BURNER OPERATION
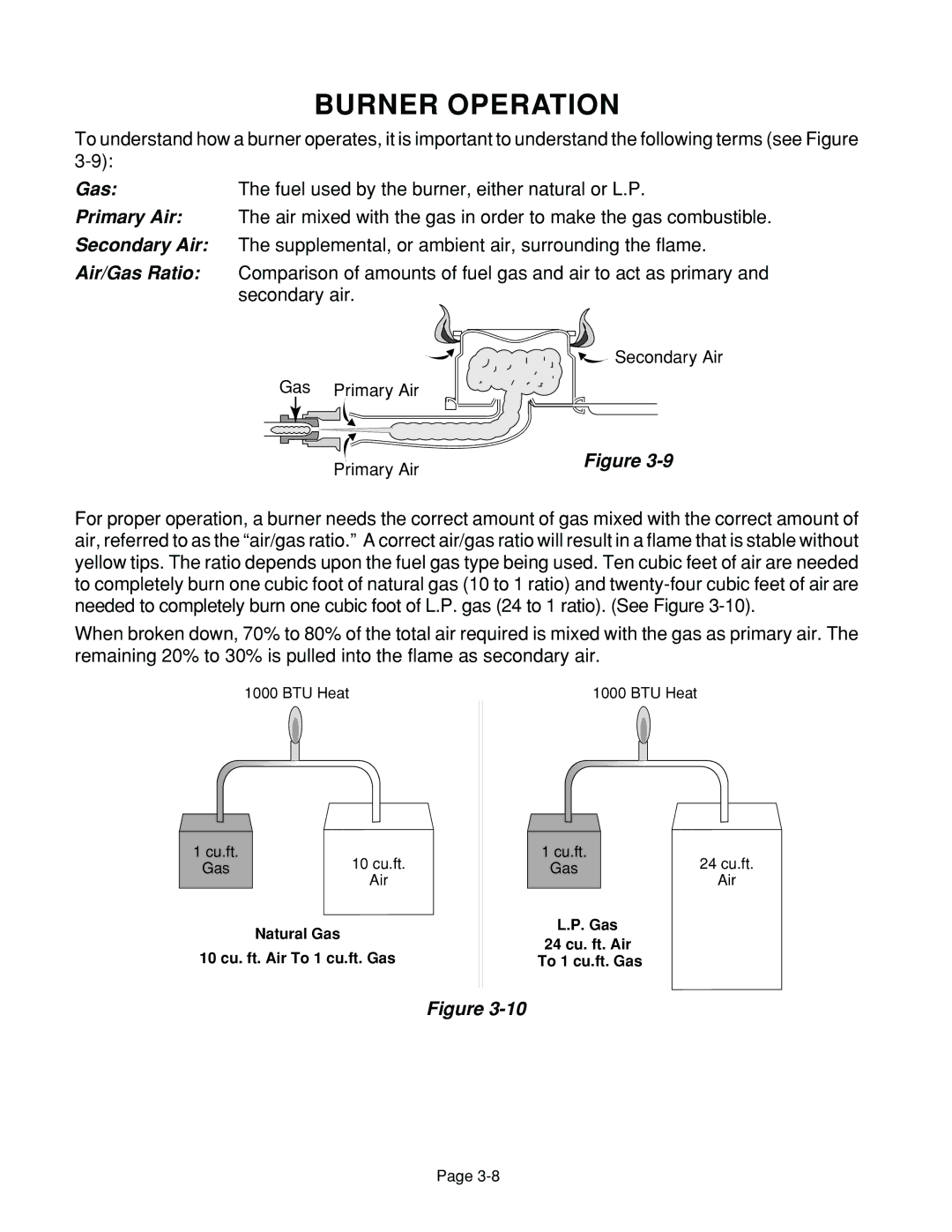
To understand how a burner operates, it is important to understand the following terms (see Figure
Gas:The fuel used by the burner, either natural or L.P.
Primary Air: The air mixed with the gas in order to make the gas combustible.
Secondary Air: The supplemental, or ambient air, surrounding the flame.
Air/Gas Ratio: Comparison of amounts of fuel gas and air to act as primary and secondary air.
![]() Secondary Air
Secondary Air
Gas Primary Air
Primary Air | Figure |
|
For proper operation, a burner needs the correct amount of gas mixed with the correct amount of air, referred to as the “air/gas ratio.” A correct air/gas ratio will result in a flame that is stable without yellow tips. The ratio depends upon the fuel gas type being used. Ten cubic feet of air are needed to completely burn one cubic foot of natural gas (10 to 1 ratio) and
When broken down, 70% to 80% of the total air required is mixed with the gas as primary air. The remaining 20% to 30% is pulled into the flame as secondary air.
1000 BTU Heat
1 cu.ft.
Gas10 cu.ft. Air
Natural Gas
10 cu. ft. Air To 1 cu.ft. Gas
1000 BTU Heat
1 cu.ft.
Gas24 cu.ft. Air
L.P. Gas
24 cu. ft. Air To 1 cu.ft. Gas
Figure
Page