desired comment
Selecting a Position Comment
Entering Status Text
Press UP/ DWN to select a character
17 4 Press OK
All calls
Programming a Group Code
Special
Alternate net
Repeat steps 3 and 4 to enter up to 32 digits
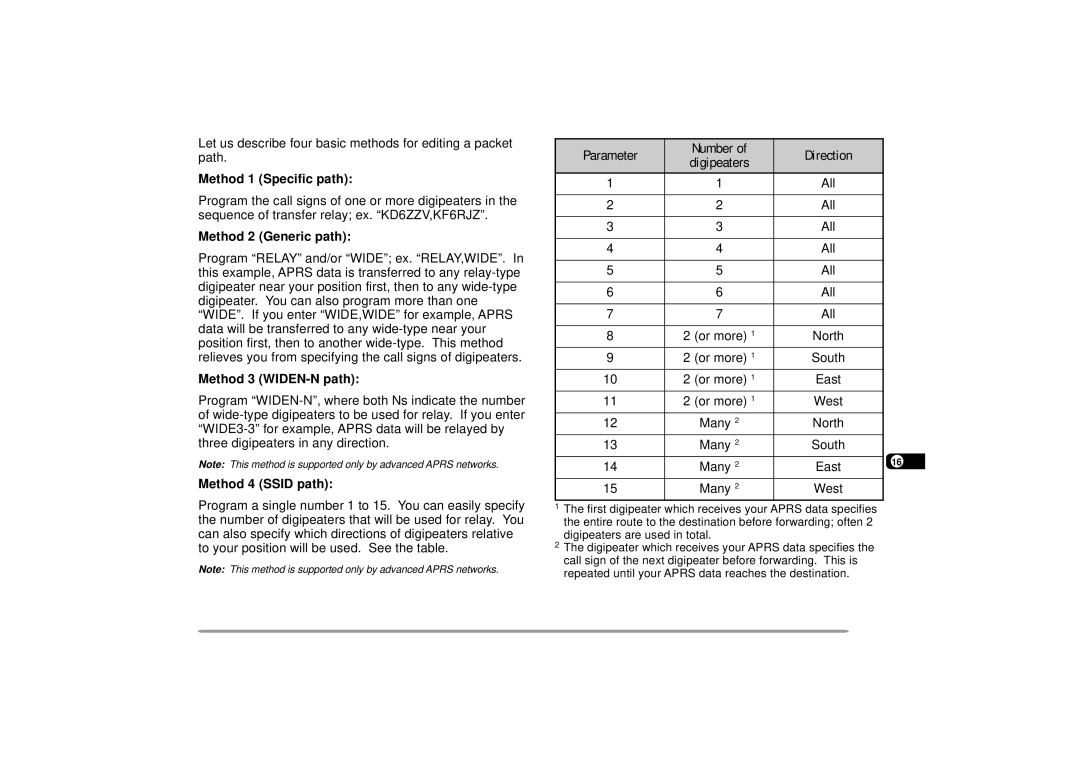
Programming a Packet Path
Method 2 Generic path
Method 1 Specific path
Method 3 WIDEN-N path
Method 4 Ssid path
Selecting Beacon Transmit Method
Press 2, 9 to select 2-9 Data TX
Bcon again
Restricting Reception of Aprs Data
Selecting Beacon Transmit Interval
Press UP/ DWN to select the desired interval
Press UP/ DWN to select the desired distance
Aprs Message
KEY+NEW Data
Press MSG
Accessing Received Aprs Messages
Message Type
Status
Entering a Message
Repeat steps 4 and 5 to enter up to 9 digits
Repeat to enter a message or bulletin with up to 45 digits
Press OK to start transmitting
Transmitting a Message
Press PTT+VFO+ Power on
Wireless Remote Control TH-D7A only
Preparation
Press a numeric key 0 to 9 to enter a 3-digit secret number
Press PTT+MR+ Power on
Control Operation
ENT or VFO UP/ DWN To recall a memory channel
SKY Command 2 TH-D7A only
You can use the optional cables PG-4R to connect
Transceiver
Transporter with the HF transceiver. For these cables
Contact your authorized Kenwood dealer
On the Commander Access Menu 4-4 and select Commander
Programming Call Signs
On Commander
Programming a Tone Frequency
On Transporter
UP/ DWN
Power
Mode
CLR
Page
Service
Maintenance
Service Note
Cleaning
Troubleshooting
Problem Probable Cause Corrective Action
Press A/B+ Power on to exit
Press BAL, then UP/ DWN to
Page
Problem Probable Cause Corrective Action
SMC-32 SMC-33 SMC-34
Optional Accessories
HMC-3
EMC-3 PB-38 PB-39 BT-11
PG-4W
PG-3J
VC-H1 PG-4V
PG-4R
Equipment Connections
Connecting Other External Equipment
General VHF Band UHF Band
Specifications
Transmitter VHF Band UHF Band
TNC Commands List
Short Default Parameter Description
Appendix
Echo ON/ OFF
Dwait
Firmrnr FIR OFF ON/ OFF
Flow ON/ OFF
Location LOC Every
Hbaud
Lpath LPA GPS
Ltext
Txdelay
Reset
Persist
Ppersist ON/ OFF
Index