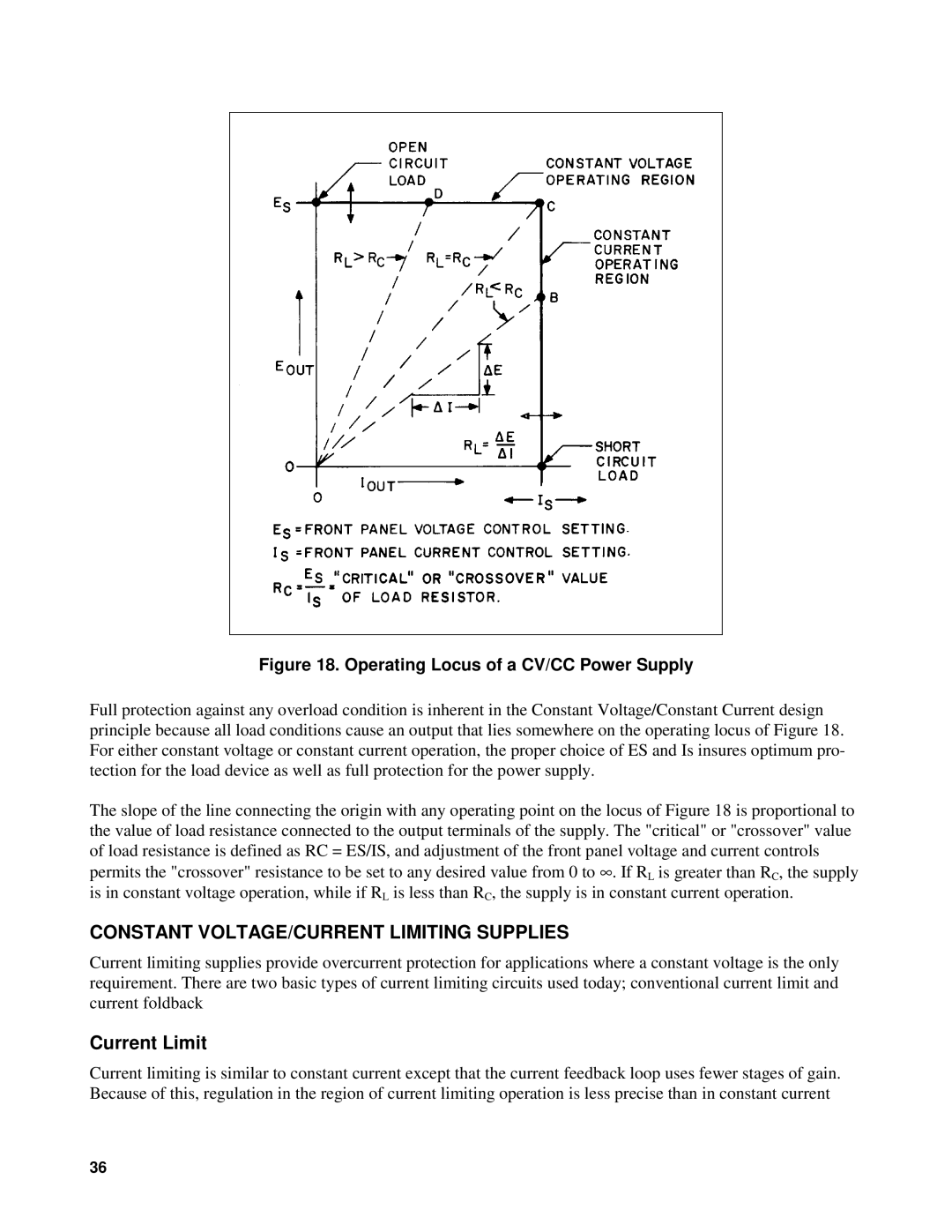
Figure 18. Operating Locus of a CV/CC Power Supply
Full protection against any overload condition is inherent in the Constant Voltage/Constant Current design principle because all load conditions cause an output that lies somewhere on the operating locus of Figure 18. For either constant voltage or constant current operation, the proper choice of ES and Is insures optimum pro- tection for the load device as well as full protection for the power supply.
The slope of the line connecting the origin with any operating point on the locus of Figure 18 is proportional to the value of load resistance connected to the output terminals of the supply. The "critical" or "crossover" value of load resistance is defined as RC = ES/IS, and adjustment of the front panel voltage and current controls permits the "crossover" resistance to be set to any desired value from 0 to ∞ . If RL is greater than RC, the supply is in constant voltage operation, while if RL is less than RC, the supply is in constant current operation.
CONSTANT VOLTAGE/CURRENT LIMITING SUPPLIES
Current limiting supplies provide overcurrent protection for applications where a constant voltage is the only requirement. There are two basic types of current limiting circuits used today; conventional current limit and current foldback
Current Limit
Current limiting is similar to constant current except that the current feedback loop uses fewer stages of gain. Because of this, regulation in the region of current limiting operation is less precise than in constant current
36