Automatic IP Parameter Distribution
The modem can also operate in more advanced local networks that rely on a BOOTP server for centralized IP configuration.
The modem contains a BOOTP client that issues BOOTP requests during the first two minutes after
The modem is compliant with RFC 951 Bootstrap Protocol and supports option 1 (Subnet Mask) and option 3 (Default Gateway) of RFC 2132 DHCP Options and BOOTP Vendor Extensions.
Note:
The modem also supports logical
Advanced Networks
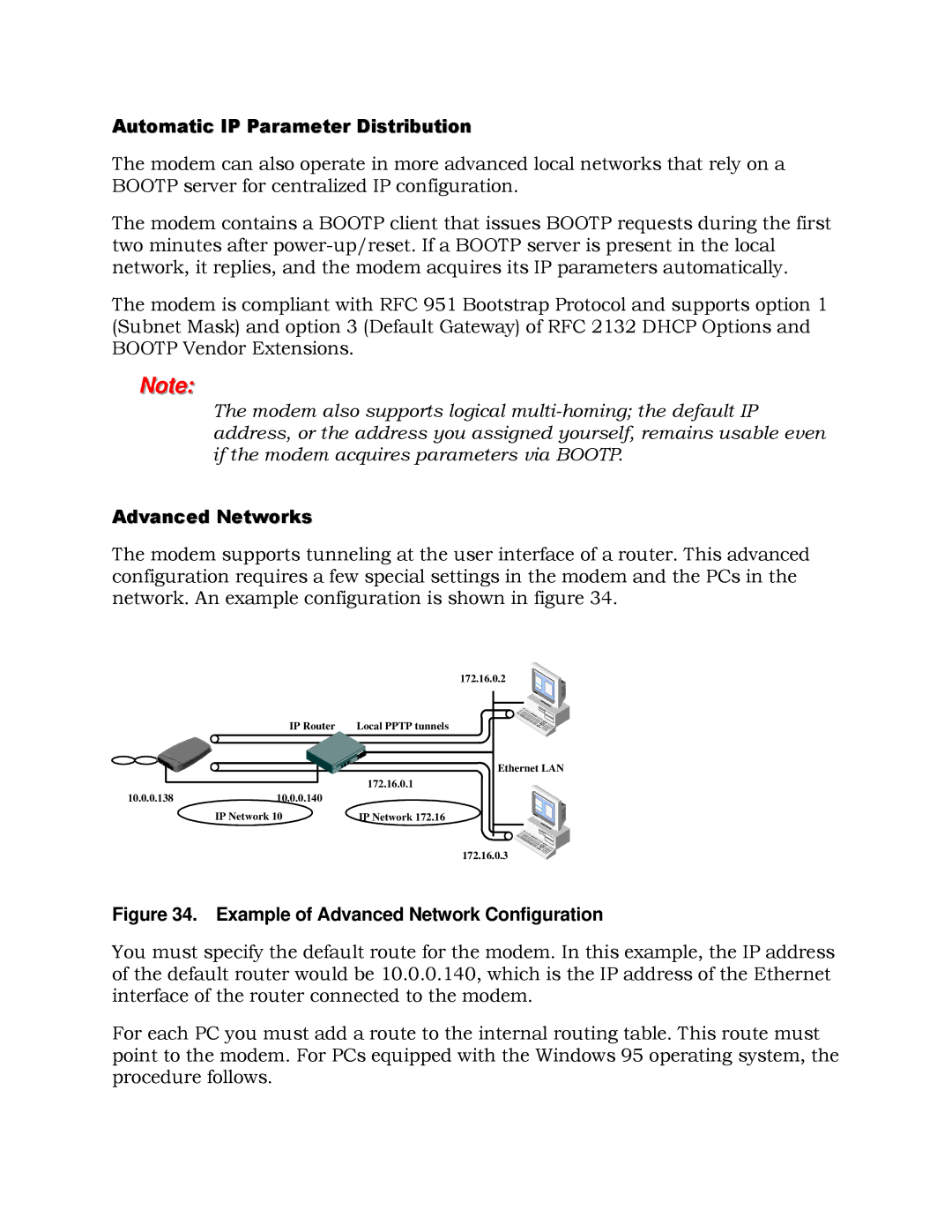
The modem supports tunneling at the user interface of a router. This advanced configuration requires a few special settings in the modem and the PCs in the network. An example configuration is shown in figure 34.
|
| 172.16.0.2 |
| IP Router | Local PPTP tunnels |
|
| Ethernet LAN |
|
| 172.16.0.1 |
10.0.0.138 | 10.0.0.140 |
|
| IP Network 10 | IP Network 172.16 |
|
| 172.16.0.3 |
Figure 34. Example of Advanced Network Configuration
You must specify the default route for the modem. In this example, the IP address of the default router would be 10.0.0.140, which is the IP address of the Ethernet interface of the router connected to the modem.
For each PC you must add a route to the internal routing table. This route must point to the modem. For PCs equipped with the Windows 95 operating system, the procedure follows.