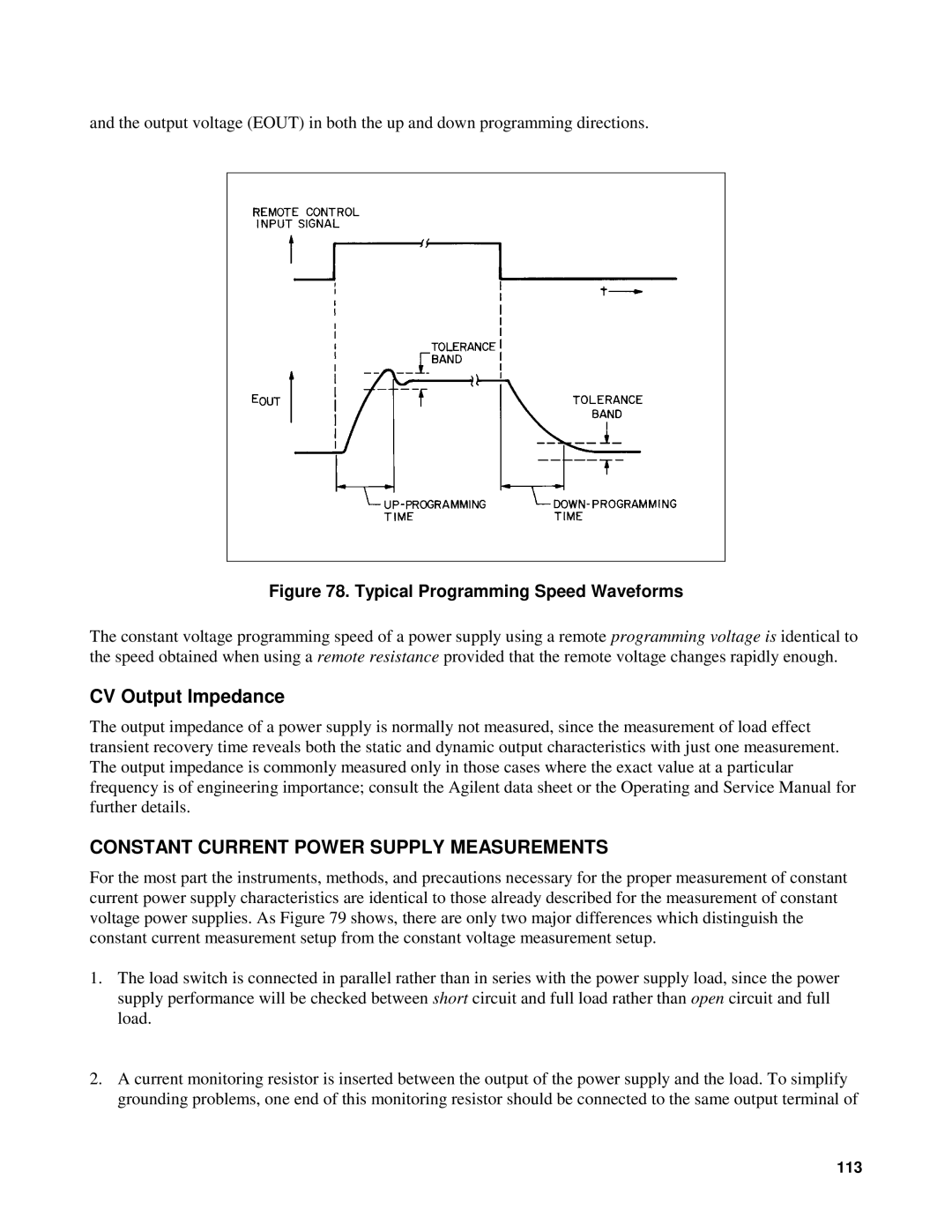
and the output voltage (EOUT) in both the up and down programming directions.
Figure 78. Typical Programming Speed Waveforms
The constant voltage programming speed of a power supply using a remote programming voltage is identical to the speed obtained when using a remote resistance provided that the remote voltage changes rapidly enough.
CV Output Impedance
The output impedance of a power supply is normally not measured, since the measurement of load effect transient recovery time reveals both the static and dynamic output characteristics with just one measurement. The output impedance is commonly measured only in those cases where the exact value at a particular frequency is of engineering importance; consult the Agilent data sheet or the Operating and Service Manual for further details.
CONSTANT CURRENT POWER SUPPLY MEASUREMENTS
For the most part the instruments, methods, and precautions necessary for the proper measurement of constant current power supply characteristics are identical to those already described for the measurement of constant voltage power supplies. As Figure 79 shows, there are only two major differences which distinguish the constant current measurement setup from the constant voltage measurement setup.
1.The load switch is connected in parallel rather than in series with the power supply load, since the power supply performance will be checked between short circuit and full load rather than open circuit and full load.
2.A current monitoring resistor is inserted between the output of the power supply and the load. To simplify grounding problems, one end of this monitoring resistor should be connected to the same output terminal of
113