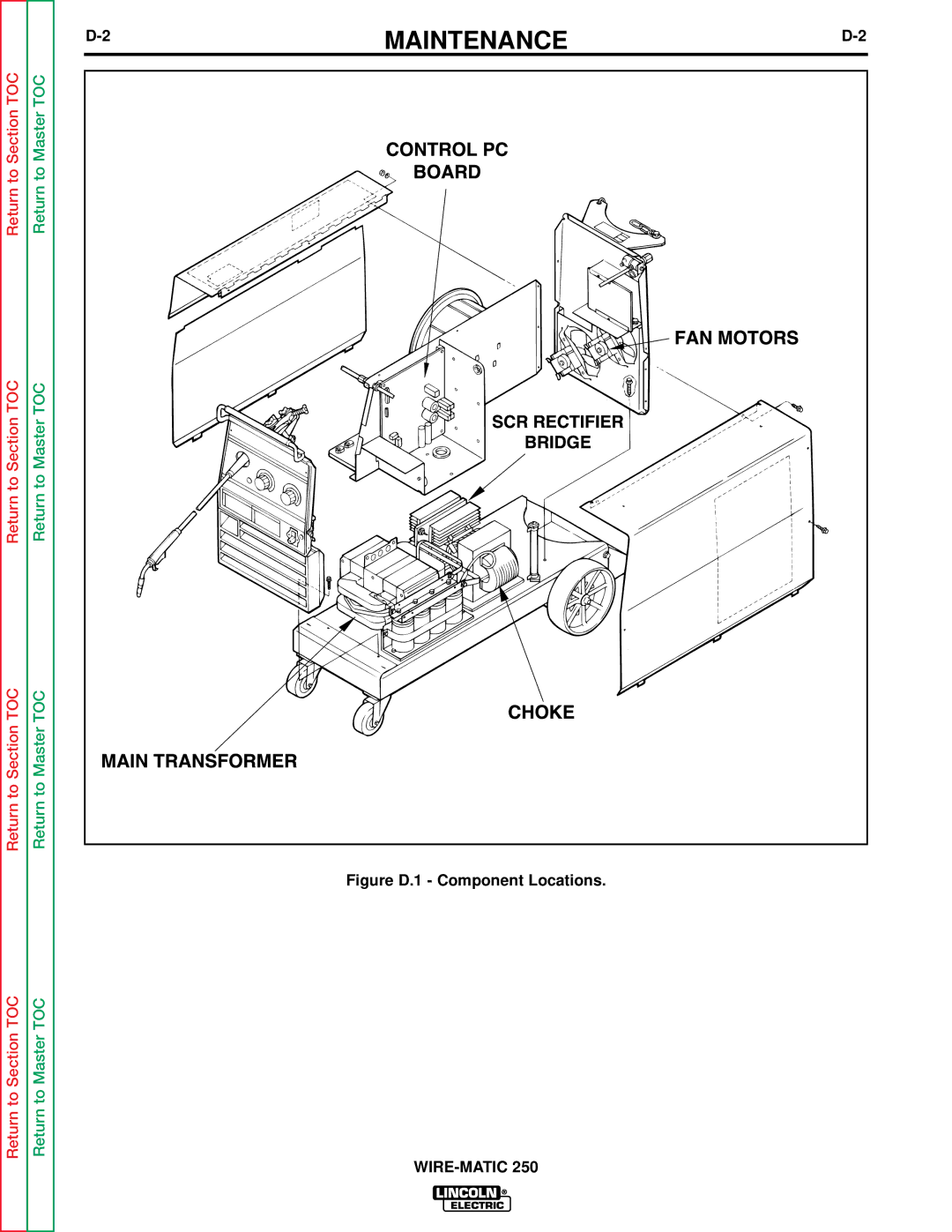
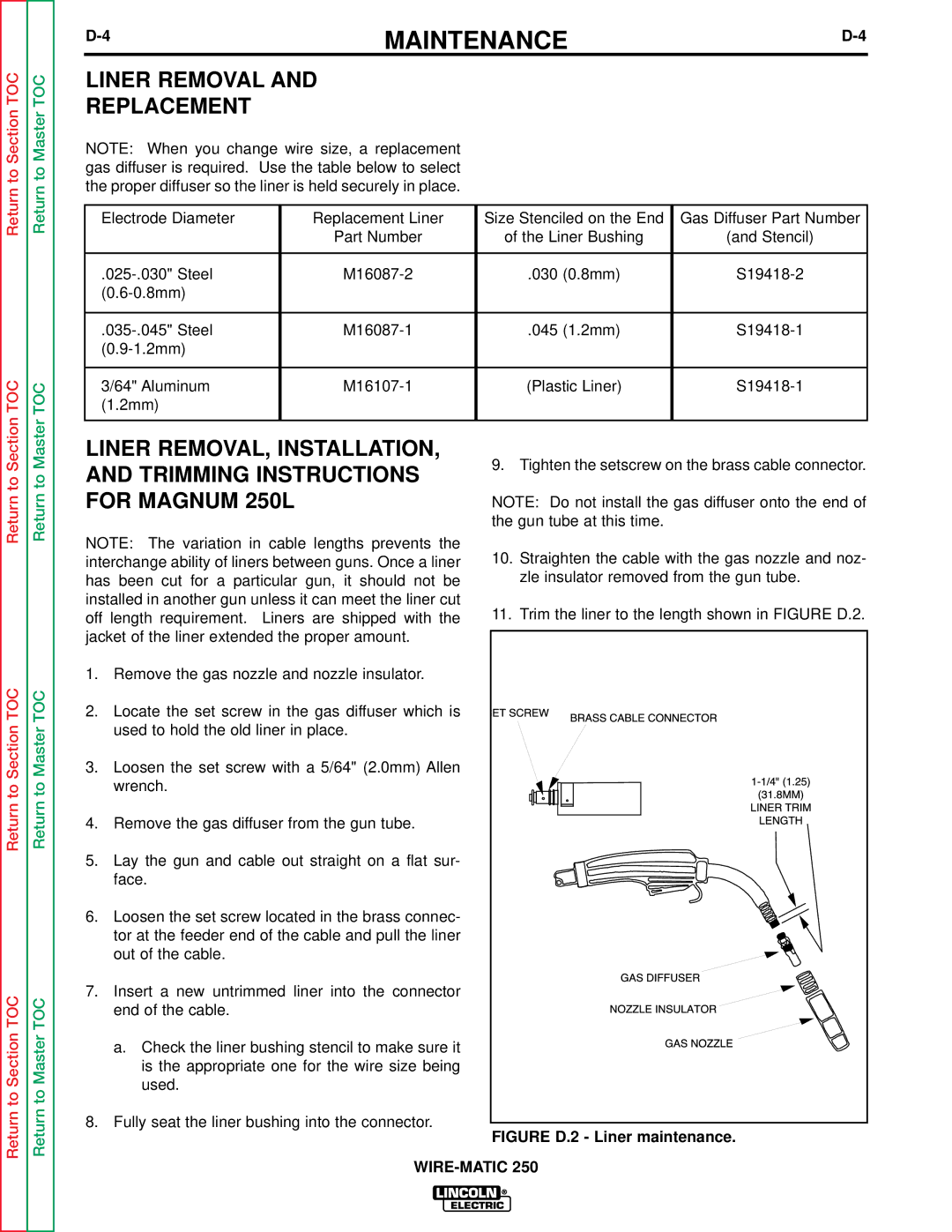
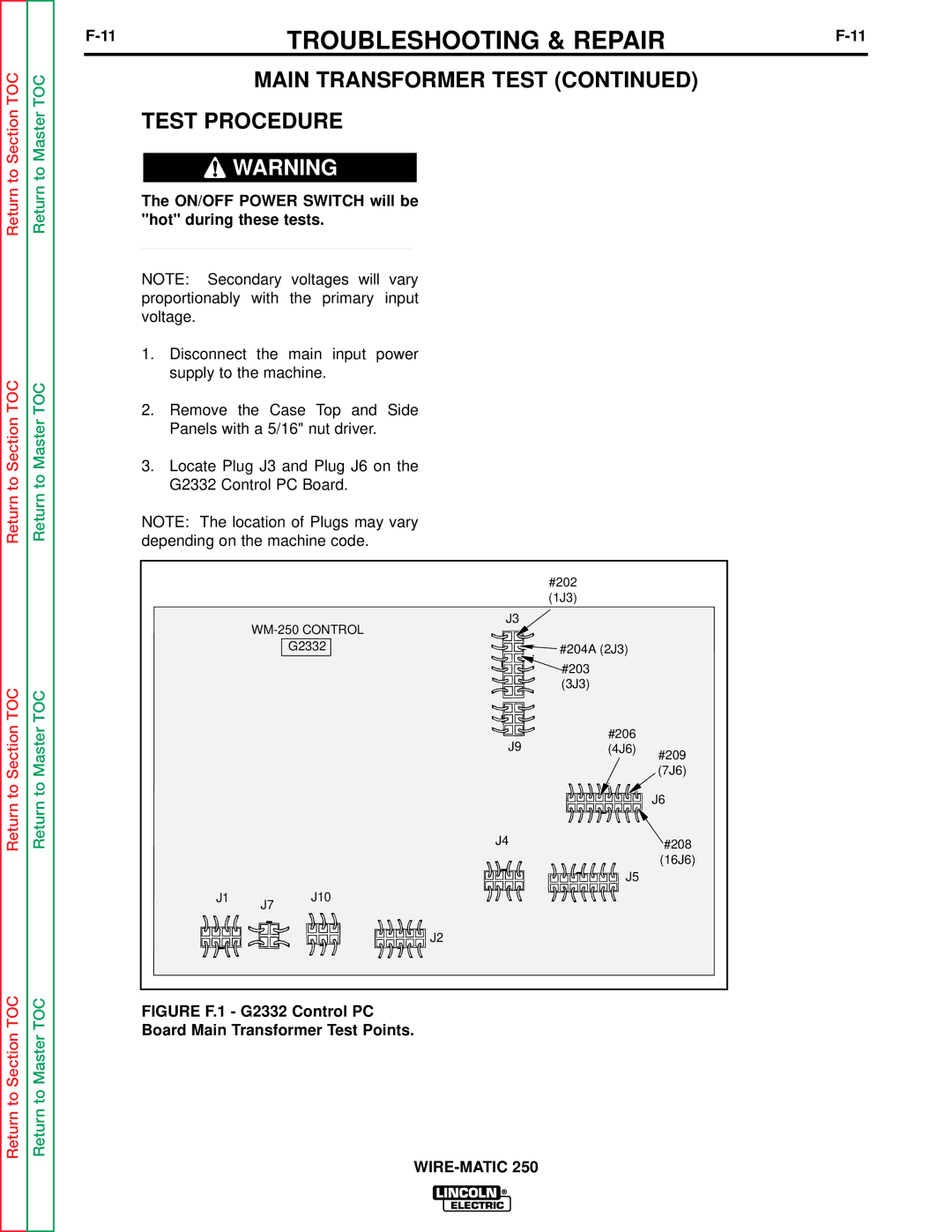
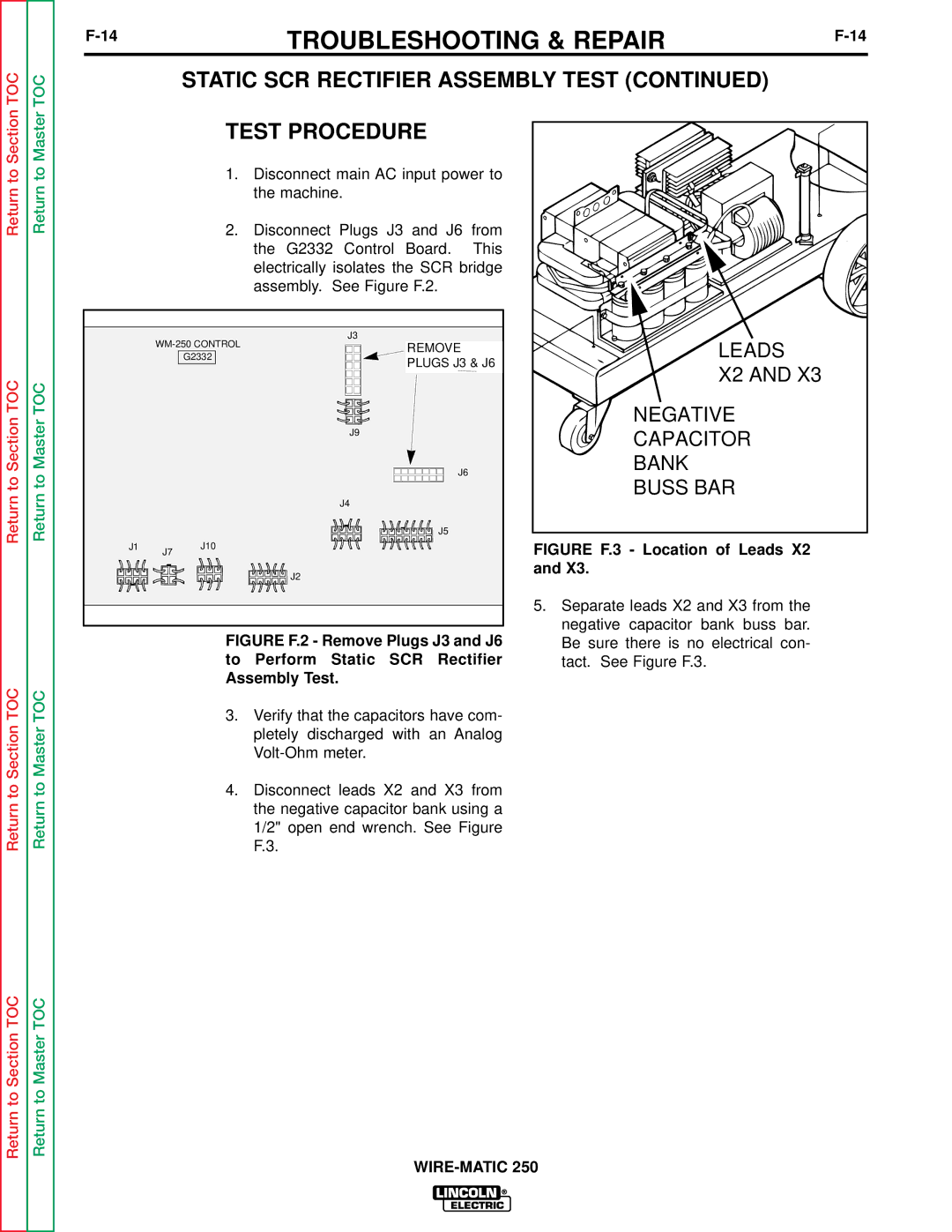
