Using the MSS | Emulating a Direct Serial Connection |
5.3 Emulating a Direct Serial Connection
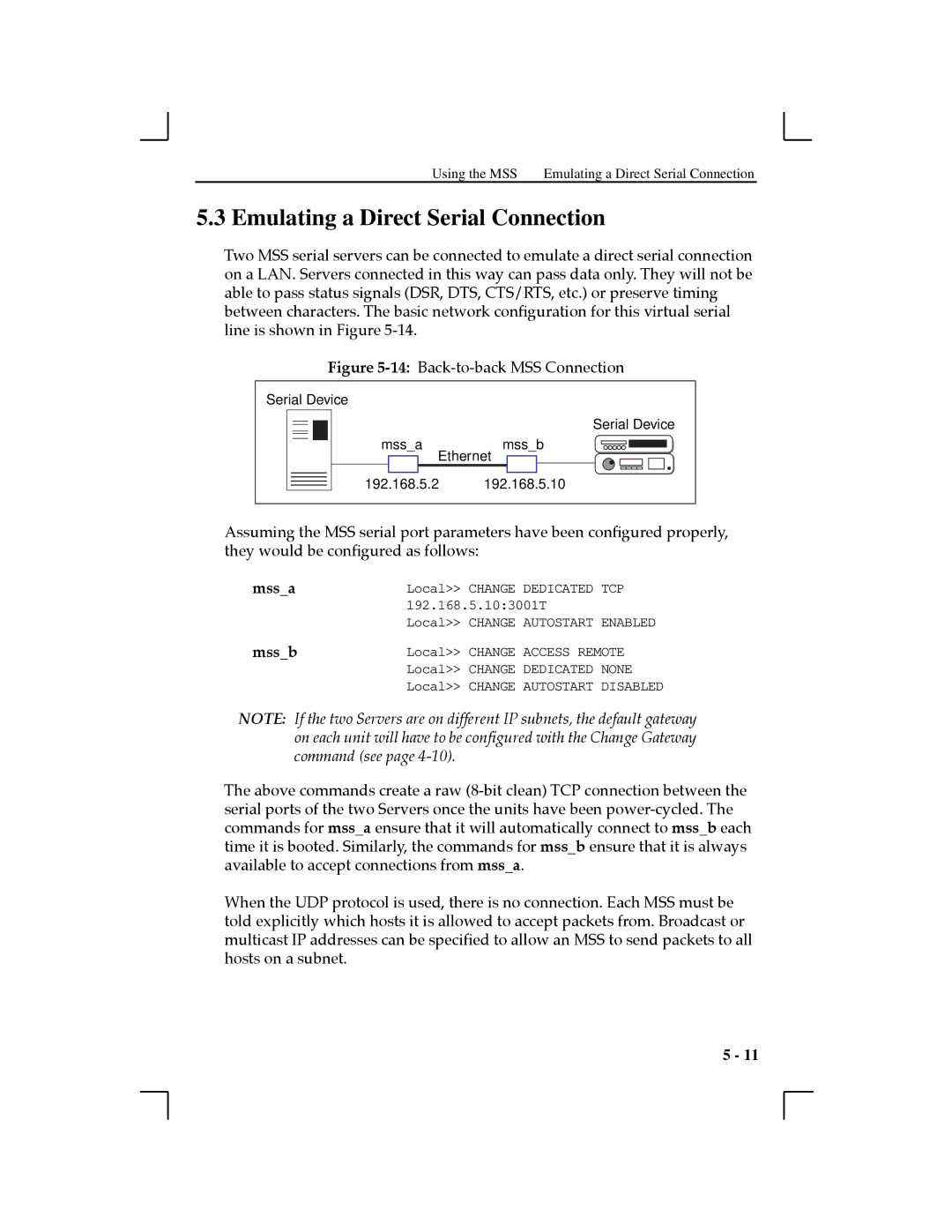
Two MSS serial servers can be connected to emulate a direct serial connection on a LAN. Servers connected in this way can pass data only. They will not be able to pass status signals (DSR, DTS, CTS/RTS, etc.) or preserve timing between characters. The basic network conÞguration for this virtual serial line is shown in Figure
Figure 5-14: Back-to-back MSS Connection
Serial Device
Serial Device
mss_amss_b Ethernet
192.168.5.2 192.168.5.10
Assuming the MSS serial port parameters have been conÞgured properly, they would be conÞgured as follows:
mss_a | Local>> CHANGE DEDICATED TCP |
| 192.168.5.10:3001T |
| Local>> CHANGE AUTOSTART ENABLED |
mss_b | Local>> CHANGE ACCESS REMOTE |
| Local>> CHANGE DEDICATED NONE |
| Local>> CHANGE AUTOSTART DISABLED |
NOTE: If the two Servers are on different IP subnets, the default gateway on each unit will have to be configured with the Change Gateway command (see page
The above commands create a raw
When the UDP protocol is used, there is no connection. Each MSS must be told explicitly which hosts it is allowed to accept packets from. Broadcast or multicast IP addresses can be speciÞed to allow an MSS to send packets to all hosts on a subnet.
5 - 11