Operational Theory | BDS 3960 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The main advantage of the BDS technology lies in the unique second potentiostat. It is designed to remove dissolved oxygen and other impurities in the electrolyte. It eliminates the internal background current which previously limited the detection process.
The second potentiostat is located adjacent to the sensing electrode. It uses a novel material, Reticulated Vitreous Carbon (RVC) and precise control of the potential to remove the dissolved oxygen and impurities in the electrolyte efficiently. As the result, the BDS sensor achieves an outstanding feature of absolute zero output in the absence of oxygen.
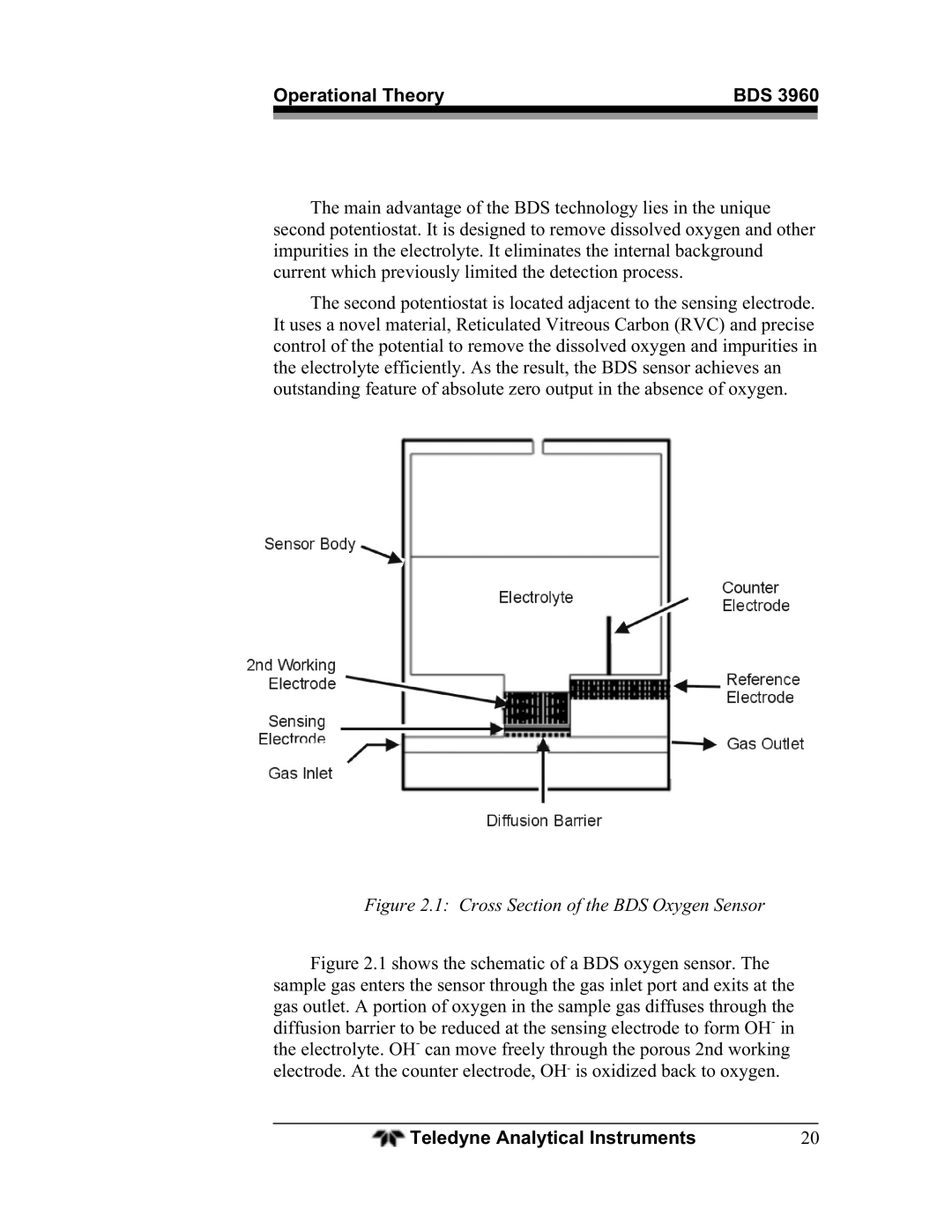
Figure 2.1: Cross Section of the BDS Oxygen Sensor
Figure 2.1 shows the schematic of a BDS oxygen sensor. The sample gas enters the sensor through the gas inlet port and exits at the gas outlet. A portion of oxygen in the sample gas diffuses through the diffusion barrier to be reduced at the sensing electrode to form OH- in the electrolyte. OH- can move freely through the porous 2nd working electrode. At the counter electrode, OH- is oxidized back to oxygen.
Teledyne Analytical Instruments | 20 |