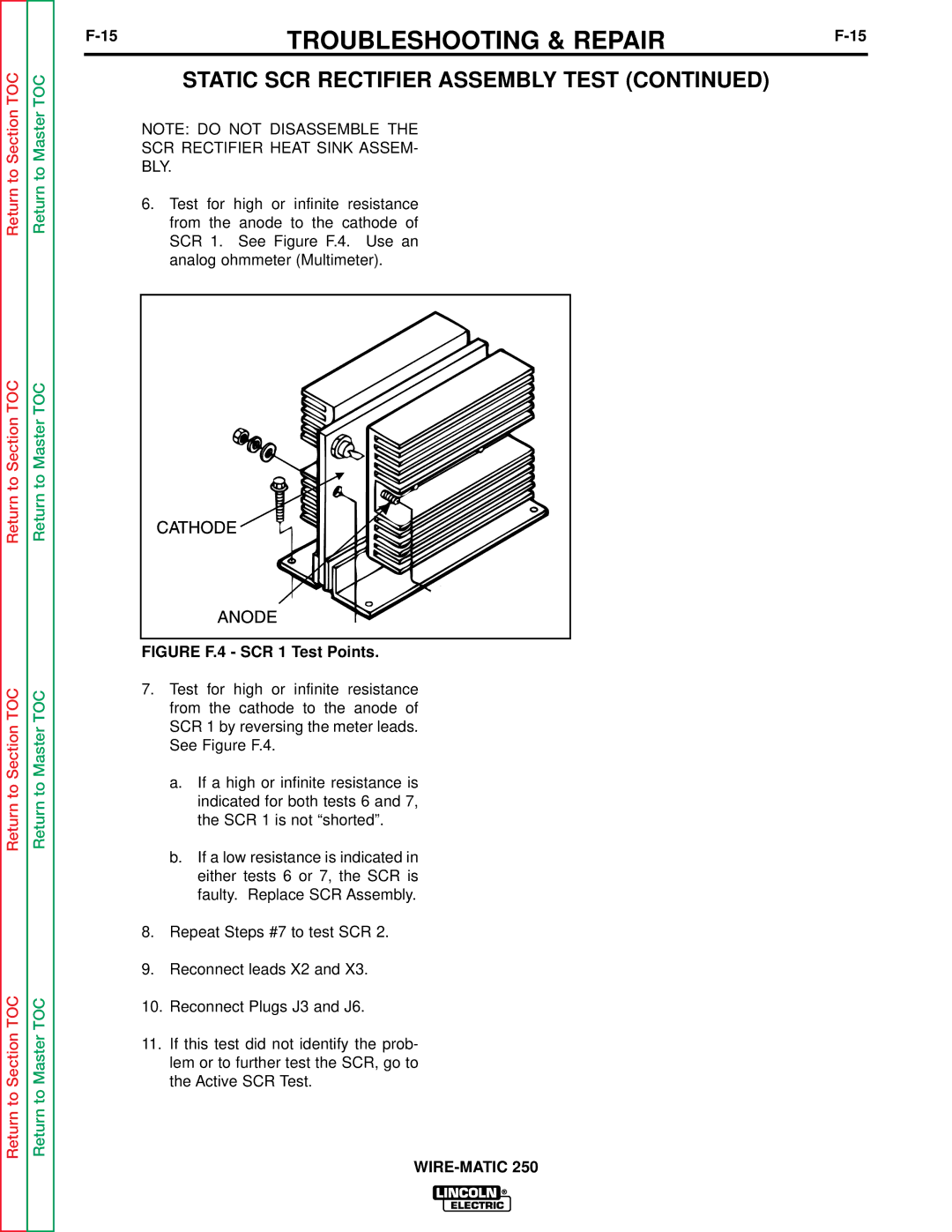
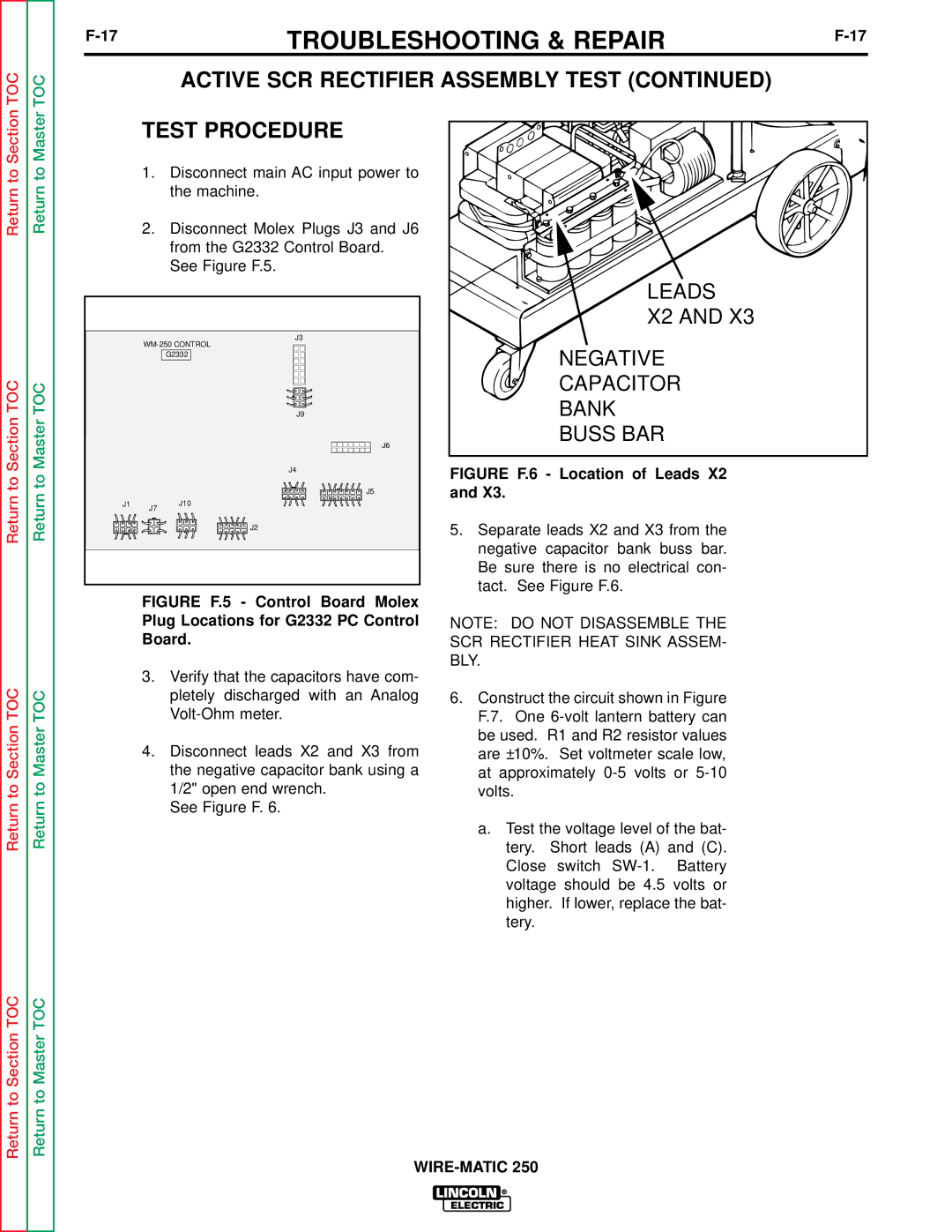
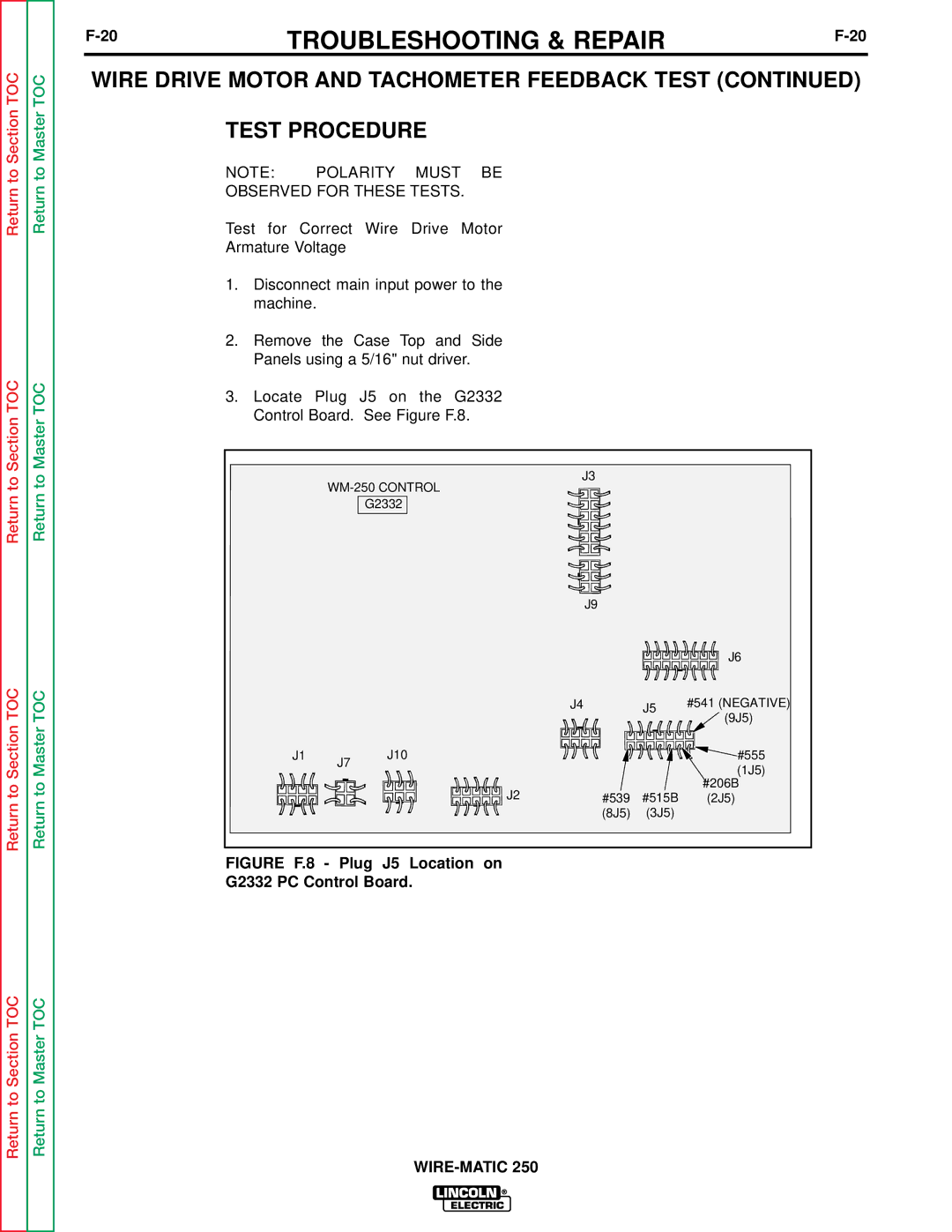
Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
