System Description
3.0SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
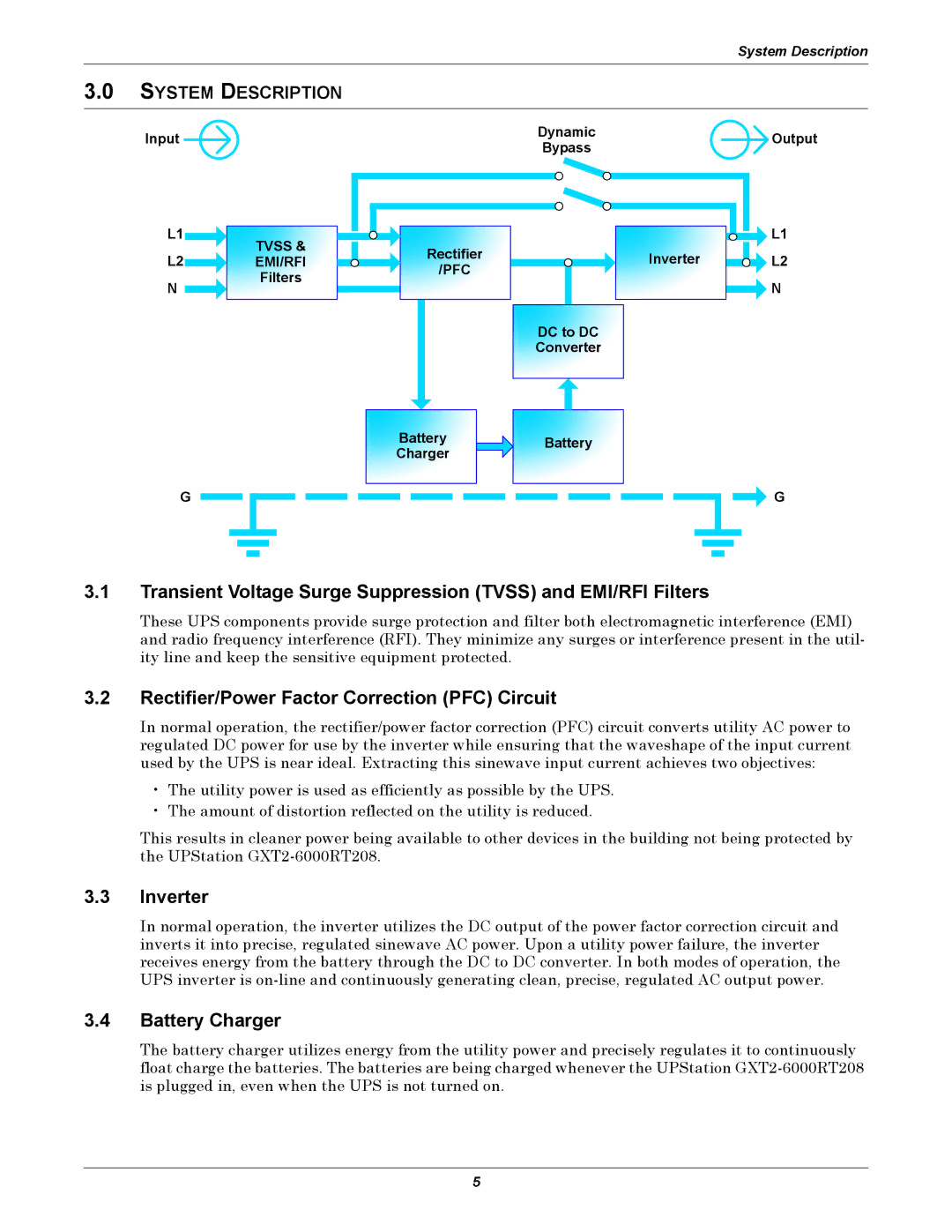
Input![]()
Dynamic | Output | |
Bypass | ||
|
L1 | TVSS & | |
L2 | ||
EMI/RFI | ||
N | Filters | |
|
G
Rectifier |
/PFC |
Battery |
Charger |
| L1 |
Inverter | L2 |
| N |
DC to DC |
Converter |
Battery |
G |
3.1Transient Voltage Surge Suppression (TVSS) and EMI/RFI Filters
These UPS components provide surge protection and filter both electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). They minimize any surges or interference present in the util- ity line and keep the sensitive equipment protected.
3.2Rectifier/Power Factor Correction (PFC) Circuit
In normal operation, the rectifier/power factor correction (PFC) circuit converts utility AC power to regulated DC power for use by the inverter while ensuring that the waveshape of the input current used by the UPS is near ideal. Extracting this sinewave input current achieves two objectives:
•The utility power is used as efficiently as possible by the UPS.
•The amount of distortion reflected on the utility is reduced.
This results in cleaner power being available to other devices in the building not being protected by the UPStation
3.3Inverter
In normal operation, the inverter utilizes the DC output of the power factor correction circuit and inverts it into precise, regulated sinewave AC power. Upon a utility power failure, the inverter receives energy from the battery through the DC to DC converter. In both modes of operation, the UPS inverter is
3.4Battery Charger
The battery charger utilizes energy from the utility power and precisely regulates it to continuously float charge the batteries. The batteries are being charged whenever the UPStation
5