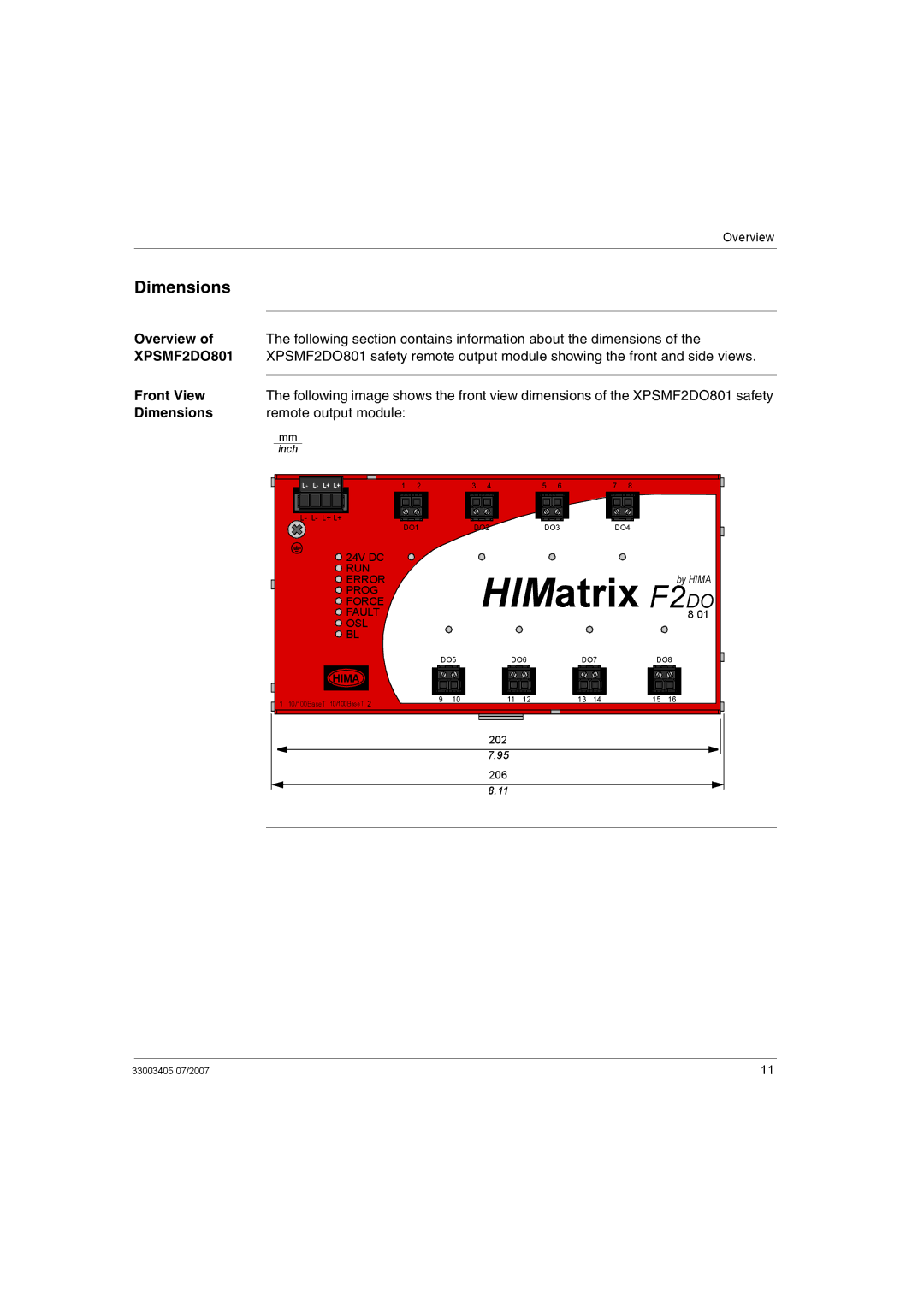
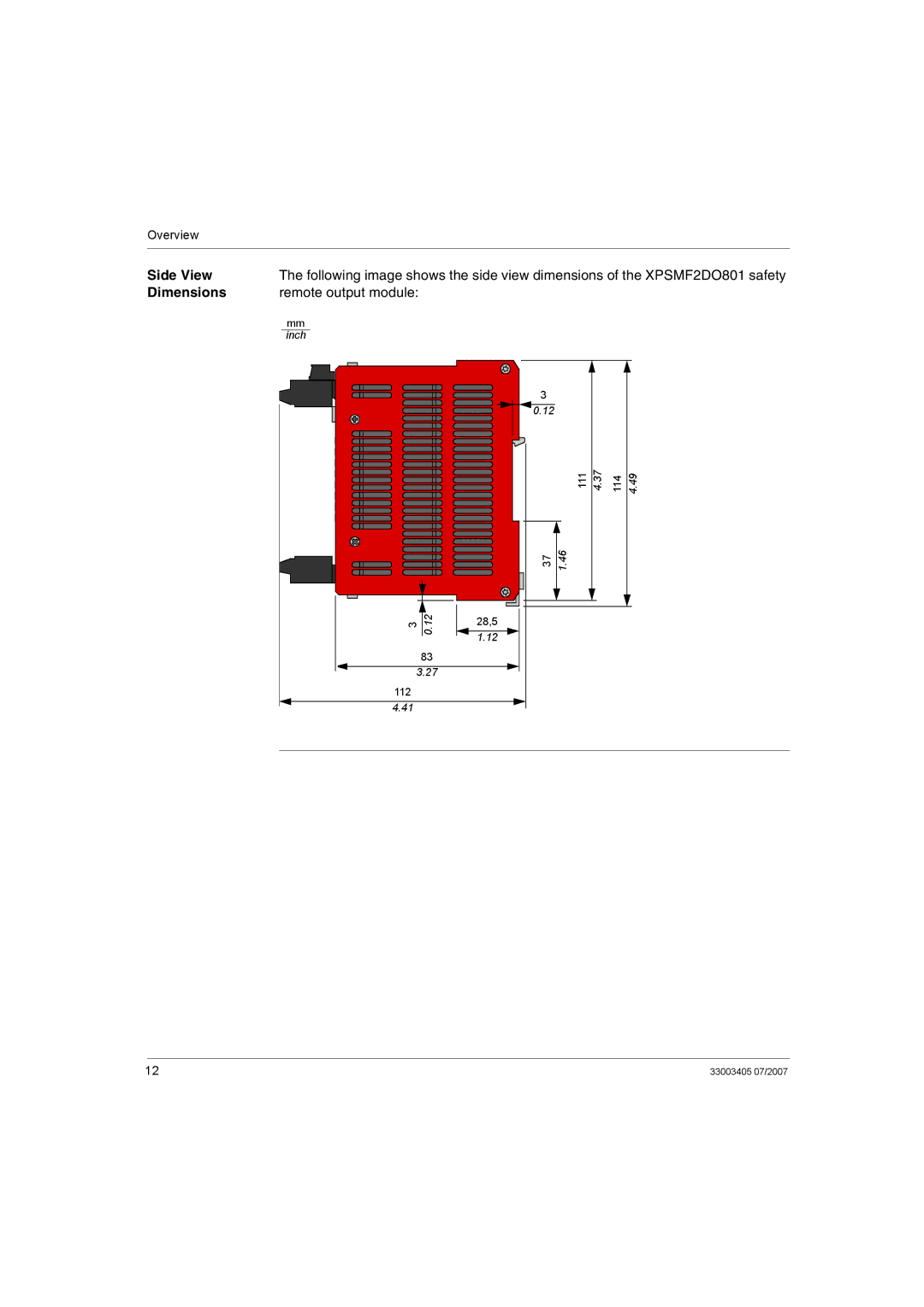
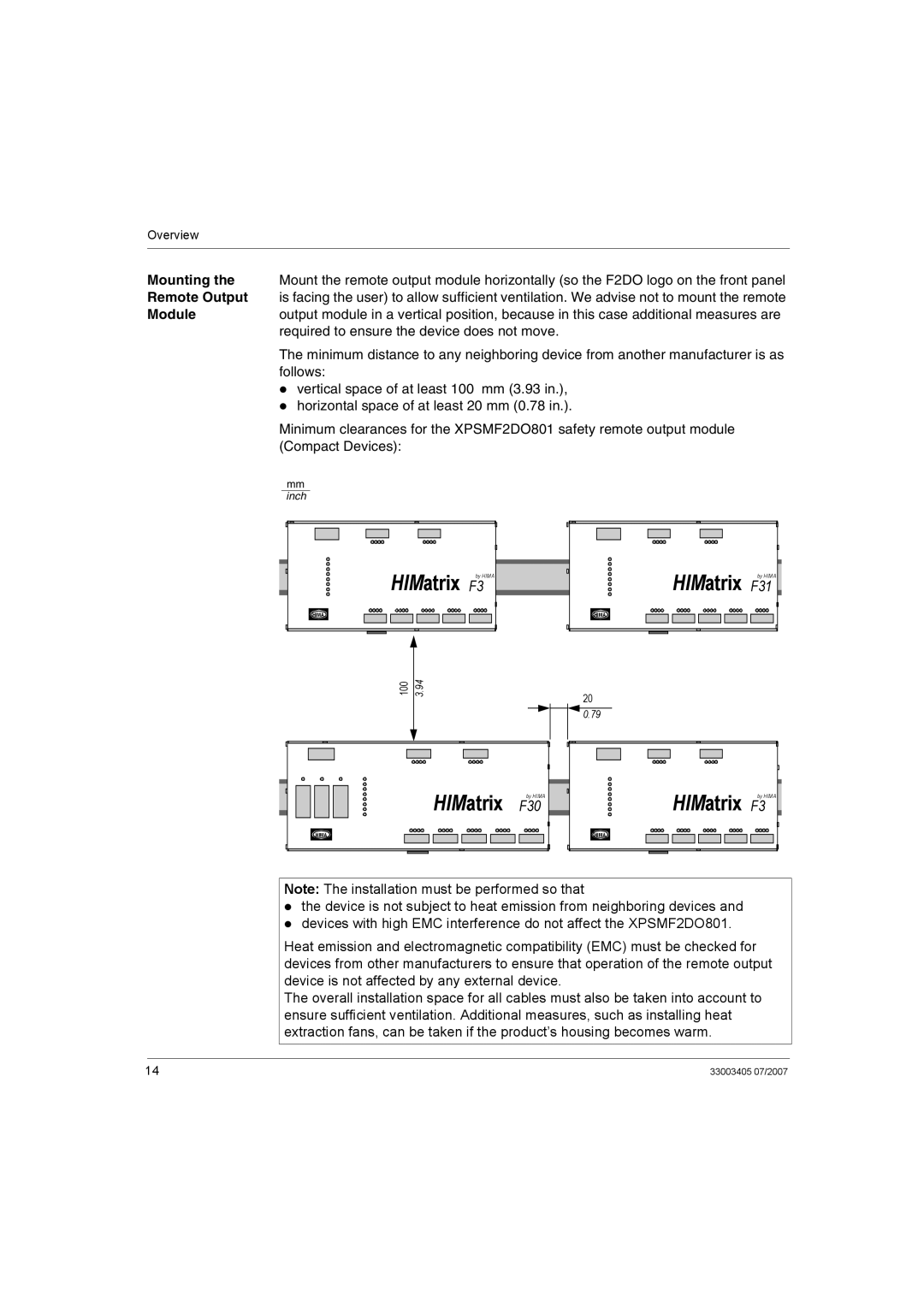
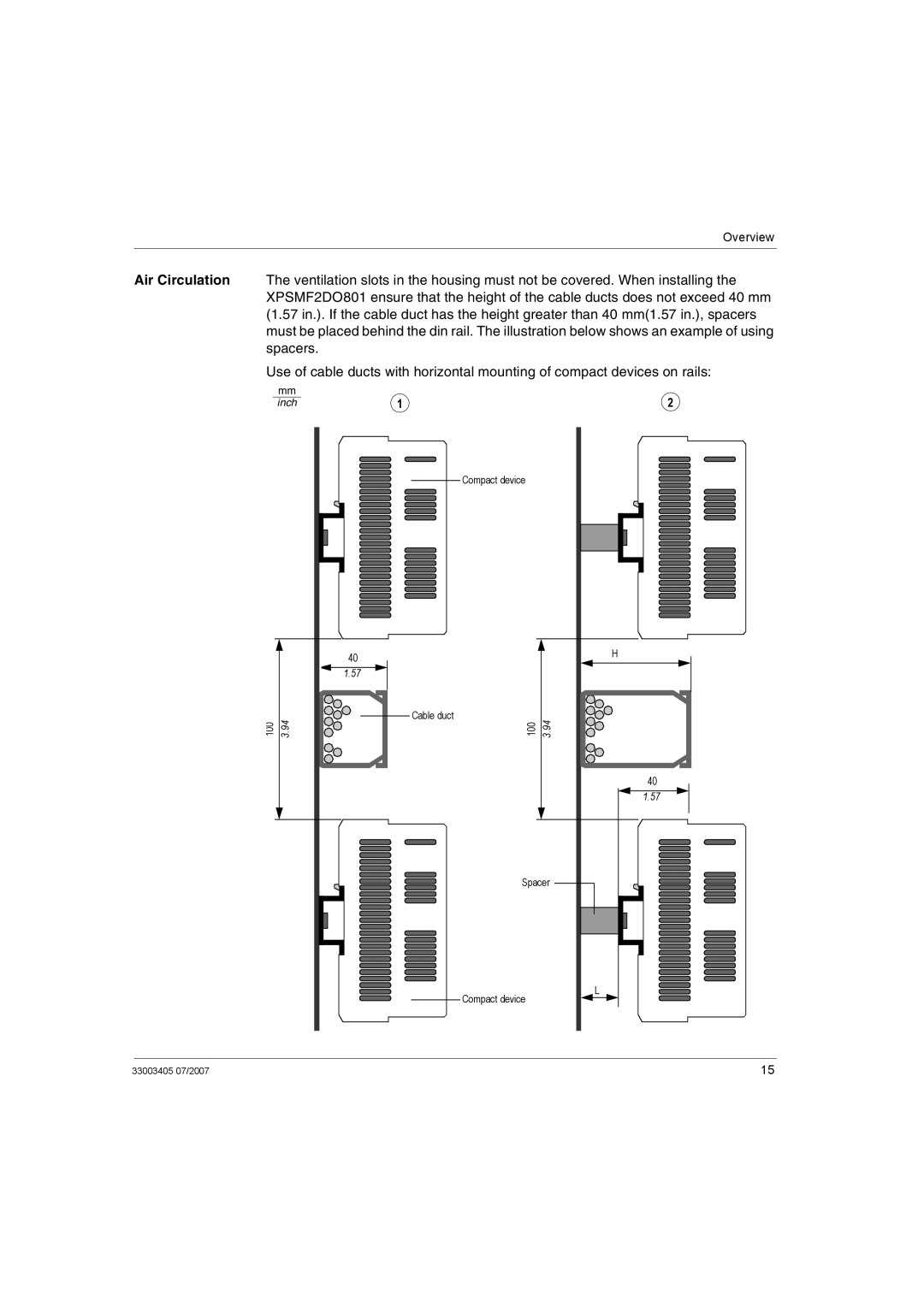
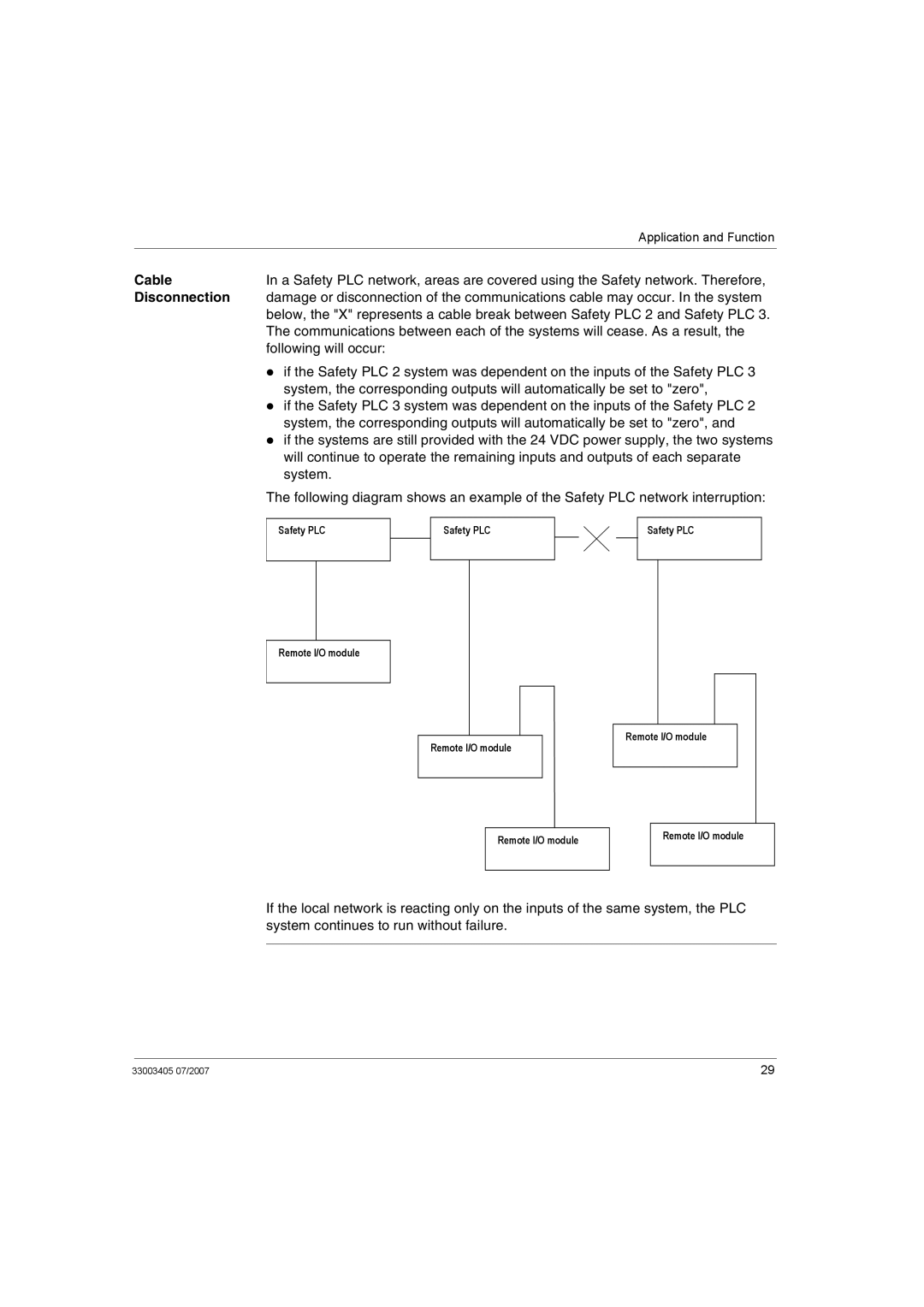