THEORY OF OPERATION | ||
|
|
THERMAL PROTECTION
THERMAL PROTECTION
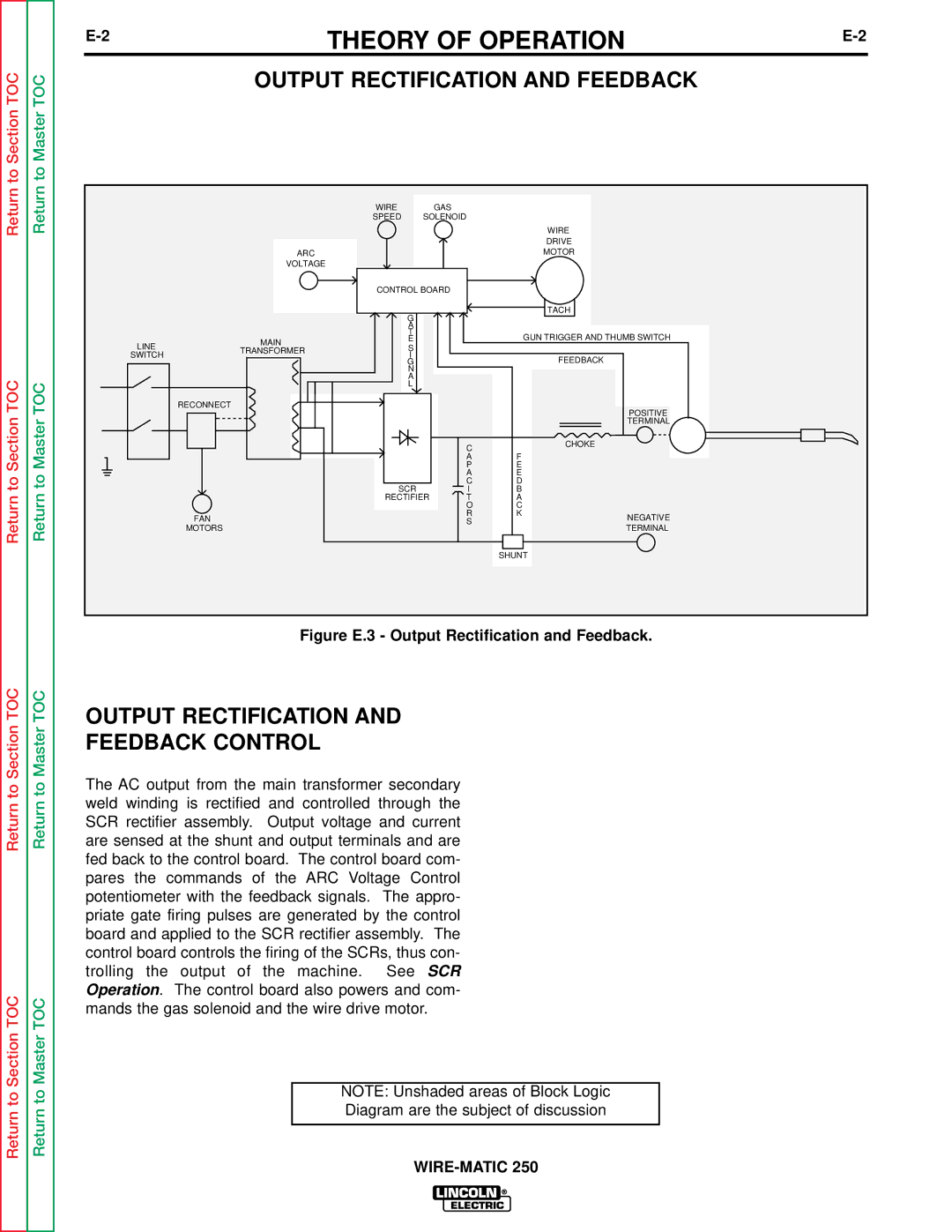
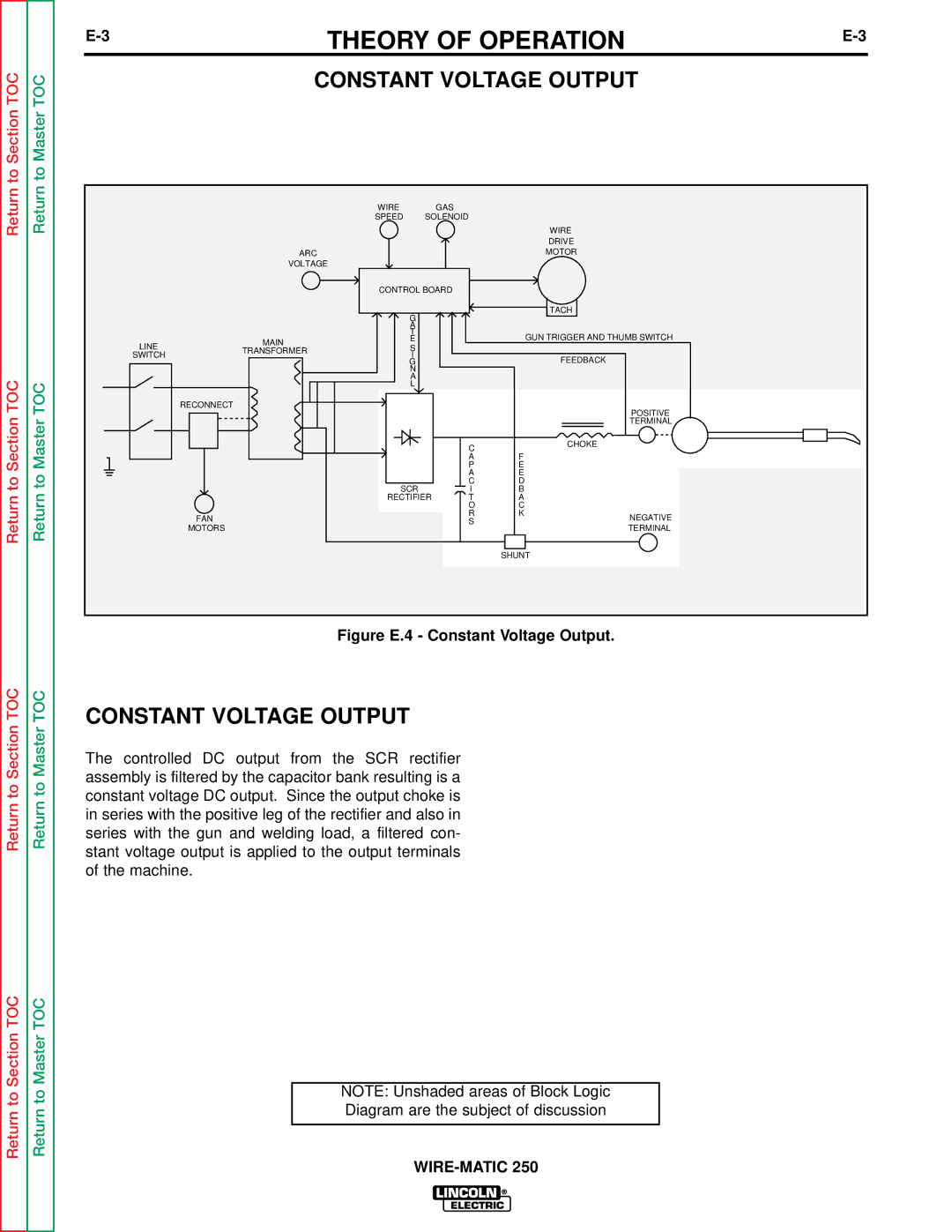
