CHARACTERISTICS OF GAS FUELS
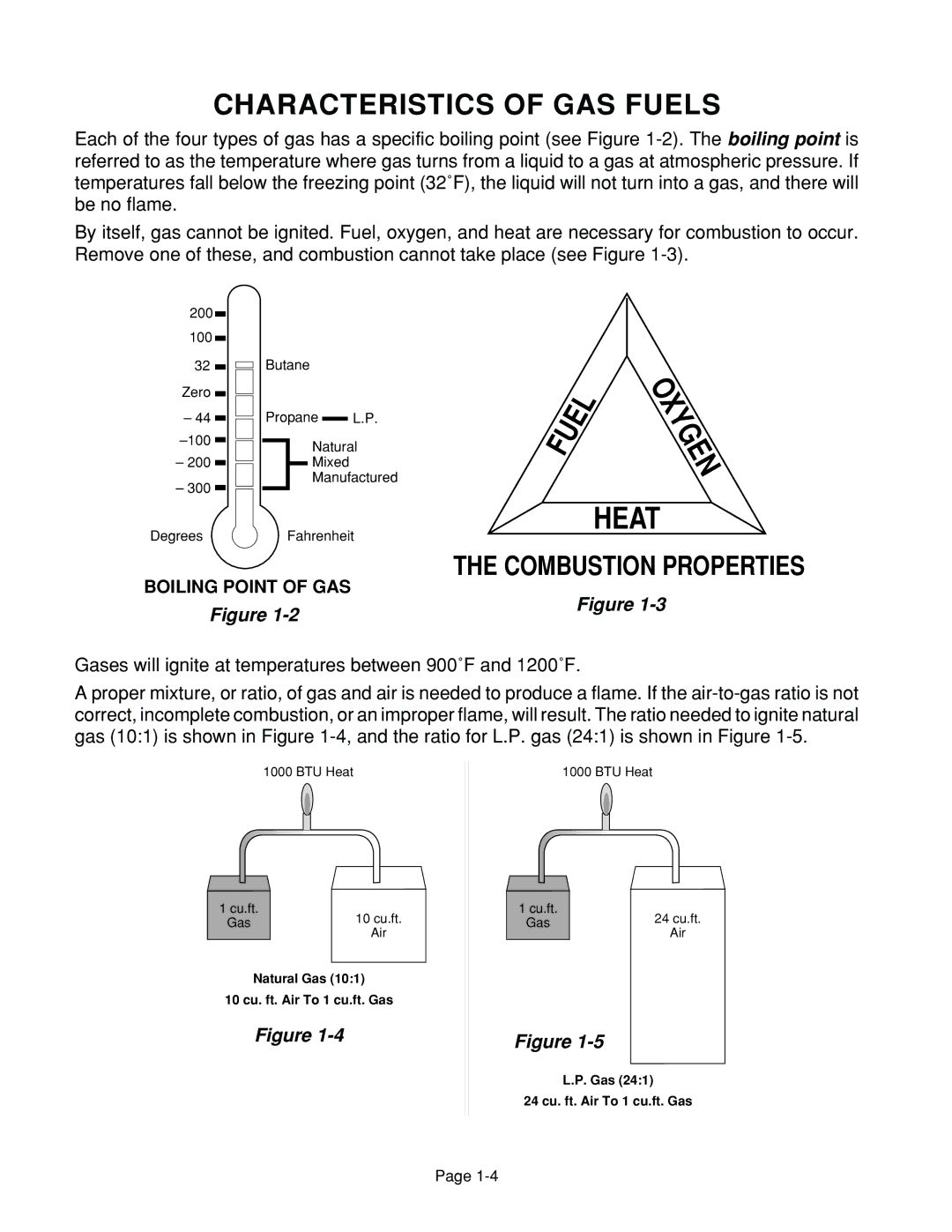
Each of the four types of gas has a specific boiling point (see Figure
By itself, gas cannot be ignited. Fuel, oxygen, and heat are necessary for combustion to occur. Remove one of these, and combustion cannot take place (see Figure
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
100 |
|
|
|
| Butane |
| ||||
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
32 |
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
Zero |
|
|
|
| Propane |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
– 44 |
|
|
|
|
|
| L.P. | |||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
| Natural | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
– 200 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Mixed |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
– 300 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Manufactured | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Degrees |
|
|
|
|
| Fahrenheit | ||||
BOILING POINT OF GAS
Figure
FUEL | OXYGEN |
HEAT
THE COMBUSTION PROPERTIES
Figure
Gases will ignite at temperatures between 900˚F and 1200˚F.
A proper mixture, or ratio, of gas and air is needed to produce a flame. If the
1000 BTU Heat
1 cu.ft.
Gas10 cu.ft. Air
Natural Gas (10:1)
10 cu. ft. Air To 1 cu.ft. Gas
Figure
1000 BTU Heat
1 cu.ft.
Gas24 cu.ft. Air
Figure
L.P. Gas (24:1)
24 cu. ft. Air To 1 cu.ft. Gas
Page