causing the output voltage to rise to some value higher than the maximum voltage rating of the supply. With some loads this could result in serious damage. To protect loads from accidental opening of the remote programming leads, a zener diode should be placed directly across the power supply programming terminals. This zener diode is selected to have a breakdown voltage equal to the maximum power supply voltage that can be tolerated by the load. Thus, if the programming terminals open, the programming current will cause the zener diode to break down, and the output voltage will be limited to the zener diode voltage. Such a zener diode must be capable of dissipating a power equal to the product of its breakdown voltage times the programming current IP.
CONSTANT VOLTAGE REMOTE PROGRAMMING WITH VOLTAGE CONTROL
Instead of controlling a power supply by means of a programming resistance, it is possible to control the output of any remotely programmable supply with an input voltage. Thus, the power supply becomes a low frequency dc amplifier. Remote Programming Speed (later in this section) stresses the bandwidth and speed of response of this configuration, whereas these paragraphs deal only with the method of control.
Two distinct methods can be employed to voltage program: unity and variable voltage gain.
Programming with Unity Voltage Gain
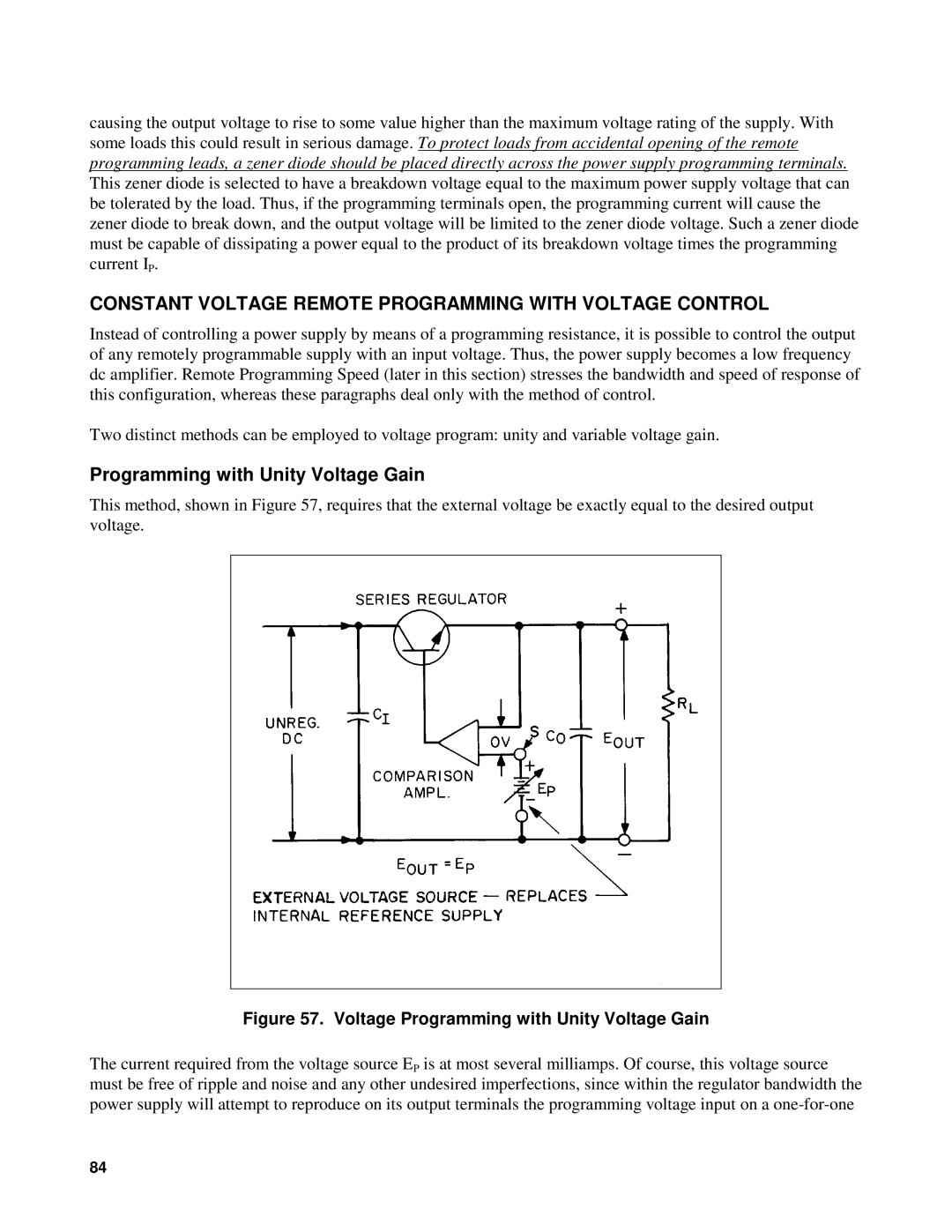
This method, shown in Figure 57, requires that the external voltage be exactly equal to the desired output voltage.
Figure 57. Voltage Programming with Unity Voltage Gain
The current required from the voltage source EP is at most several milliamps. Of course, this voltage source must be free of ripple and noise and any other undesired imperfections, since within the regulator bandwidth the power supply will attempt to reproduce on its output terminals the programming voltage input on a
84