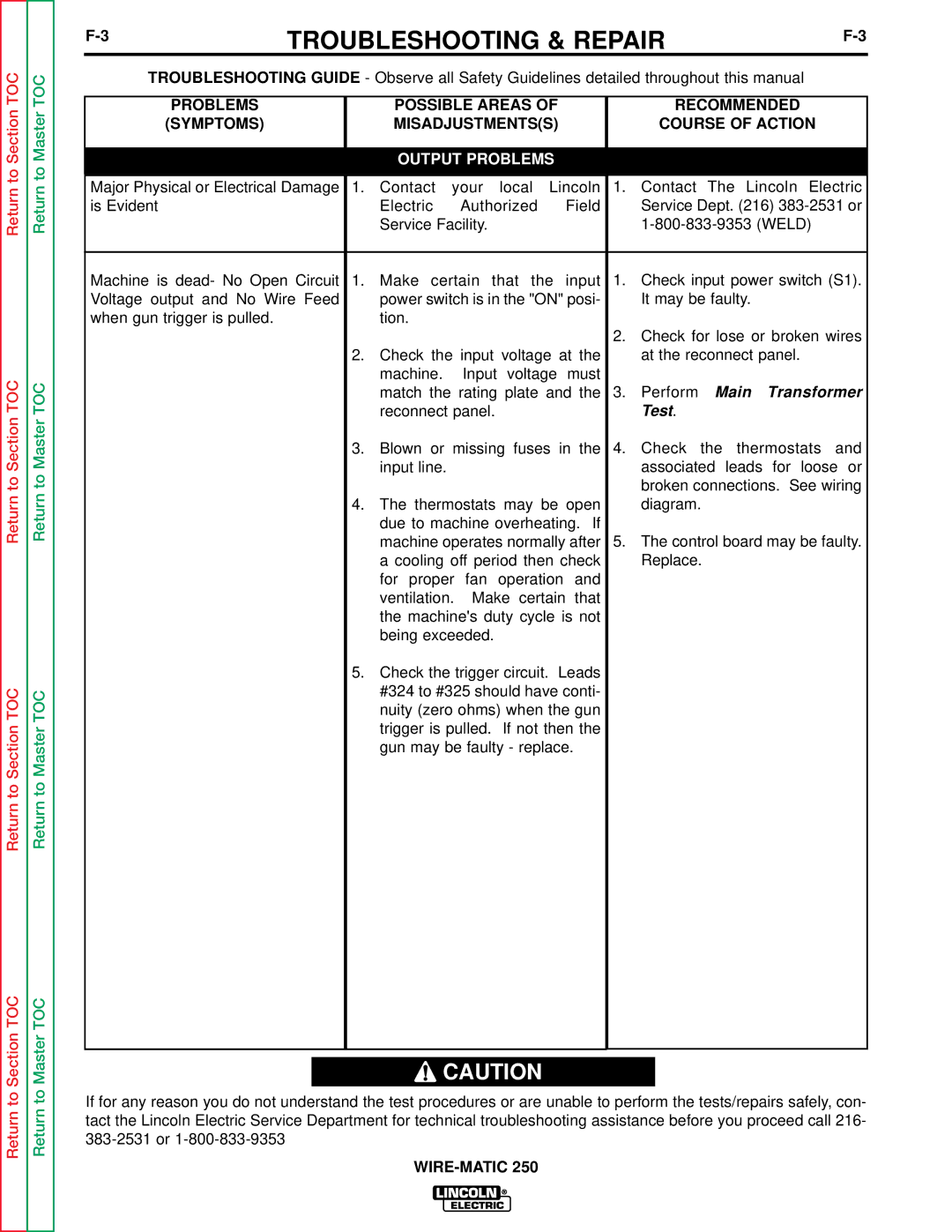
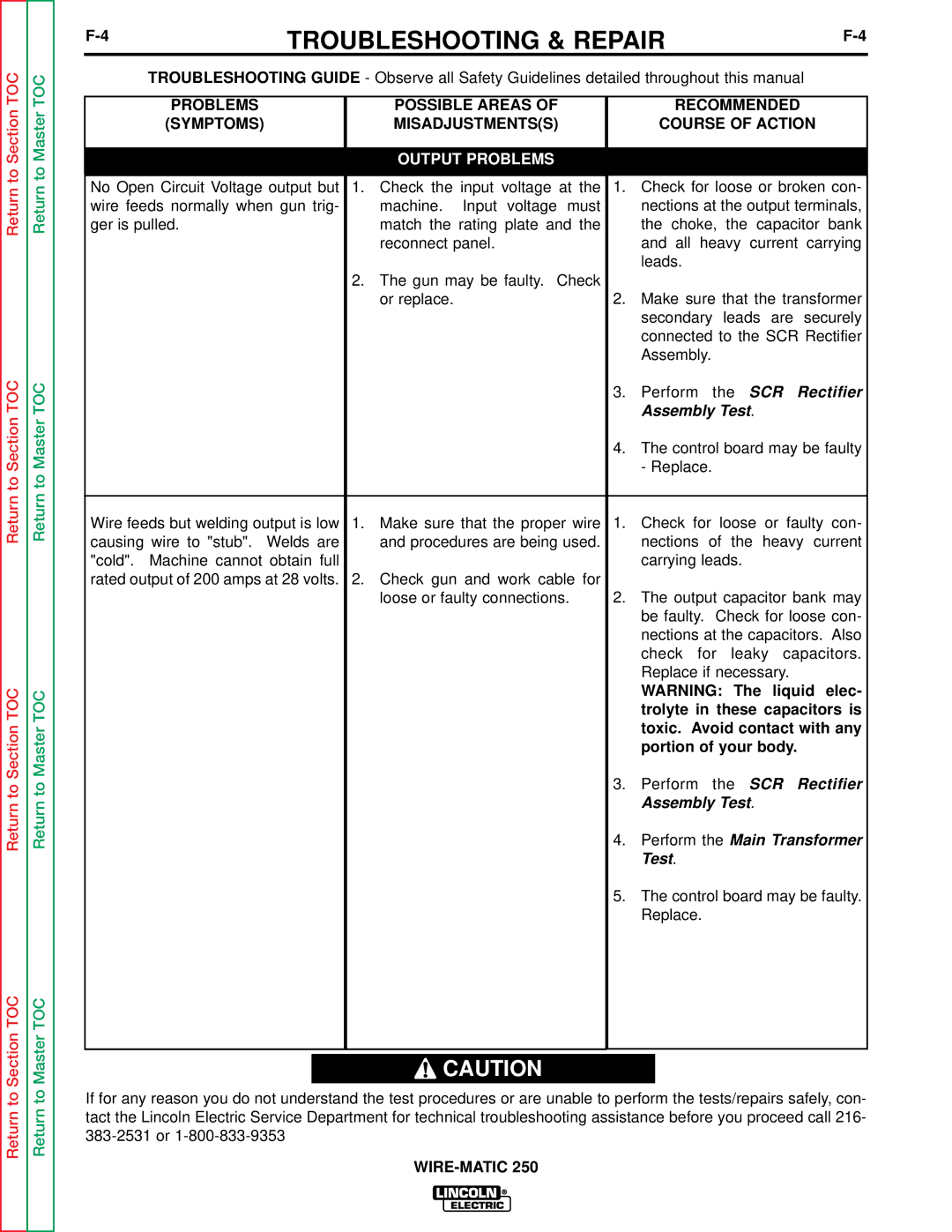
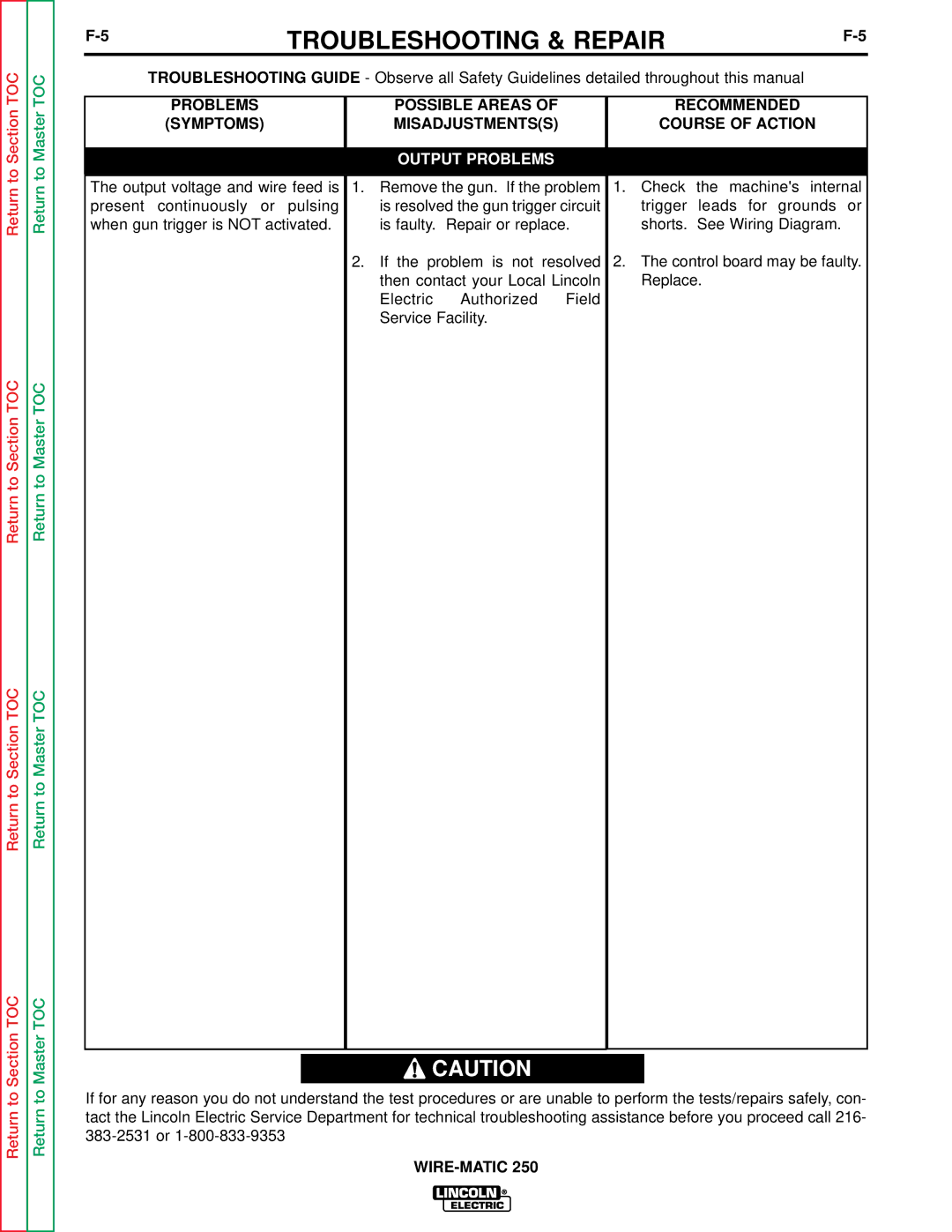
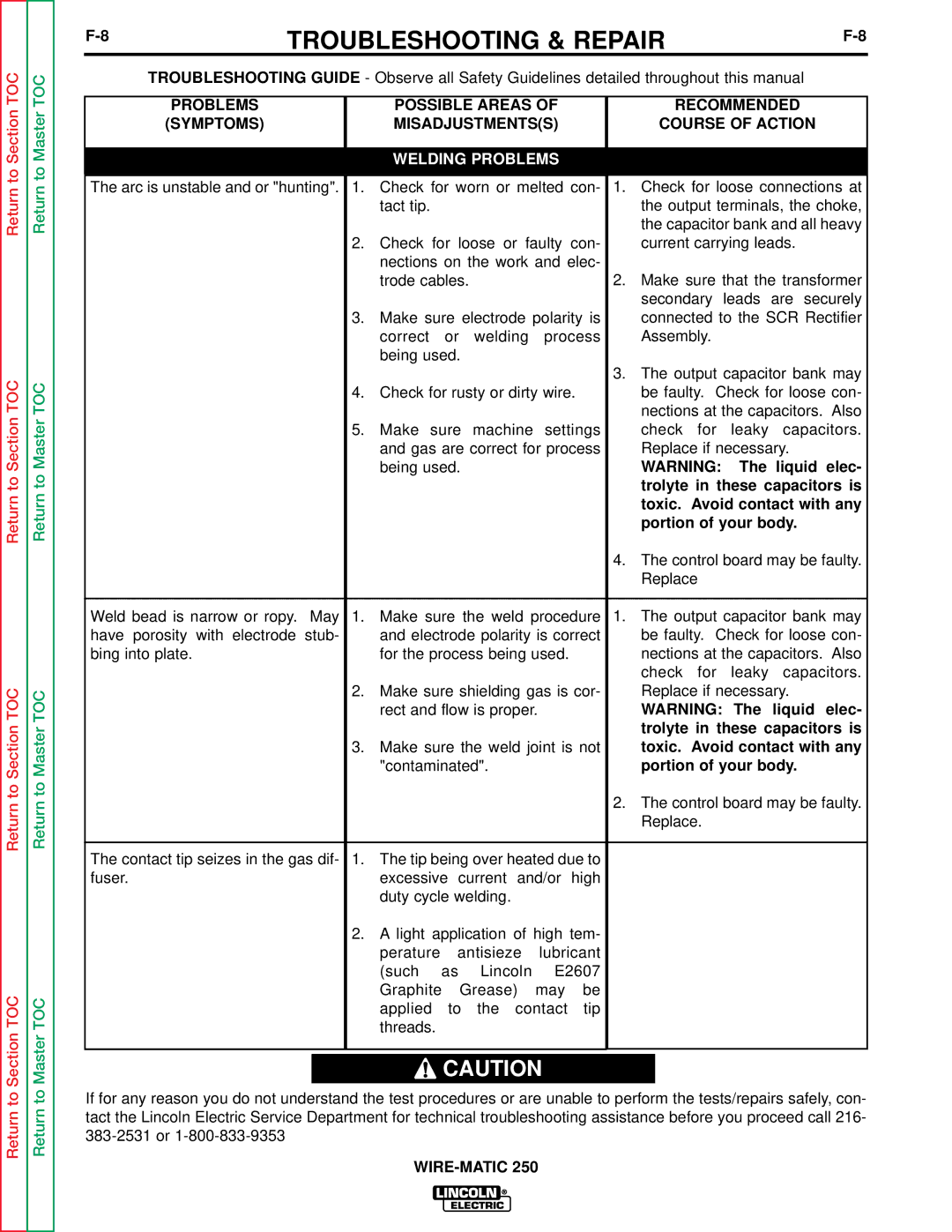
A thermostat protects the machine from excessive operating temperatures. Excessive operating temper- atures may be caused by a lack of cooling air or oper- ating the machine beyond the duty cycle and output rating. There are three thermostats within the WIRE- MATIC 250 machine. One of the thermostats, located on the output choke, energizes the cooling fan motors when required. The other choke thermostat "opens" the trigger circuit, preventing machine weld output and wire feed, if excessive operating temperatures are detected. The third thermostat insures that the fan motors are operating when required.
The thermostats are
NOTE: Unshaded areas of Block Logic
Diagram are the subject of discussion