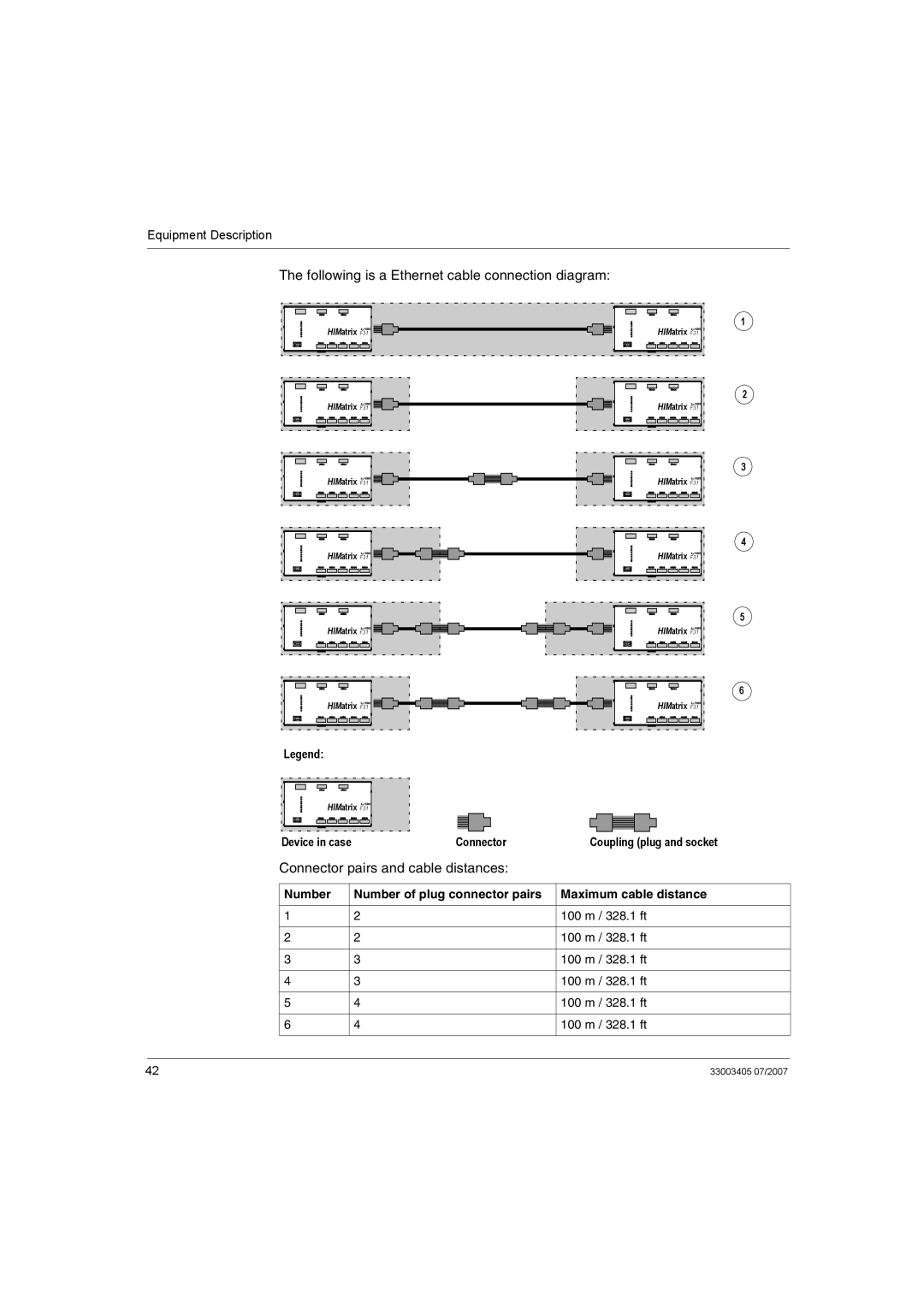
Overview
Internal | With internal heat convection, the heat is dissipated outside through the walls of the | |
Convection | housing. This is possible when the ambient temperature is lower than that inside the | |
| housing. |
|
| The following table describes the variables used to calculate the internal convection: | |
|
|
|
| Variable | Description |
|
|
|
| Pv [W] | heat output (heat dissipation) of the electronic components |
|
|
|
| A [m2]* | effective surface area of the housing |
| k [W/m2 K]* | the housing heat transfer coefficient |
|
| (e.g., Steel sheet: approximately 5.5 W/m2 K)* |
* (1m2 = 10.76ft2)
The maximum temperature increase of all electronic devices inside the housing is calculated as follows:
(∆ ) Pv
T max =
k • A
The power dissipation Pv can be calculated based on the values of the electrical power of the controller, its inputs, and outputs.
20 | 33003405 07/2007 |